Abstract
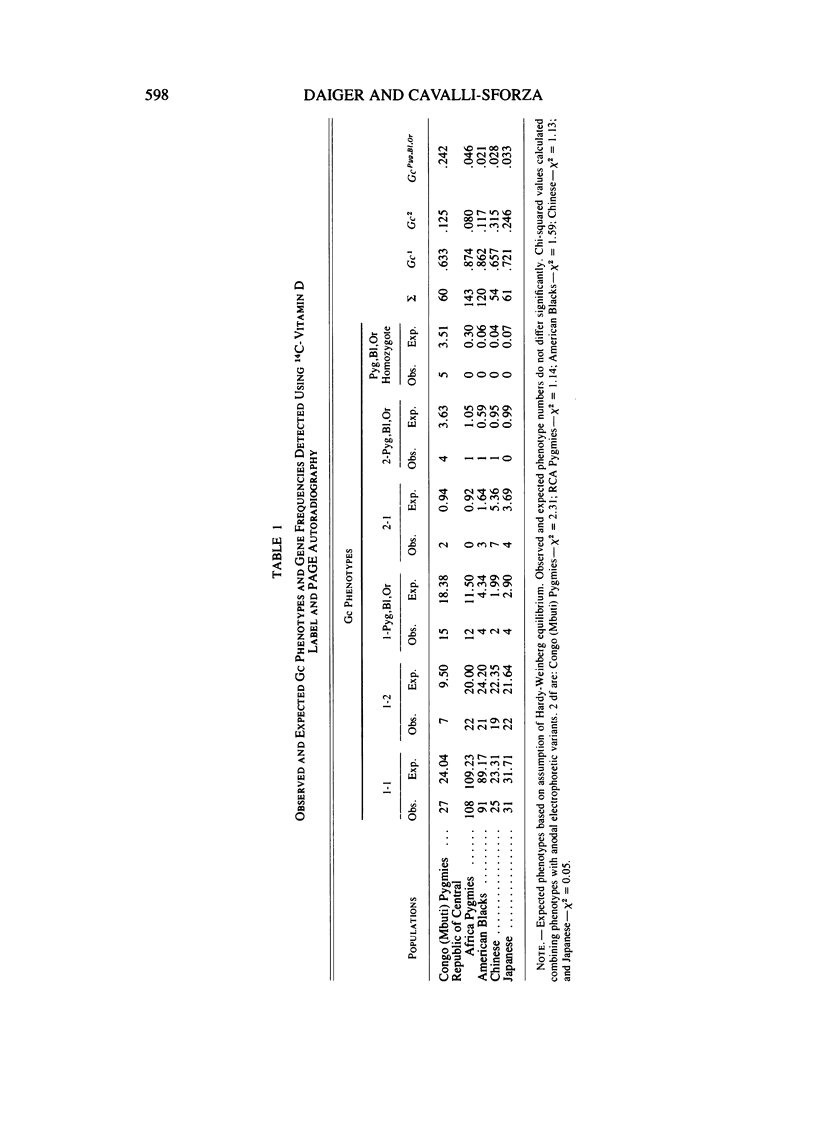
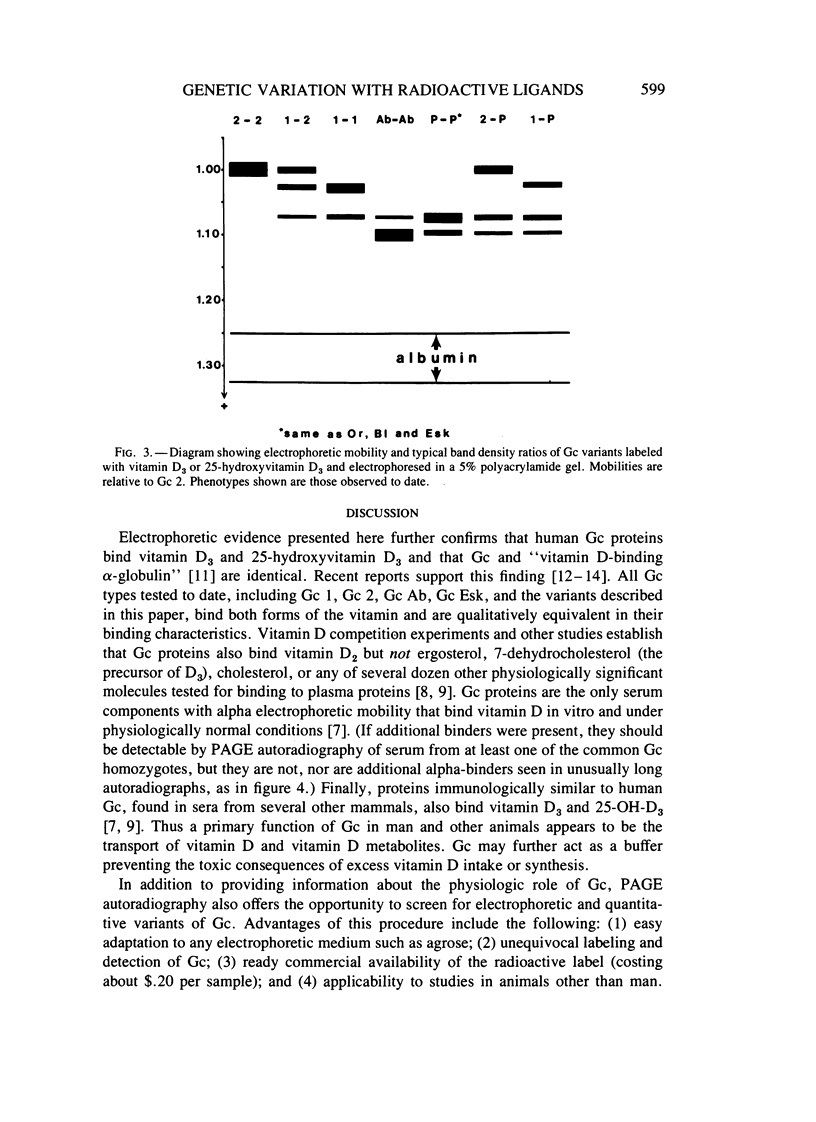
A novel technique for detecting electrophoretic and quantitative variants of group-specific component (Gc) proteins is described. The technique, in vitro labeling with radioactive vitamin D followed by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and autoradiography (PAGE autoradiography), permits sensitive, high resolution detection of Gc variants by virtue of a physiologically significant property: the ability of Gc to bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Using this procedure, anodal Gc variants, with mobility similar to Gc Aborigine and Gc Eskimo, were observed in Chinese, Japanese, African Pygmies, and American Blacks. The gene frequency of these variants ranges from 2.6% to 15%; they were not previously known to be polymorphic in these populations. In addition to qualitative variants, individual variation in Gc band density ratios is documented and discussed. These studies not only illustrate the utility of PAGE autoradiography in screening Gc, but also confirm that a major functional role of Gc in man and other animals is the transport of vitamin D and vitamin D metabolites.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLUMBERG B. S., WORKMAN P. L., HIRSCHFELD J. GAMMA-GLOBULIN, GROUP SPECIFIC, AND LIPOPROTEIN GROUPS IN A U.S. WHITE AND NEGRO POPULATION. Nature. 1964 May 9;202:561–563. doi: 10.1038/202561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsey R., Clark M. B., Bernat M., Glowacki J., Holick M. F., DeLuca H. F., Potts J. T., Jr The physiologic significance of plasma transport of vitamin D and metabolites. Am J Med. 1974 Jul;57(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90767-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon R., Van Baelen H., Rombauts W., De Moor P. The purification and characterisation of the human-serum binding protein for the 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (transcalciferin). Identity with group-specific component. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):285–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Daiger S. P., Rummel D. P. Detection of genetic variation with radioactive ligands. I. Electrophoretic screening of plasma proteins with a selected panel of compounds. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):581–592. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli-Sforza L. L., Zonta L. A., Nuzzo F., Bernini L., de Jong W. W., Meera Khan P., Ray A. K., Went L. N., Siniscalco M., Nijenhuis L. E. Studies on African Pygmies. I. A pilot investigation of Babinga Pygmies in the Central African Republic (with an analysis of genetic distances). Am J Hum Genet. 1969 May;21(3):252–274. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H., Kitchin F. D., Kirchberg G., Wendt G. G. A faster migrating Gc-variant: Gc Darmstadt. Humangenetik. 1970;9(1):26–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00696010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H. The variants of the group-specific component. A review of their distribution in human populations. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Sep-Oct;9(9):1133–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daiger S. P., Schanfield M. S., Cavalli-Sforza L. L. Group-specific component (Gc) proteins bind vitamin D and 25-hydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNIG W., HOPPE H. H. A NEW ALLELE IN THE GC-SYSTEM: GC. Vox Sang. 1965 Mar-Apr;10:214–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb04341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCHFELD J. Immune-electrophoretic demonstration of qualitative differences in human sera and their relation to the haptoglobins. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1959;47:160–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1959.tb04844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddad J. G., Jr, Walgate J. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D transport in human plasma. Isolation and partial characterization of calcifidiol-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 25;251(16):4803–4809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imawari M., Goodman D. S. Immunological and immunoassay studies of the binding protein for vitamin D and its metabolites in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):432–442. doi: 10.1172/JCI108657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Cleve H., Alper C. Variants of the group-specific component system as demonstrated by immunofixation electrophoresis. Report of a new variant, Gc Boston (Ge B). Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Nov;27(6):728–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK R. L., CLEVE H., BEARN A. G. THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE GROUP SPECIFIC COMPONENT (GC) IN SELECTED POPULATIONS IN SOUTH EAST ASIA AND OCEANIA. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1963;13:140–149. doi: 10.1159/000151794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F. Skin-pigment regulation of vitamin-D biosynthesis in man. Science. 1967 Aug 4;157(3788):501–506. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3788.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermid E. M., Cleve H. A comparison of the fast migrating Gc-variant of Australian aborigines, New Guinean indigenes, South African Bantu, and black Americans. Hum Hered. 1972;22(3):249–253. doi: 10.1159/000152494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Okura K. The distribution of several serological and biochemical traits in east Asia. 3. The distribution of gamma-globulin (Gm(1), Gm(2), Gm(5) and Inv(1) and Gc groups in Taiwan and Ryukyu. Hum Hered. 1971;21(4):362–370. doi: 10.1159/000152427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinskou T. A new variant in the Gc system. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1965;15(3):248–255. doi: 10.1159/000151917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner C., Dahr P. Gc Norway (Ge1C): a second mother-child combination. Vox Sang. 1969 Jun;16(6):510–513. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb04782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speiser P., Pausch V., Cleve H. A new rapid migrating variant in the Gc-system: Gc Wien. Humangenetik. 1972;17(1):81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01789606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Yachi A., Otani H. Immunoelectrophoretic study of group specific components (Gc system). Frequency of distribution of Gc system in Japanese population. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1966 Mar;10(4):157–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]