Abstract
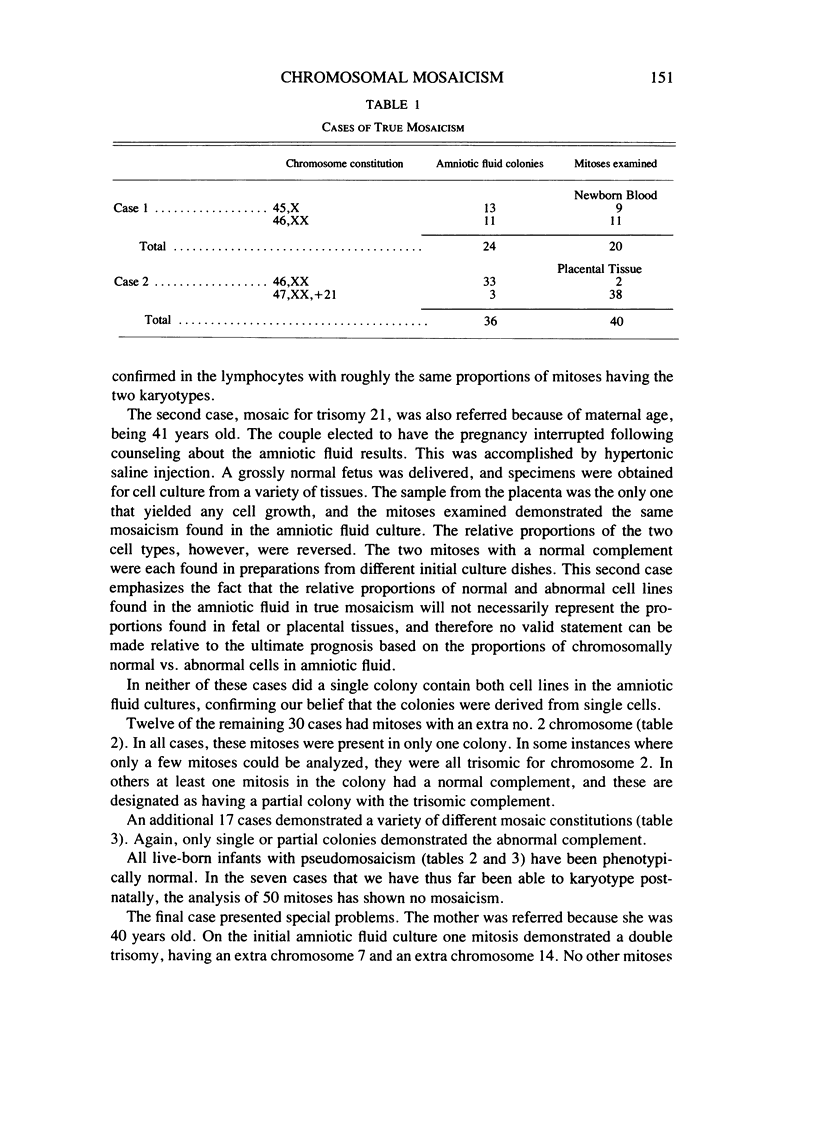
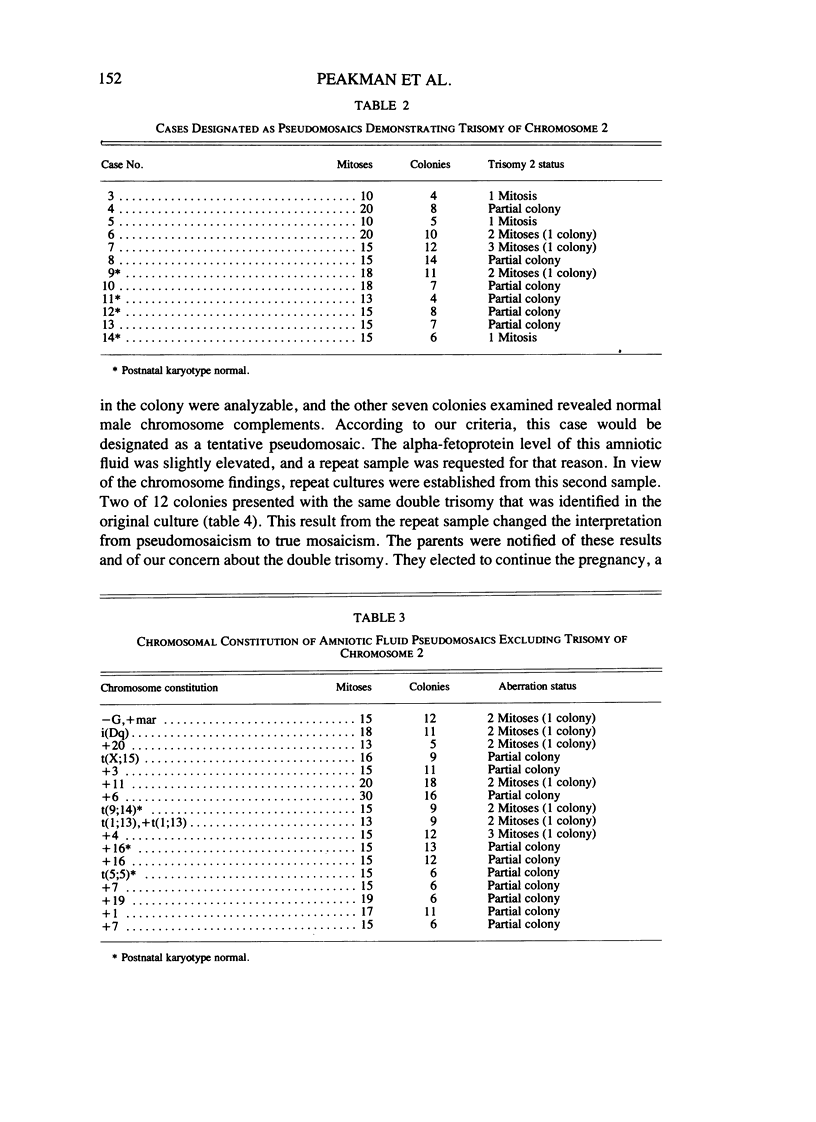
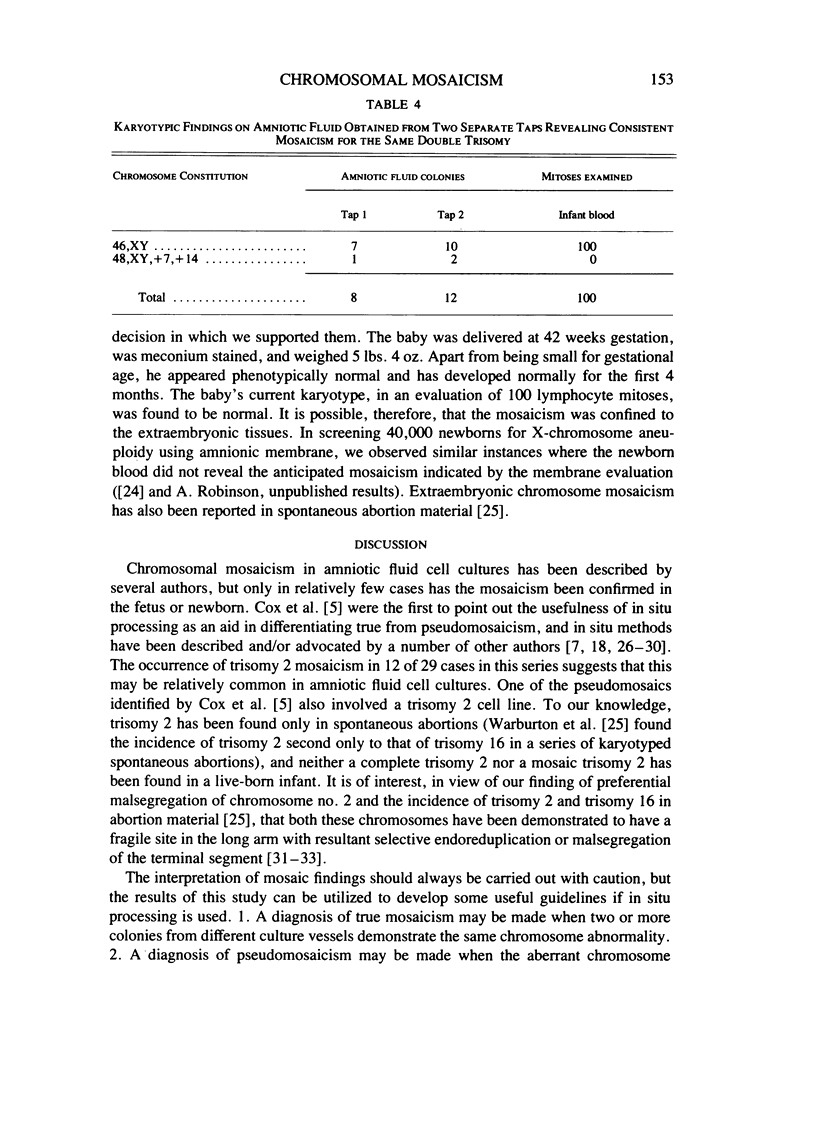
Over the past 6 years, using in situ processing methods, we have identified 32 cases of mosaicism in amniotic fluid cell cultures prepared from 1,100 samples. Two of these (45,X/46,XX and 46,XX/47,XX, + 21) were called true mosaics because multiple colonies demonstrated the same abnormal chromosome complement, and on subsequent evaluation of the newborn blood or fetal tissues, mosaicism was confirmed. Of the remaining cases, 29 were designated as pseudomosaics because only single or partial colonies exhibited an aberrant chromosome complement, 12 having a trisomy 2 line. In the final case, a double trisomy was demonstrated in only one of eight colonies in the first culture, but in the culture from a repeat sample an additional two colonies showed the same double trisomy. Since no abnormal cells were observed in infant blood, it was postulated that the mosaicism may only have been present in the extraembryonic tissues. It is our conviction that the use of these cloning methods should diminish the danger of misdiagnosis in genetic amniocentesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbo G., Zellweger H. Prenatal determination of fetal sex and chromosomal complement. Lancet. 1970 Jan 31;1(7640):216–217. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. D., Schmickel R., Barr M., Burdi A. R. Prenatal detection of autosomal mosaicism. J Pediatr. 1974 May;84(5):732–733. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(74)80021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. M., Niewczas-Late V., Riffell M. I., Hamerton J. L. Chromosomal mosaicism in diagnostic amniotic fluid cell cultures. Pediatr Res. 1974 Jun;8(6):679–683. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197406000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandall B. F., Lebherz T. B. Prenatal genetic diagnosis in 350 amniocenteses. Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Aug;48(2):158–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran T. A., Rudd N. L., Gardner H. A., Lowden J. A., Benzie R. J., Liedgren S. I. The antenatal diagnosis of genetic disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Feb 1;118(3):314–321. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)33785-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray C., Davidson R. G., Cohen M. M. A simplified technique for the culture of amniotic fluid cells. J Pediatr. 1971 Jul;79(1):119–122. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80070-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greensher A., Gersh R., Peakman D., Robinson A. Screening of newborn infants for abnormalities of the Y chromosome. J Pediatr. 1971 Aug;79(2):305–306. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Dubin E. C., Kerenyi T., Hirschhorn K. Results and pitfalls in prenatal cytogenetic diagnosis. J Med Genet. 1973 Jun;10(2):112–119. doi: 10.1136/jmg.10.2.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu L. Y., Kim H. J., Hausknecht R., Hirschhorn K. Prenatal diagnosis of 45,X/46,XY mosaicism with postnatal confirmation in a phenotypically normal male infant. Clin Genet. 1976 Oct;10(4):232–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1976.tb00040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajii T. Pseudomosaicism in cultured amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet. 1971 Nov;2(7732):1037–1037. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardon N. B., Chernay P. R., Hsu L. Y., Martin J. L., Hirschhorn K. Problems in prenatal diagnosis resulting from chromosomal mosaicism. Clin Genet. 1972;3(2):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1972.tb01730.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardon N. B., Krauss M., Davis J. G., Jenkins E. C. Chromosomal mosaicism in amniotic fluid cell cultures. J Pediatr. 1977 Mar;90(3):501–502. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K. P., Park I. J., Heller R. H., Barakat B. Y., Preston E., Jones H. W., Jr Errors of prenatal cytogenetic diagnosis. Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Nov;44(5):693–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn G., Mennuti M. T., Kaback M., Schwartz R. M., Chemke J., Goldman B., Mellman W. J. Chromosomal mosaicism in amniotic cell culture. A diagnostic Dilemma. Isr J Med Sci. 1975 May;11(5):476–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladda R., Hildebrandt R., Dobelle Y. Sex chromosomal mosaicism undetected by prenatal study. J Pediatr. 1977 May;90(5):841–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurence K. M., Gregory P. Prenatal diagnosis of chromosome disorders. Br Med Bull. 1976 Jan;32(1):9–15. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Bendel R. P., Brooker D. C. Aneuploidy in cultured amniotic cells. JAMA. 1972 Feb 28;219(9):1211–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune J., Dutrillaux B., Lafourcade J., Berger R., Abonyi D., Rethoré M. O. Endoréduplication sélective du bras long du chromosome 2 chez une femme et sa fille. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1968 Jan 3;266(1):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Hecht F., Lovrien E. W. Heritable fragile site on chromosome 16: probable localization of haptoglobin locus in man. Science. 1970 Oct 2;170(3953):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3953.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milunsky A., Atkins L. Letter: Prenatal diagnois of chromosomal mosaicism. J Pediatr. 1976 Feb;88(2):365–366. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niermeijer M. F., Sachs E. S., Jahodova M., Tichelaar-Klepper C., Kleijer W. J., Galjaard H. Prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders. J Med Genet. 1976 Jun;13(3):182–194. doi: 10.1136/jmg.13.3.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noël B., Quack B., Mottet J., Nantois Y., Dutrillaux B. Selective endoreduplication or branched chromosome? Exp Cell Res. 1977 Feb;104(2):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakman D. C., Moreton M. F., Robinson A. Letter to the editor: Chromosomal mosaicism in amniotic fluid cell cultures. Pediatr Res. 1975 May;9(5):516–516. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197505000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peakman D. C., Moreton M. F., Robinson A. Prenatal diagnosis: techniques used to help in ruling out maternal cell contamination. J Med Genet. 1977 Feb;14(1):37–39. doi: 10.1136/jmg.14.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson A., Puck T. T. Studies on chromosomal nondisjunction in man. II. Am J Hum Genet. 1967 Mar;19(2):112–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W. A technique for in situ karyotyping of primary amniotic fluid cell cultures. Humangenetik. 1975 Dec 23;30(4):325–330. doi: 10.1007/BF00275145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström J. Four cases of chromosome changes detected in course of prenatal diagnosis and probably originating in vitro. Hum Genet. 1978 Apr 24;41(3):265–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00284760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


