Abstract
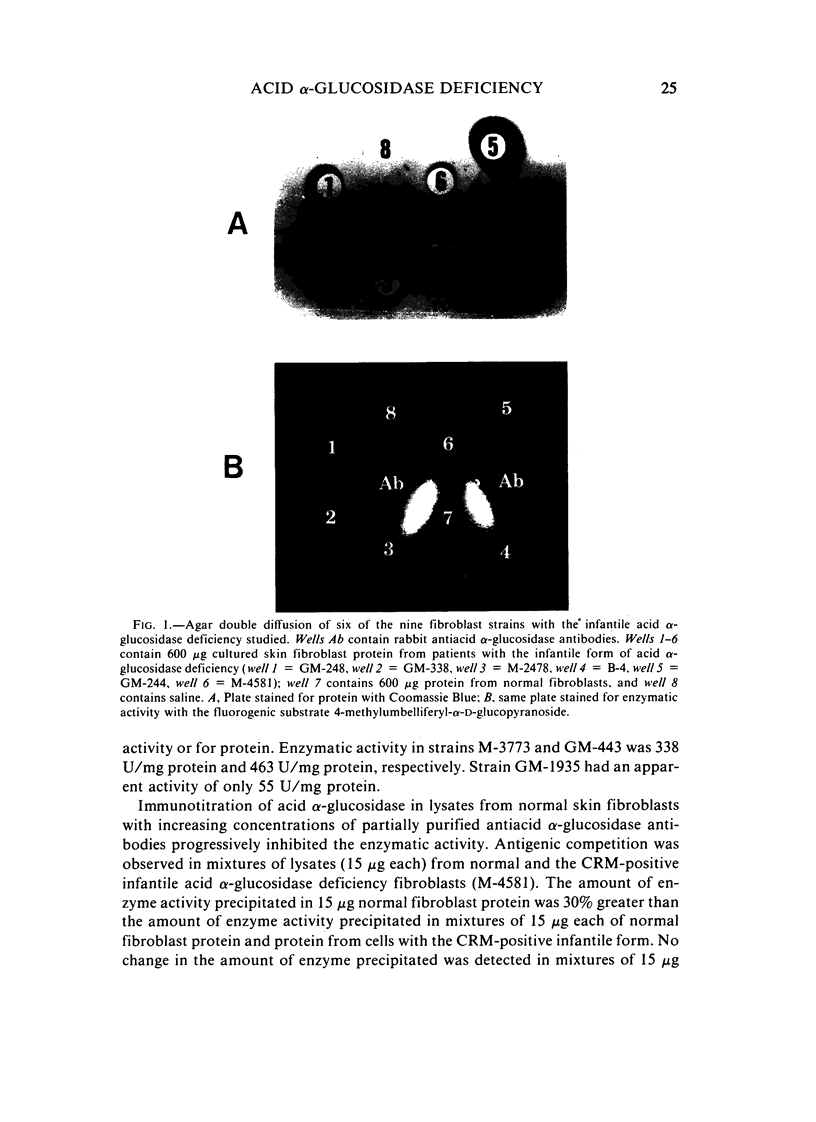
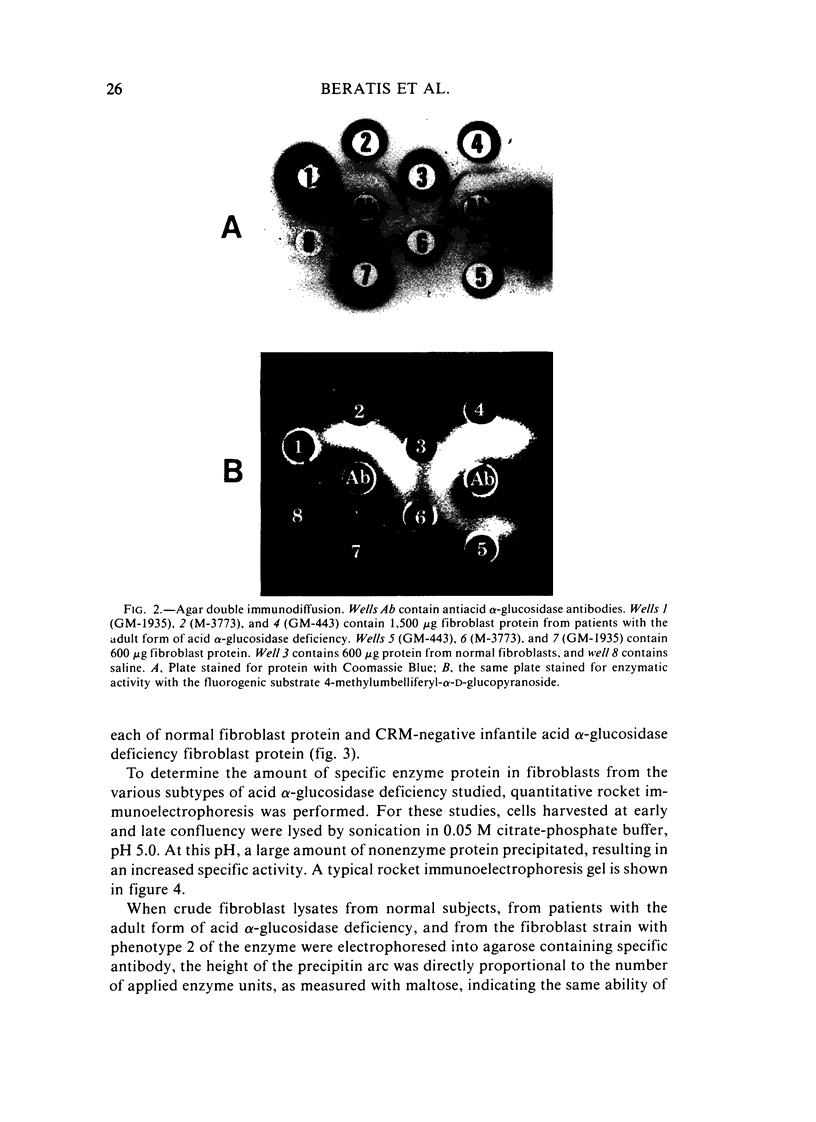
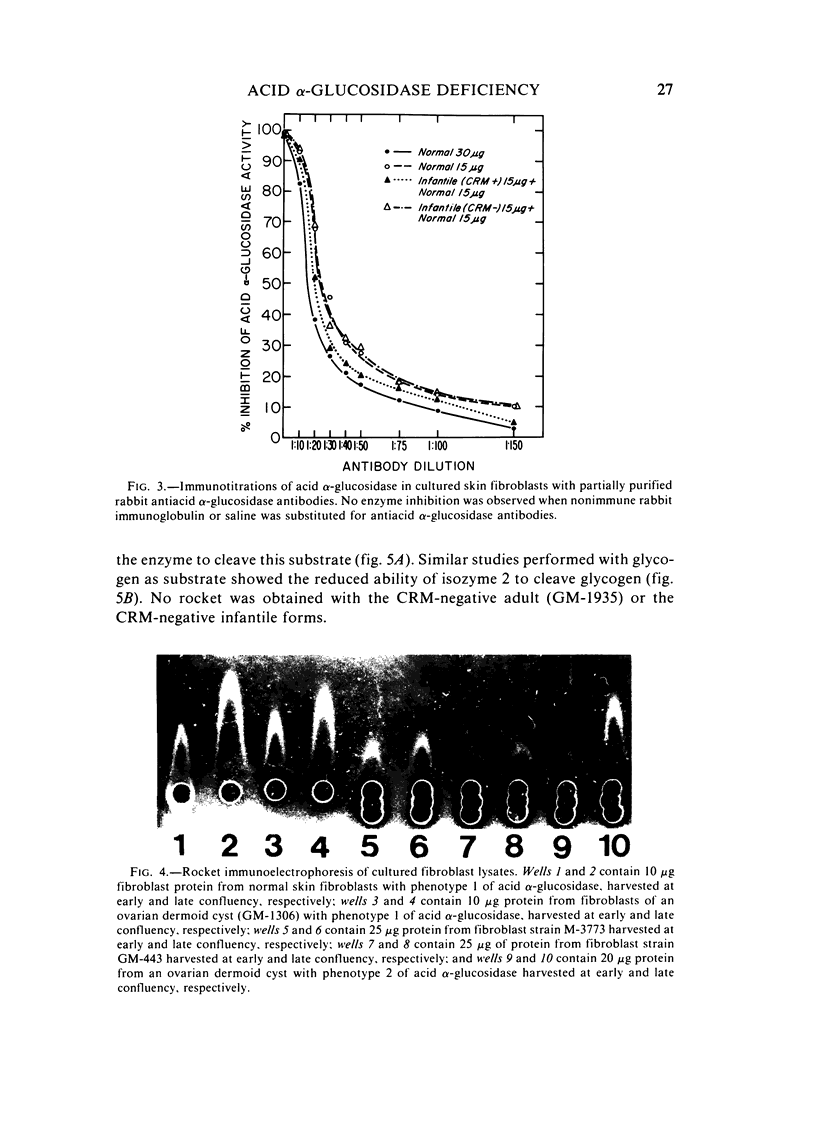
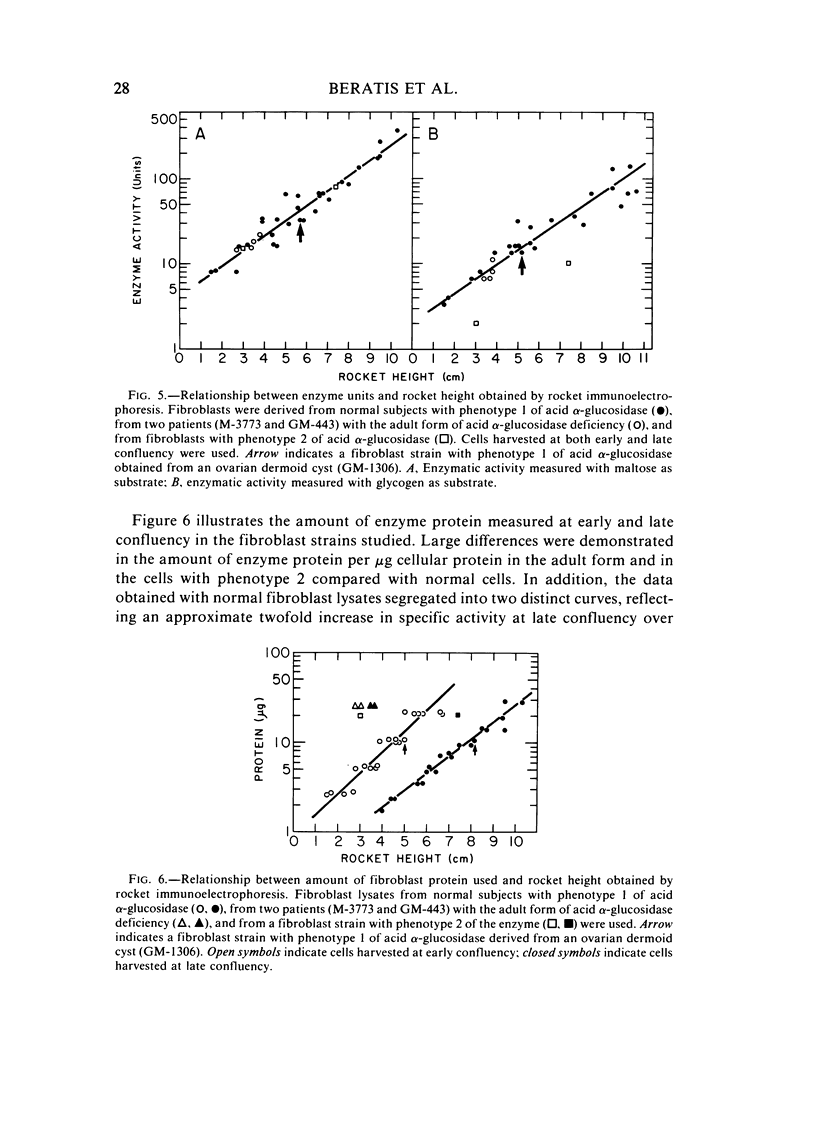
Several clinical forms of acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency have been described. Our study was planned to identify differences at the molecular level in acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency. Of nine fibroblast strains derived from patients with the infantile form of the disease, eight were crossreacting material (CRM)-negative and one CRM-positive. This was demonstrated by both agar immunodiffusion and immunotitration. No difference in apparent enzymatic activity was observed between CRM-negative and CRM-positive infantile acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency fibroblasts. In two fibroblast strains with the adult form of acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency, rocket immunoelectrophoresis demonstrated a reduction in the amount of enzyme protein, which was directly proportional to the reduction in enzyme activity. In another fibroblast strain obtained from a patient with the adult form of the disease, the activity was within the range of the infantile form and no CRM could be identified. Fibroblasts with phenotype 2 of acid alpha-glucosidase, considered a normal variant, showed a reduction both in the amount of enzyme protein and in the ability of the enzyme to cleave glycogen. However, the catalytic activity for maltose was normal. The findings demonstrate extensive genetic heterogeneity in acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency. Molecular differences were identified both between the clinical forms of the disease and within the infantile and the adult forms of acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency. It remains unknown whether or not the enzyme deficiency in homozygotes for isozyme 2 of acid alpha-glucosidase will be sufficient to cause glycogen accumulation and lead to the development of muscular dystrophy-like disease later in life.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert E., Coston R., Perrotto J. Letter: Immunoenzymatic assay for alpha-fetoprotein. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):626–626. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92684-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnon R., Shapira E. Antibodies to papain. A selective fractionation according to inhibitory capacity. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3942–3950. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., LaBadie G. U., Hirschhorn K. An isozyme of acid alpha-glucosidase with reduced catalytic activity for glycogen. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 Mar;32(2):137–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., LaBadie G. U., Hirschhorn K. Characterization of the molecular defect in infantile and adult acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1172/JCI109247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beratis N. G., Turner B. M., Weiss R., Hirschhorn K. Arylsulfatase B deficiency in Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome: Cellular studies and carrier identification. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):475–480. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. I., Brown D. H., Jeffrey P. L. Simultaneous absence of alpha-1,4-glucosidase and alpha-1,6-glucosidase activities (pH 4) in tissues of children with type II glycogen storage disease. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1423–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERS H. G. alpha-Glucosidase deficiency in generalized glycogenstorage disease (Pompe's disease). Biochem J. 1963 Jan;86:11–16. doi: 10.1042/bj0860011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster J. F., Slee R. G. Some properties of human liver acid alpha-glucosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 12;482(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90357-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Electroimmuno assay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1972;124:21–37. doi: 10.3109/00365517209102748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder D., McCaw B. K., Hecht F. Parthenogenic origin of benign ovarian teratomas. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jan 9;292(2):63–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197501092920202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehler M., DiMauro S. Residual acid maltase activity in late-onset acid maltase deficiency. Neurology. 1977 Feb;27(2):178–184. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. K., Brown B. I., Brown D. H. The molecular heterogeneity of purified human liver lysosomal alpha-glucosidase (acid alpha-glucosidase). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Jan 30;185(2):511–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuser A. J., Koster J. F., Hoogeveen A., Galjaard H. Biochemical, immunological, and cell genetic studies in glycogenosis type II. Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Mar;30(2):132–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schram A. W., Brouwer-Kelder B., Donker-Koopman W. E., Loonen C., Hamers M. N., Tager J. M. Use of immobilized antibodies in investigating acid alpha-glucosidase in urine in relation to Pompe's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 12;567(2):370–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swallow D. M., Corney G., Harris H., Hirschhorn R. Acid alpha-glucosidase: a new polymorphism in man demonstrable by 'affinity' electrophoresis. Ann Hum Genet. 1975 May;38(4):391–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1975.tb00629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Barsy T., Jacquemin P., Devos P., Hers H. G. Rodent and human acid -glucosidase. Purification, properties and inhibition by antibodies. Investigation in type II glycogenosis. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Nov 21;31(1):156–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]