Abstract
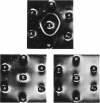
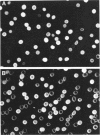
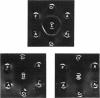
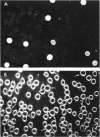
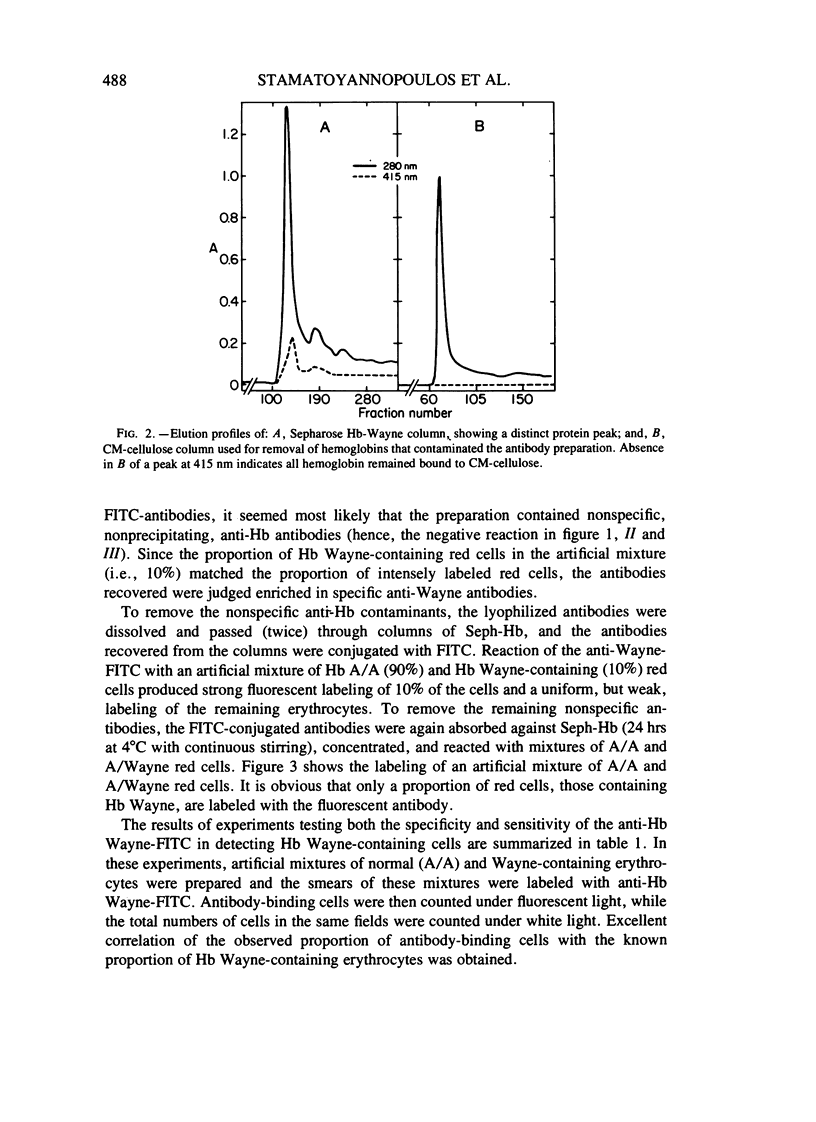
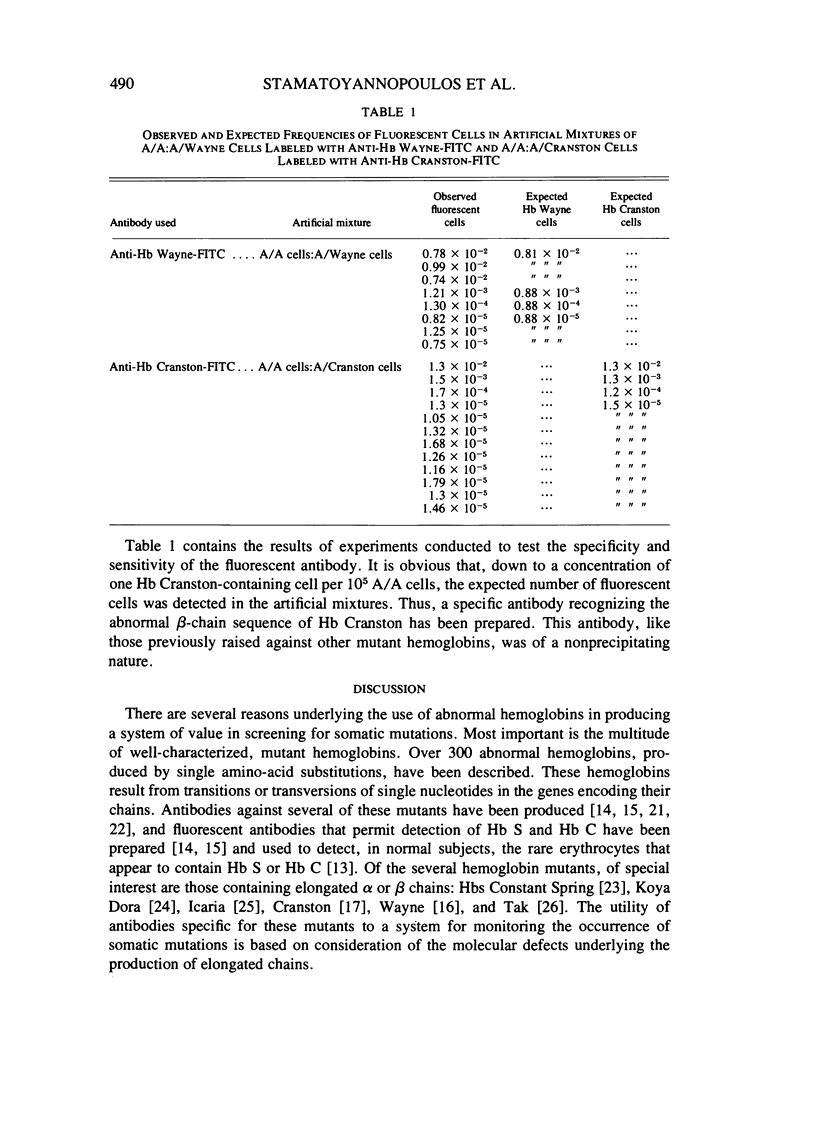
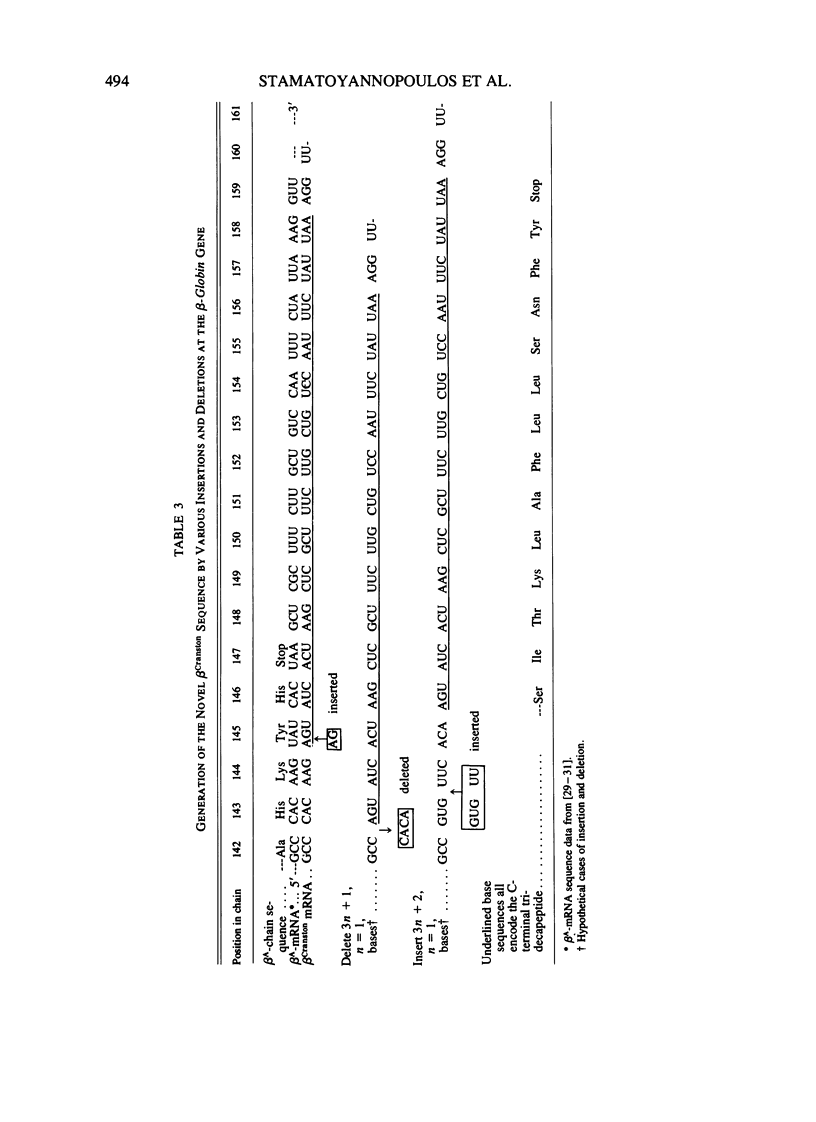
The production and purification of antibodies detecting Hb Wayne, an alpha-globin frameshift mutant, and Hb Cranston, a beta-globin frameshift mutant, are described. The antibodies are of a nonprecipitating nature, and they permit strong fluorescent labeling of erythrocytes containing Hb Wayne or Hb Cranston. Studies using artificial mixtures containing cells with either of the two mutants in frequencies ranging from 1 in 10(2) to 1 in 10(5) showed that fluorescent antibodies can detect rare mutant red cells in the presence of vast excesses of normal erythrocytes. On the basis of the structures and the molecular lesions underlying production of the two abnormal hemoglobins, we predict that the anti-Hb Wayne antibody will detect several frameshift mutants resulting from deletion of 3n + 1 nucleotides or insertion of 3n + 2 nucleotides at the 5' side of the codon normally specifying residue 139 of the alpha chain. The anti-Hb Cranston antibody should be capable of detecting beta chains, the corresponding genes of which have sustained insertions of 3n + 2 nucleotides or deletions of 3n + 1 nucleotides on the 5' side of the codon normally specifying residue 144. The two antibodies may, therefore, prove to be valuable in the development of a system aimed at detecting rare erythrocytes that express mutations which arise in the hemopoietic stem cells of normal individuals and subjects exposed to mutagens.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bunn H. F., Schmidt G. J., Haney D. N., Dluhy R. G. Hemoglobin Cranston, an unstable variant having an elongated beta chain due to nonhomologous crossover between two normal beta chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3609–3613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Contopolou-Griva I., Caroutsos K., Poungouras P., Tsevrenis H. Haemoglobin Icaria, a new chain-termination mutant with causes alpha thalassaemia. Nature. 1974 Sep 20;251(5472):245–247. doi: 10.1038/251245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg J. B., Weatherall D. J., Milner P. F. Haemoglobin Constant Spring--a chain termination mutant? Nature. 1971 Dec 10;234(5328):337–340. doi: 10.1038/234337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford T. B., McGuire T. C., Henson J. B. Detection of equine infectious anemia virus in vitro by immunofluorescence. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1971;34(4):332–339. doi: 10.1007/BF01242979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong W. W., Meera Khan P., Bernini L. F. Hemoglobin Koya Dora: high frequency of a chain termination mutant. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jan;27(1):81–90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Environmental mutagenic hazards. Science. 1975 Feb 14;187(4176):503–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flatz G., Kinderlerer J. L., Kilmartin J. V., Lehmann H. Haemoglobin Tak: a variant with additional residues at the end of the beta-chains. Lancet. 1971 Apr 10;1(7702):732–733. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91994-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Marotta C. A., Weissman S. M., Cohen-Solal M. Nucleotide sequences of the 3'-terminal untranslated region of messenger RNA for human beta globin chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G. Nucleotide sequence of human beta globin messenger RNA. Hemoglobin. 1977;1(8):879–881. doi: 10.3109/03630267709003915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garver F. A., Baker M. B., Jones C. S., Gravely M., Altay G., Huisman T. H. Radioimmunoassay for abnormal hemoglobins. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1334–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.867032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotta C. A., Wilson J. T., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Human beta-globin messenger RNA. III. Nucleotide sequences derived from complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5040–5053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V., Bloom A. D. The detection of environmental mutagens. Med Clin North Am. 1969 Nov;53(6):1243–1256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel J. V. The detection of increased mutation rates in human populations. Perspect Biol Med. 1971;14(4):522–537. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1971.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T. H., Mcguire T. C., Lim G., Garzel E., Nute P. E., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Identification of Haemoglobin S in red cells and normoblasts, using fluorescent anti-Hb S antibodies. Br J Haematol. 1976 Sep;34(1):25–31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb00170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papayannopoulou T., Lim G., McGuire T. C., Ahern V., Nute P. E., Stamatoyannopoulos G. Use of specific fluorescent antibodies for the identification of hemoglobin C in erythrocytes. Am J Hematol. 1977;2(2):105–112. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830020202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Quantitative immunological studies on single amino acid substitution in human hemoglobin: demonstration of specific antibodies to multiple sites. Immunochemistry. 1974 Jan;11(1):21–27. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seid-Akhavan M., Winter W. P., Abramson R. K., Rucknagel D. L. Hemoglobin Wayne: a frameshift mutation detected in human hemoglobin alpha chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):882–886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., deRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Marotta C. A., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of 3' untranslated portion of human alpha globin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jul;4(7):2353–2368. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.7.2353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. G., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Lim G., Nute P. E. F-cells in the adult: normal values and levels in individuals with hereditary and acquired elevations of Hb F. Blood. 1975 Nov;46(5):671–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]