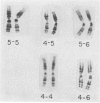
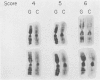
Full text
PDF

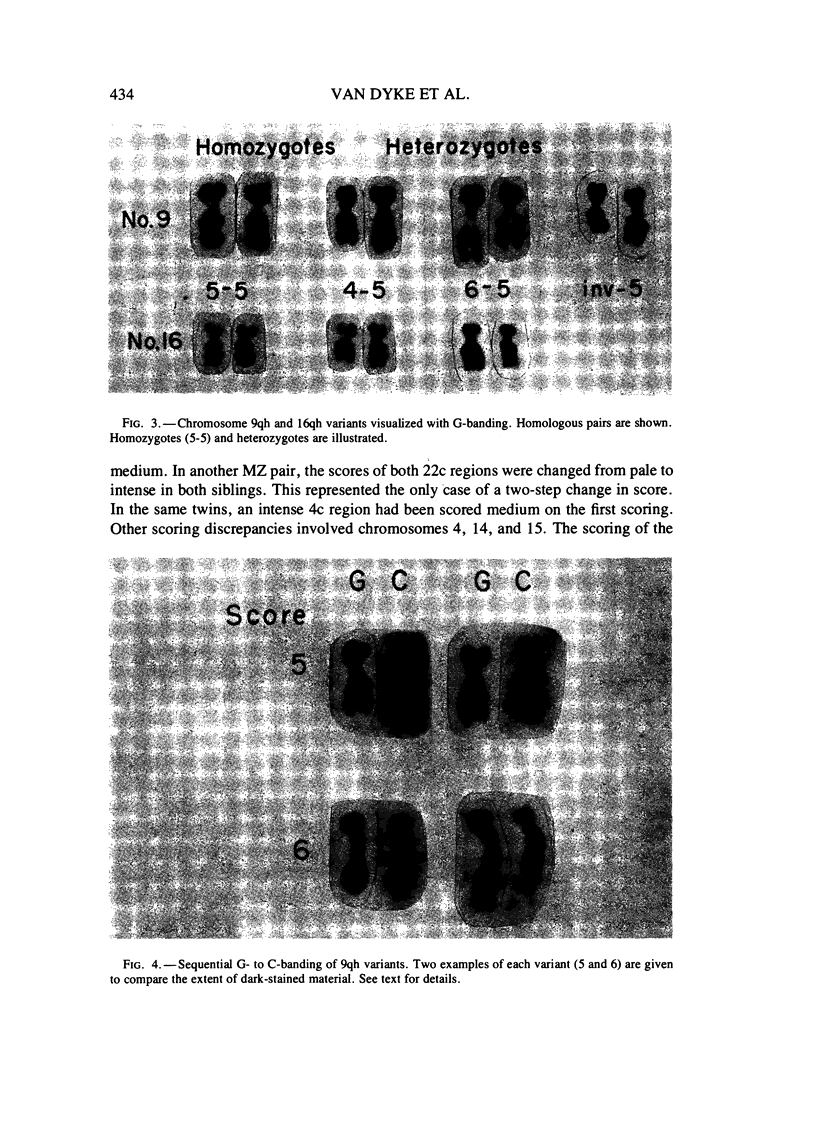
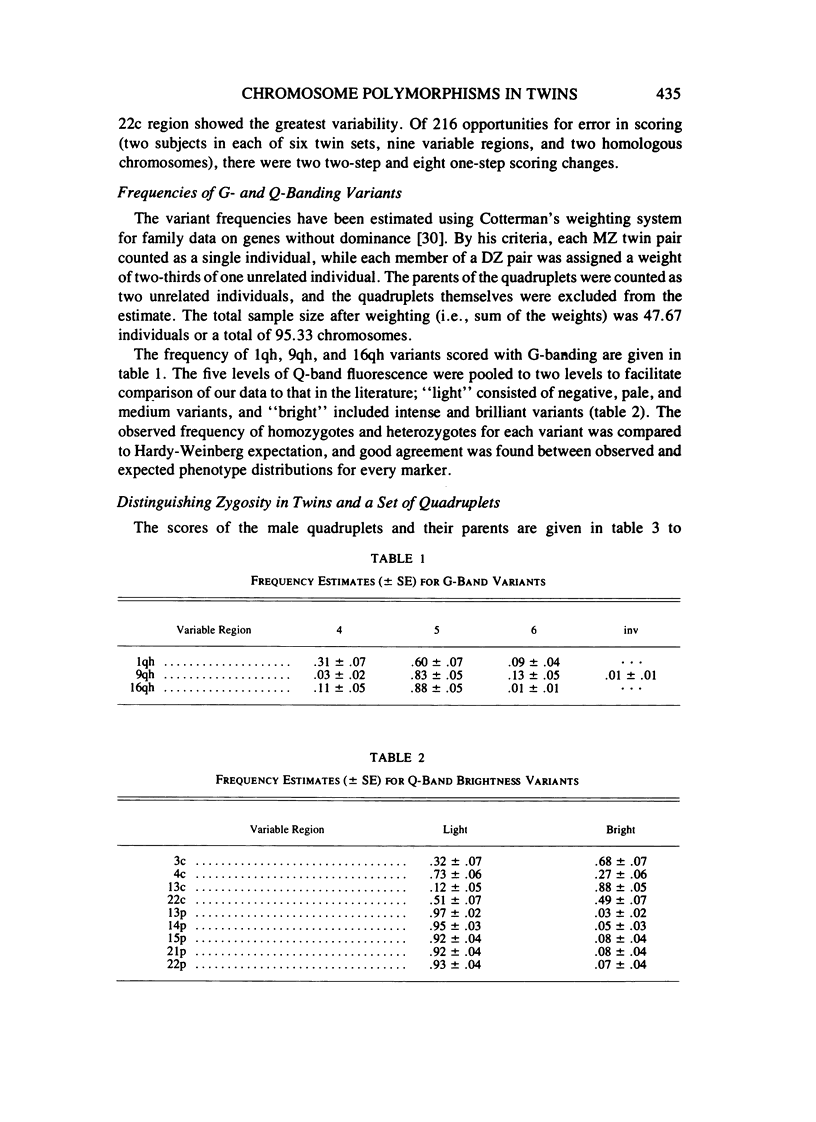
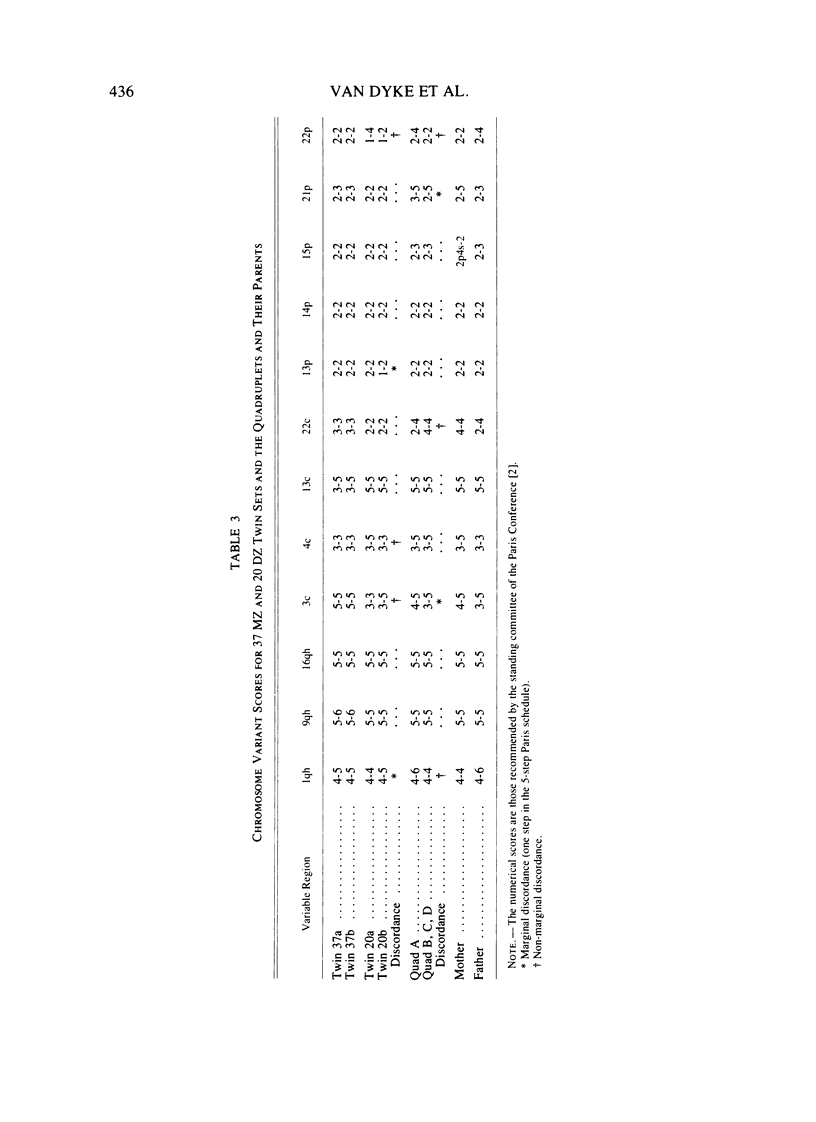



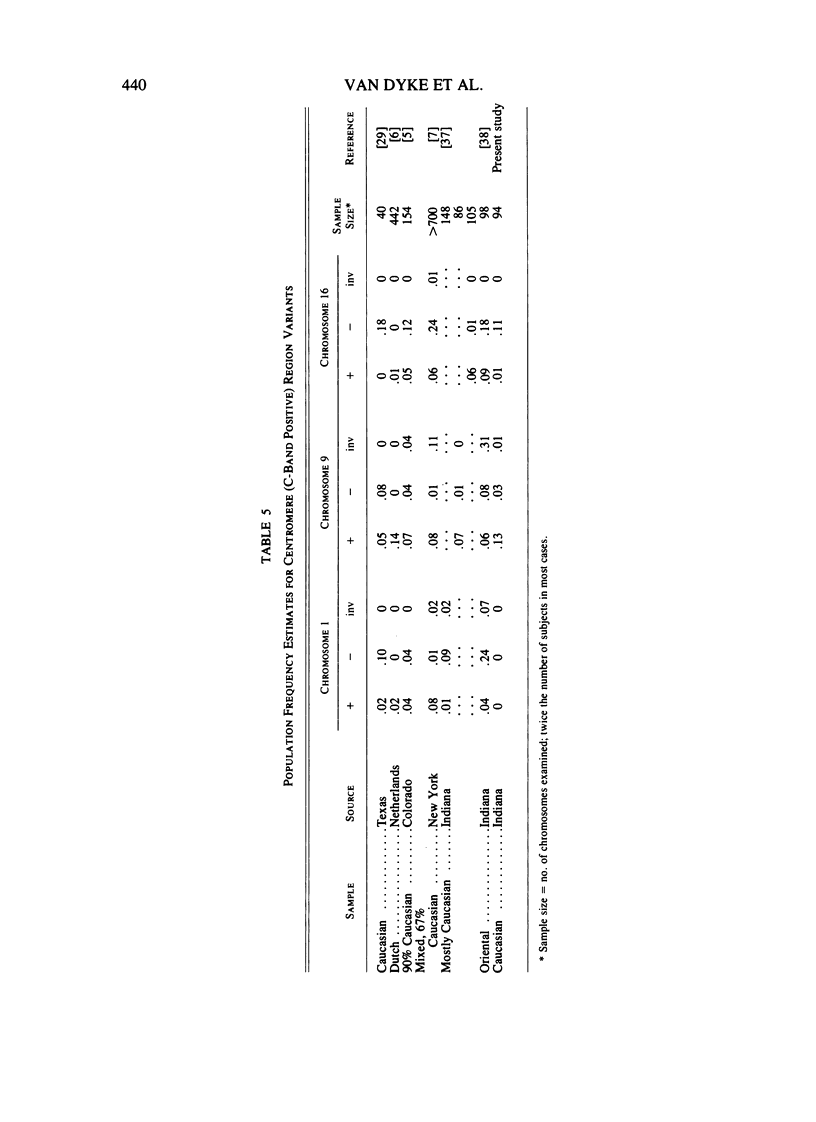

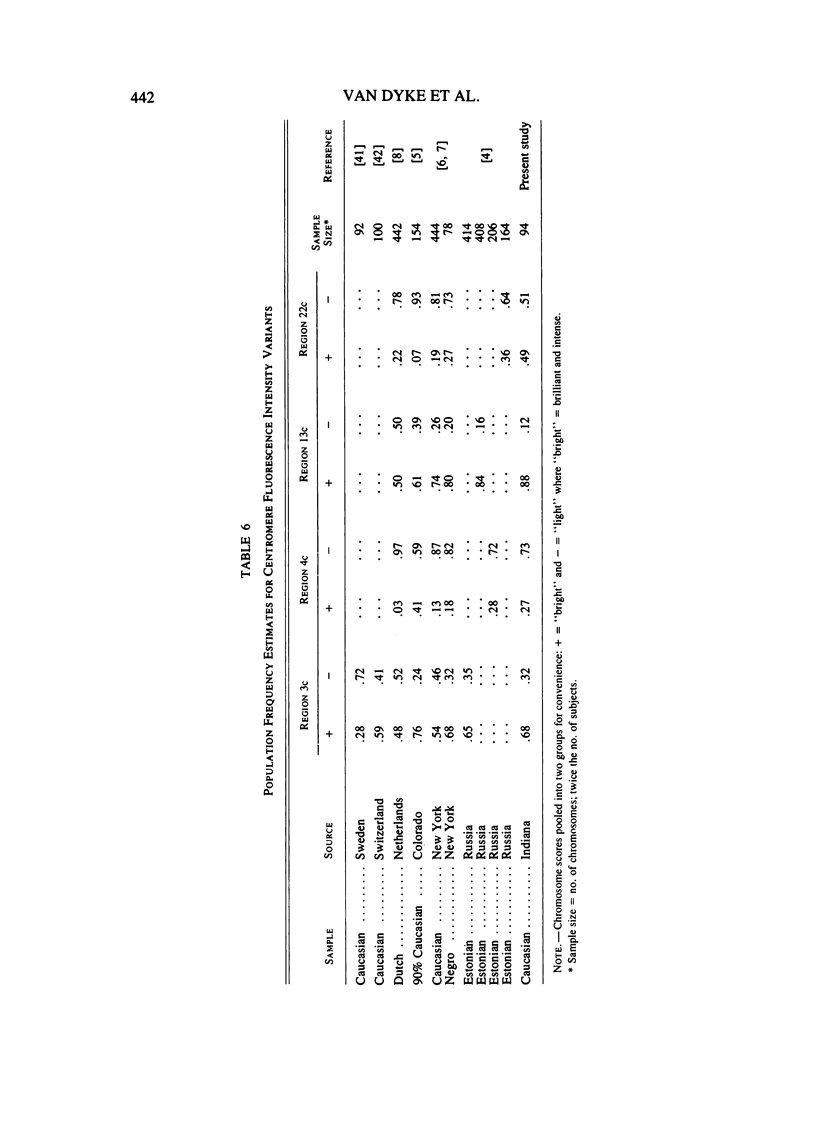





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN G. The M quadruplets: I. Probability of uniovular origin judged from qualitative traits. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 1960 Apr;9:240–254. doi: 10.1017/s1120962300018333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Hultén M., Lindsten J., Zech L. Distinction between extra G-like chromosomes by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):240–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90363-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Lomakka G., Zech L. The 24 fluorescence patterns of the human metaphase chromosomes - distinguishing characters and variability. Hereditas. 1972;67(1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1971.tb02363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Zech L., Johansson C., Lindsten J., Hultén M. Fluorescent staining of heteropycnotic chromosome regions in human interphase nuclei. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Aug;61(2):472–474. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90477-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K. R., Nielsen J. Incidence of chromosome aberrations in a child psychiatric hospital. Clin Genet. 1974;5(3):205–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb01683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig-Holmes A. P., Moore F. B., Shaw M. W. Polymorphism of human C-band heterochromatin. I. Frequency of variants. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Mar;25(2):181–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig-Holmes A. P., Moore F. B., Shaw M. W. Polymporphism of human C-band heterochromatin. II. Family studies with suggestive evidence for somatic crossing over. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Mar;27(2):178–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaines R. E., Elston R. C. On the probability that a twin pair is monozygotic. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 Sep;21(5):457–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraedts J. P., Pearson P. L. Fluorescent chromosome polymorphisms: frequencies and segregations in a Dutch population. Clin Genet. 1974;6(4):247–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1974.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauge M., Poulsen H., Halberg A., Mikkelsen M. The value of fluorescence markers in the distinction between maternal and fetal chromosomes. Humangenetik. 1975;26(3):187–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00281452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht F., Wyandt H. E., Erbe R. W. Revolutionary cytogenetics. N Engl J Med. 1971 Dec 23;285(26):1482–1484. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197112232852610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoehn H., Martin G. M. Heritable alteration of human constitutive heterochromatin induced by mitomycin C. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer S., Rosenkranz W., Glatzl J. Homozygous duplication on long arm of chromosome pair no. 1. Humangenetik. 1972;16(4):341–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00283983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze J., Mau G. Letter: A1 and C9 marker chromosomes in children with combined minor and major malformations. Lancet. 1975 Feb 1;1(7901):273–273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubs H. A., McKenzie W. H., Patil S. R., Merrick S. New staining methods for chromosomes. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;6:345–380. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIGEON B. R. FAMILIAL VARIANT AUTOSOMES: NEW HUMAN CYTOGENETIC MARKERS. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1965 Jun;116:396–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER O. R., MUKHERJEE B. B., BREG W. R. Normal variations in the human karyotype. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1962 Feb;24:372–382. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1962.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan K., Bobrow M. Structural variation in chromosome No 9. Ann Genet. 1974 Jun;17(2):81–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie W. H., Lubs H. A. Human Q and C chromosomal variations: distribution and incidence. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;14(2):97–115. doi: 10.1159/000130330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelsaar A. V., Käosaar M. E., Tür S. J., Viikmaa M. H., Talvik T. A., Läts J. Human karyotype polymorphism. III. Routine ank fluorescence microscopic investigation of chromosomes in normal adults and mentally retarded children. Humangenetik. 1975;26(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00280281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikelsaar A. V., Viikmaa M. H., Tür S. J., Käosaar M. E. Human karyotype polymorphism. II. The distribution of individuals according to the presence of brilliant bands in chromosomes 3,4, and 13 in a normal adult population. Humangenetik. 1974 Jun 26;23(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00295683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscetti G., Petriaggi M., Barbarossa C. G., Tiberti S. Fluorescence staining method for the morphological and structural study of human chromosomes. Humangenetik. 1971;12(1):56–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00291033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller H., Klinger H. P., Glasser M. Chromosome polymorphism in a human newborn population. II. Potentials of polymorphic chromosome variants for characterizing the idiogram of an individual. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;15(4):239–255. doi: 10.1159/000130522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Friedrich U., Hreidarsson A. B., Zeuthen E. Frequency of 9qh+ and risk of chromosome aberrations in the progeny of individuals with 9qh+. Humangenetik. 1974;21(3):211–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00279014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niikawa N., Kajii T. Sequential Q- and Acridine orange-marker technique. Humangenetik. 1975 Oct 20;30(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00273636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivas M. L., Conneally P. M., Hecht F., Lovrien E. W., Magenis E., Merritt A. D., Meyers D. A., Palmer C. G., Wang L. Linkage relationships of 1qh to Amy, Fy, PGM1, and Rh. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(3):239–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnedl W. Unterschiedliche Fluorescenz der beiden homologen Chromosomen Nr. 3 beim Menschen. Humangenetik. 1971;12(1):59–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00291034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner A. T., Evans H. J., Buckland R. A. New technique for distinguishing between human chromosomes. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 7;232(27):31–32. doi: 10.1038/newbio232031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma R. S., Lubs H. A. A simple R banding technic. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):110–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma R. S., Lubs H. A. Variation in human acrocentric chromosomes with acridine orange reverse banding. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 20;30(3):225–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00279188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström J. Human chromosomes and fluorescence. Humangenetik. 1971;12(1):77–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00291038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]