Abstract
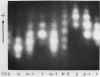
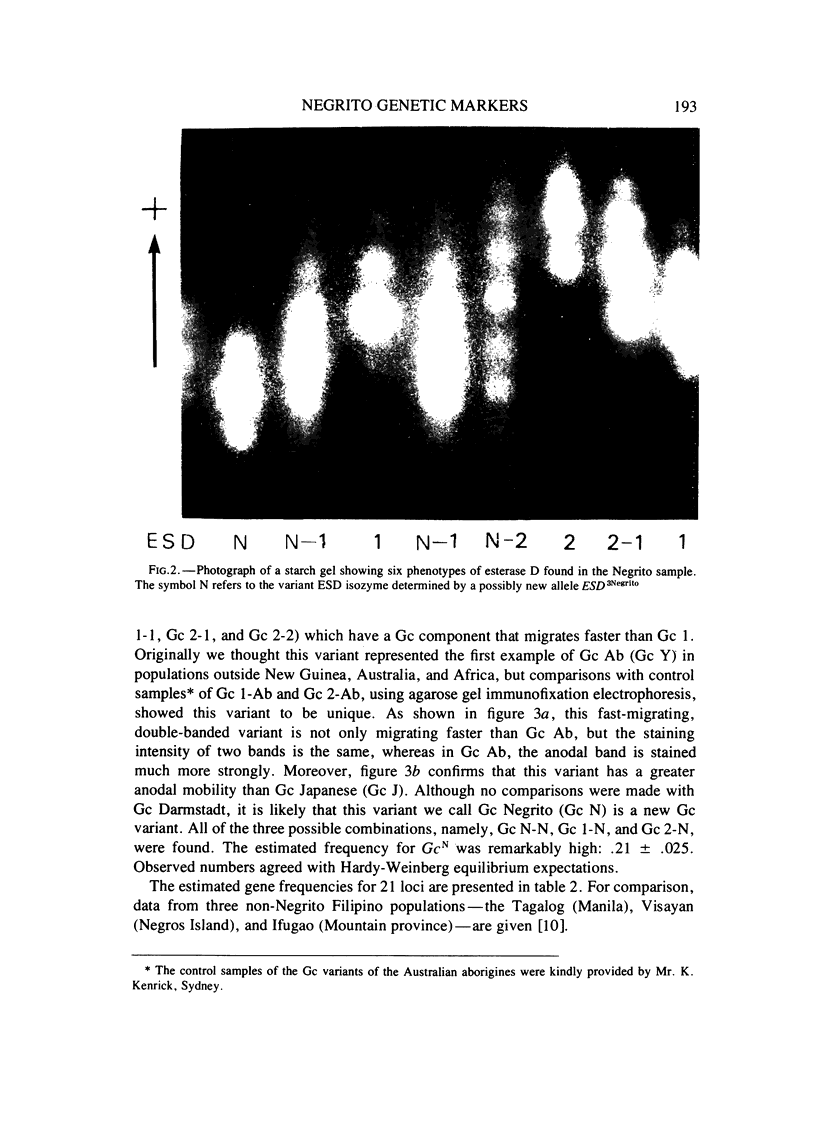
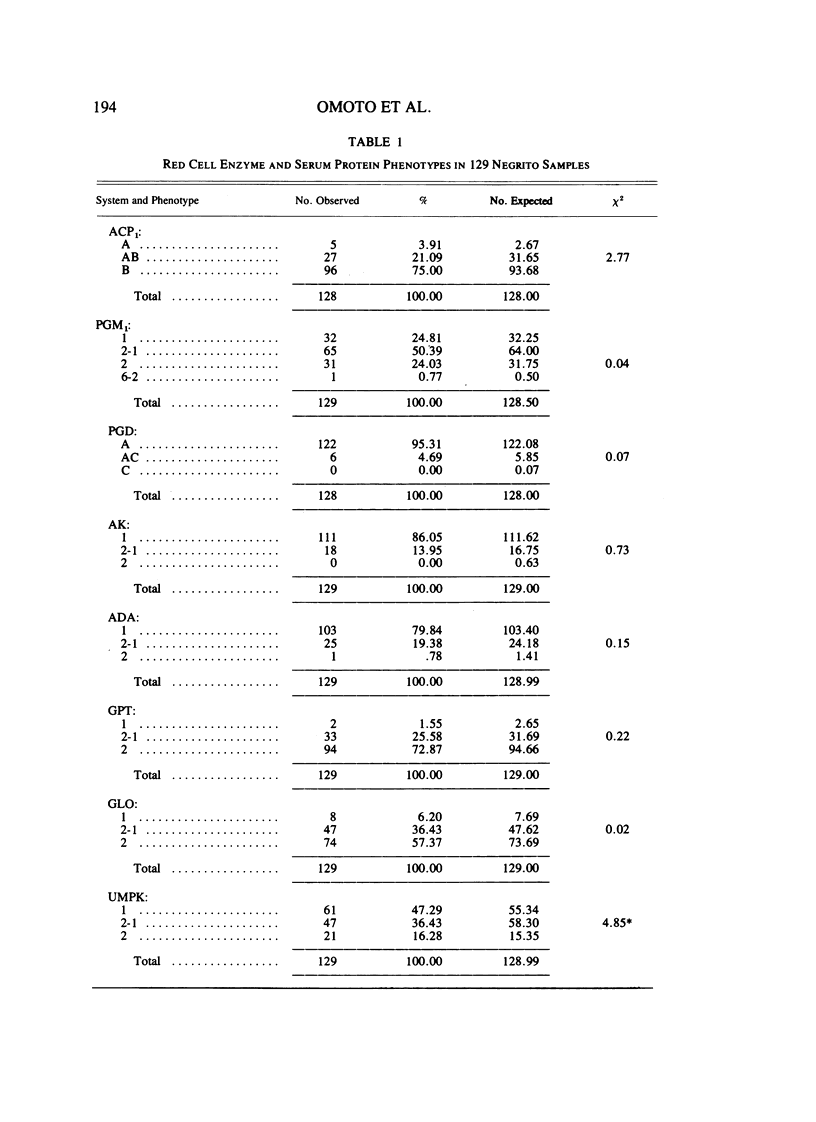
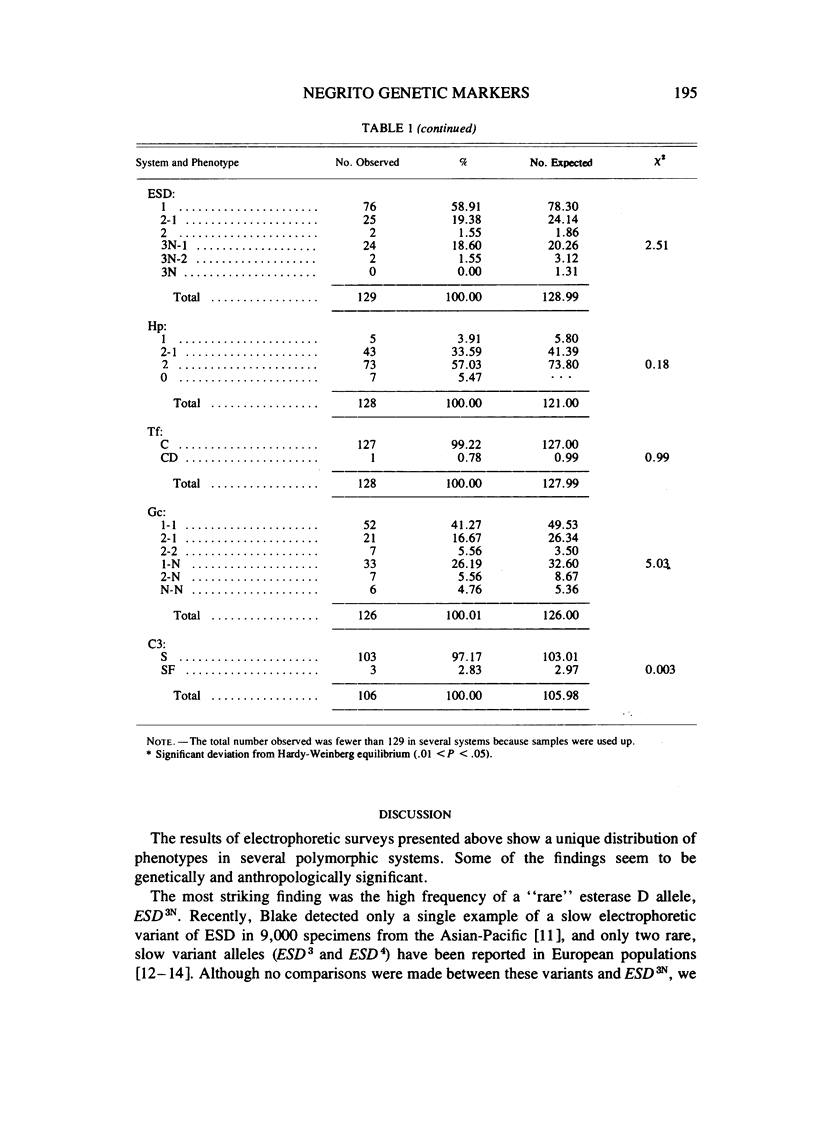
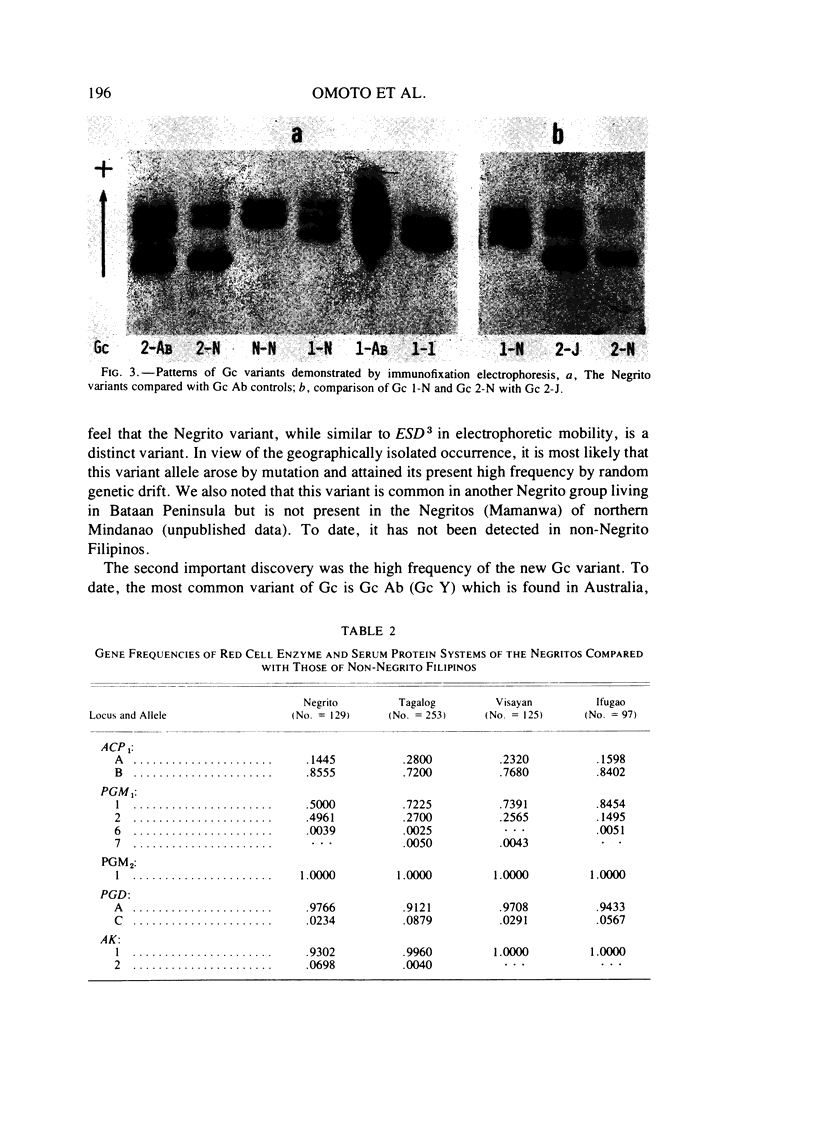
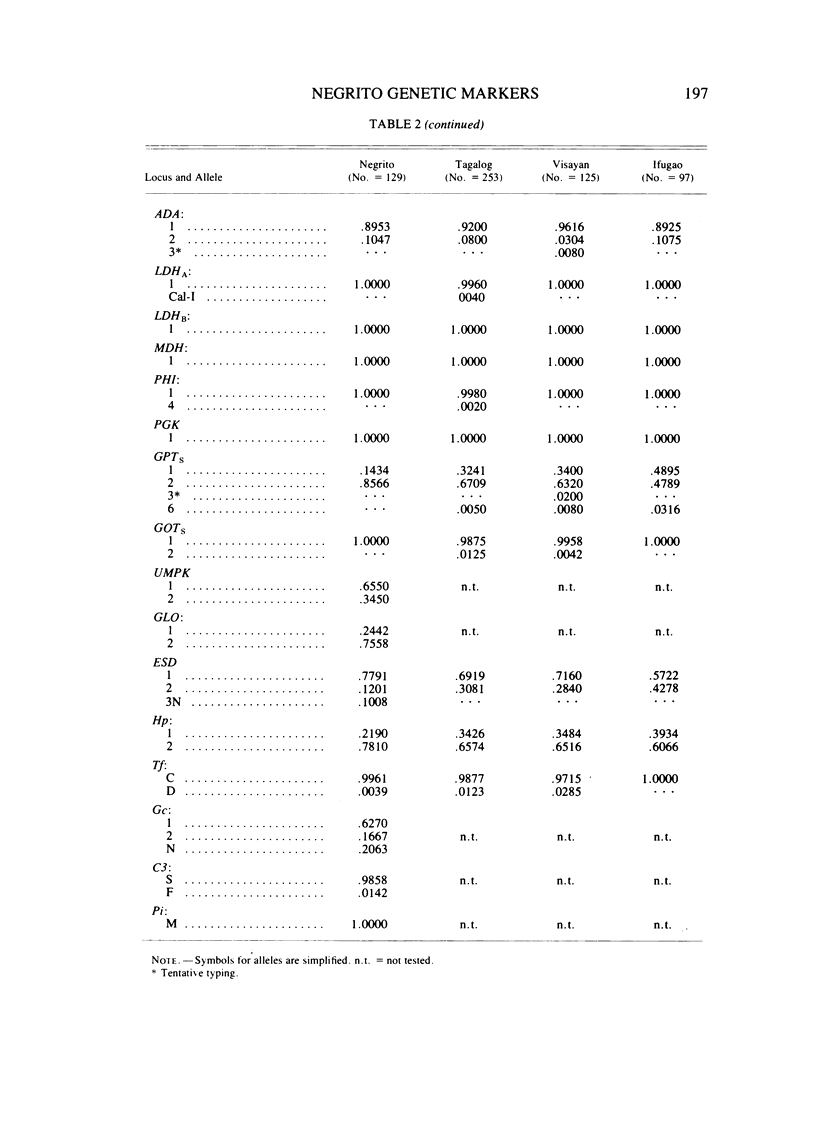
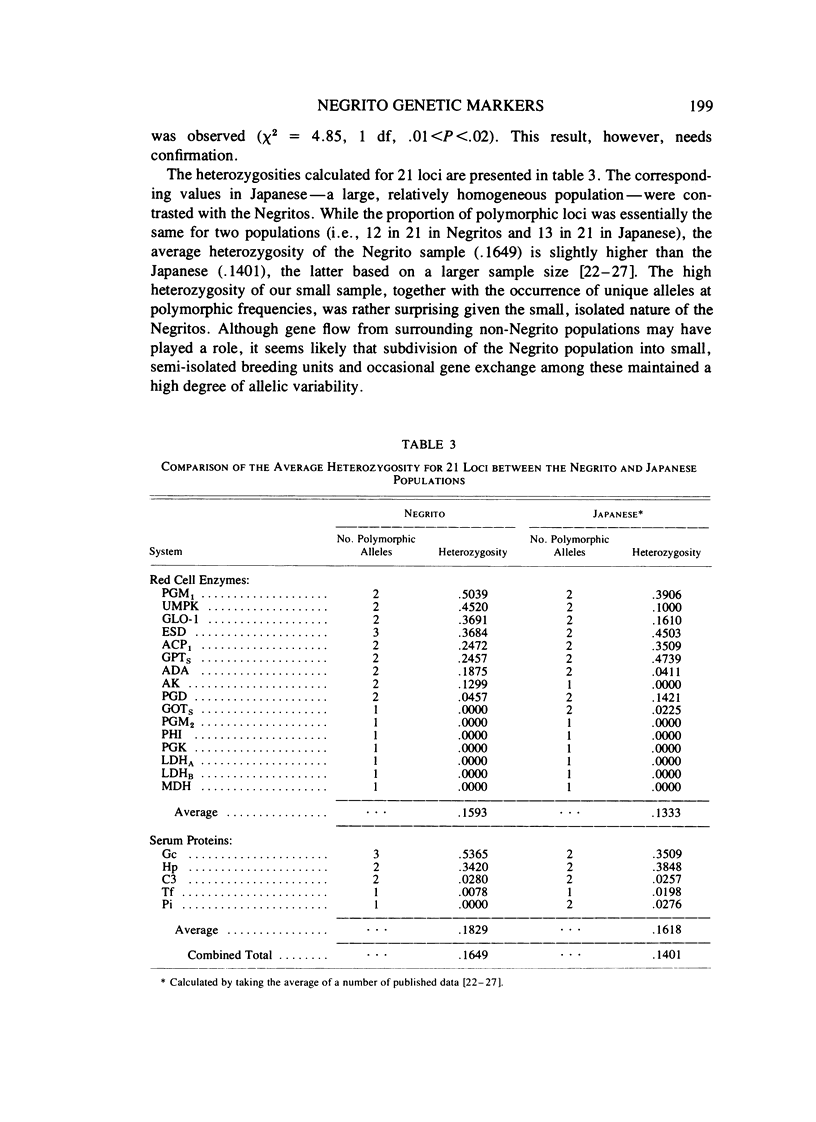
Electrophoretic surveys of red cell enzyme and serum protein systems representing 21 genetic loci were carried out on 129 blood samples of the Negritos of Pampanga, Central Luzon, the Philippines. Nine (out of 16) red cell enzyme loci and four (out of five) serum protein loci showed polymorphic variation. Low frequencies of ACP 1A, GPTs1, ESD2, and Hp1, and a markedly high frequency of PGM12 were contrasted to those in non-Negrito Filipinos. Variant ESD phenotypes with a slowly migrating isozyme occurred in high frequency. The new allele designated as ESD3Negrito (ESD3N) had a frequency of .10 +/- .019. In AK, a variant phenotype indistinguishable from AK 2-1 was observed in 14% of the sample. In the Gc system, a fast migrating variant was discovered in high frequency which was distinct from Gc Ab and Gc J. The variant allele, denoted GcNegrito (GcN), had a frequency of .21 +/- .025. A relatively high degree of allelic diversity in the Negrito sample was also suggested by the average heterozygosity for 21 loci screened (.165), which is compared to that of the Japanese population (.140).
Full text
PDF
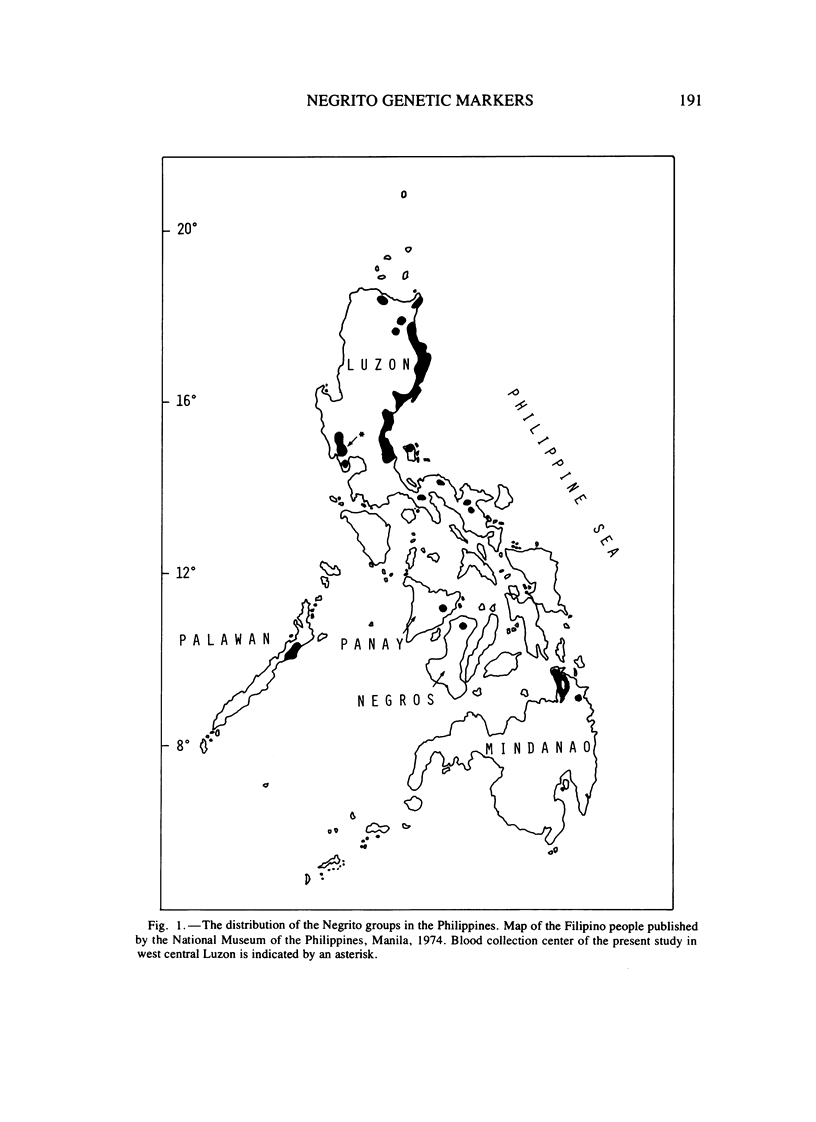




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargagna M., Domenici R., Morali A. Red cell esterase-D polymorphism in the population of Tuscany. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 23;29(3):251–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00297631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender K., Frank R. Esterase D-Polymorphismus: Darstellung in der Hochspannungselektrophorese und Mitteilung von Allelhäufigkeiten. Humangenetik. 1974;23(4):315–318. doi: 10.1007/BF00272516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg K., Schwarzfischer F., Wischerath H. Esterase D polymorphism: description of the "new" allele EsD4. Hum Genet. 1976 Apr 15;32(1):81–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00569980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake N. M. Glutamic pyruvic transaminase and esterase D types in the Asian-Pacific area. Hum Genet. 1976 Dec 29;35(1):91–102. doi: 10.1007/BF00295623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleve H. The variants of the group-specific component. A review of their distribution in human populations. Isr J Med Sci. 1973 Sep-Oct;9(9):1133–1146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Ito M., Misawa S. Red cell uridine monophosphate kinase polymorphism in Japanese. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 23;29(3):255–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00297632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Mano K., Misawa S. Genetic polymorphism of the third complement component (C'3) in Japanese. Jinrui Idengaku Zasshi. 1975 Sep;20(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Cleve H., Alper C. Variants of the group-specific component system as demonstrated by immunofixation electrophoresis. Report of a new variant, Gc Boston (Ge B). Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Nov;27(6):728–736. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp G. W., Jr, Sutton H. E. Some new phenotypes of human red cell acid phosphatase. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 Jan;19(1):54–62. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omoto K., Aoki K., Harada S. Polymorphism of esterase D in some population groups in Japan. Hum Hered. 1975;25(5):378–381. doi: 10.1159/000152749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascasio F. M., Bias W., Manipol V., Campos P. C. Genetic marker systems in Philippine Negritos. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1974;10(10):220–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saha N., Kirk R. L., Shanbhag S., Joshi S. H., Bhatia H. M. Genetic studies among the Kadar of Kerala. Hum Hered. 1974;24(2):198–218. doi: 10.1159/000152653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]