Abstract
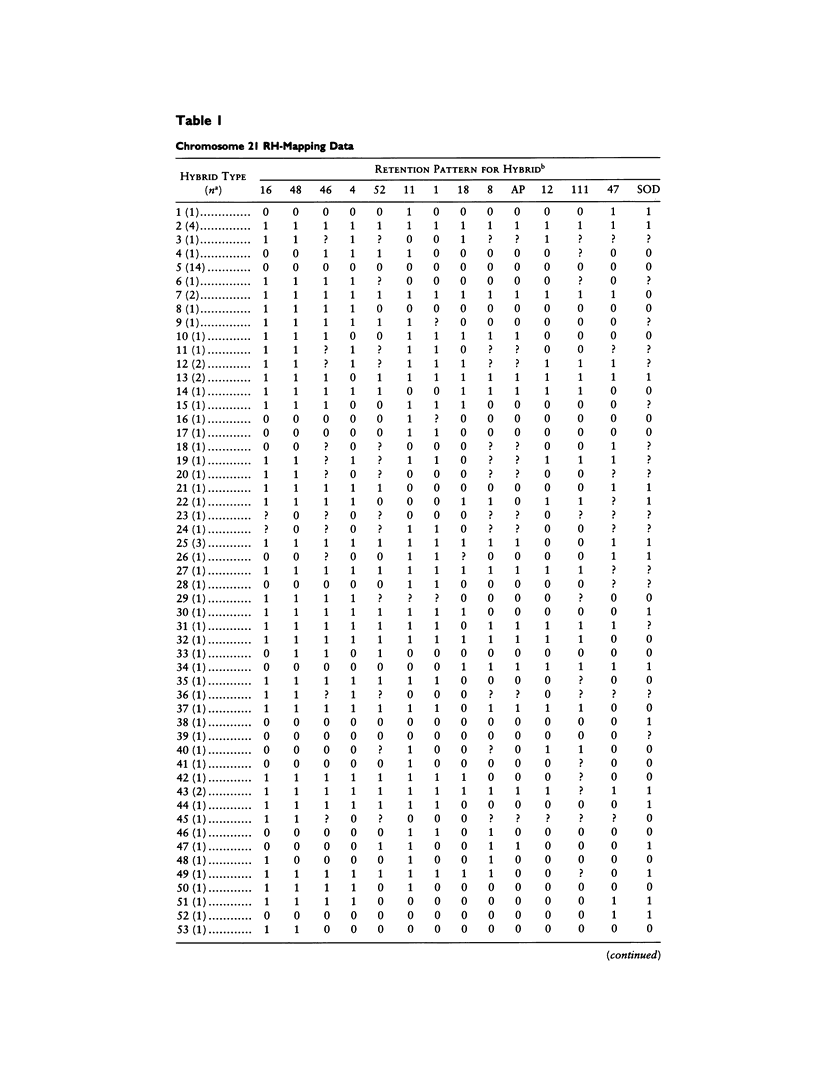
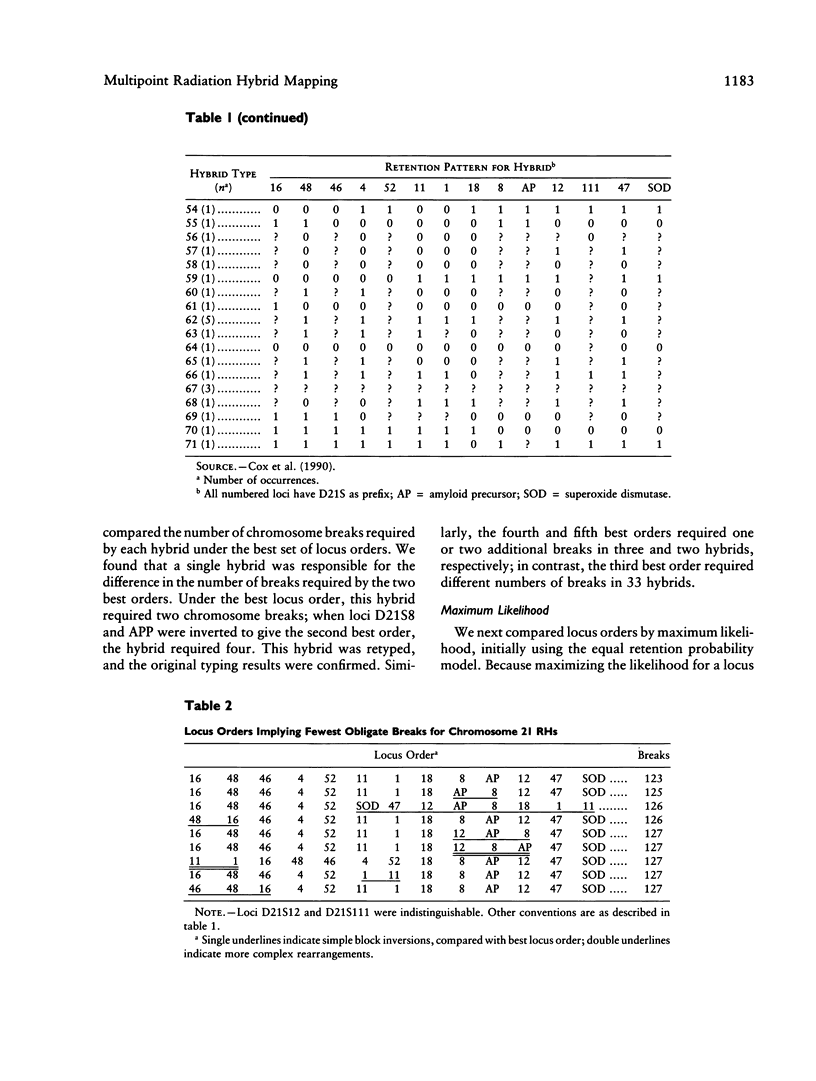
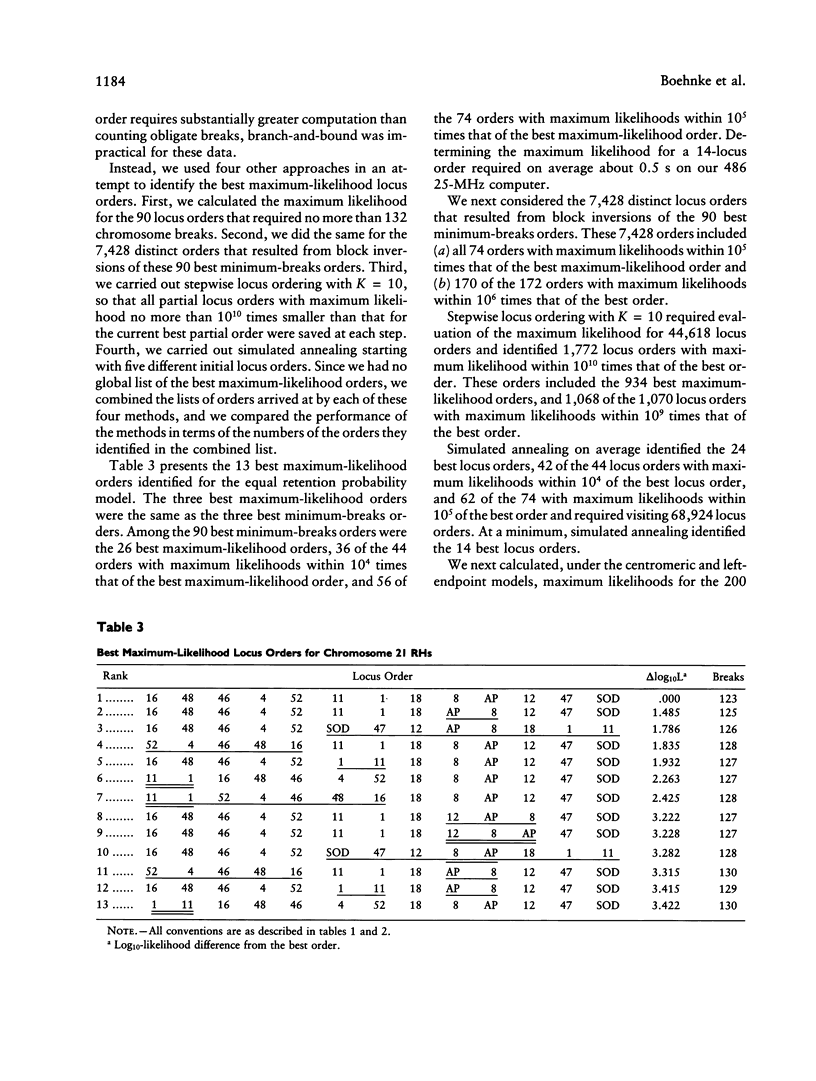
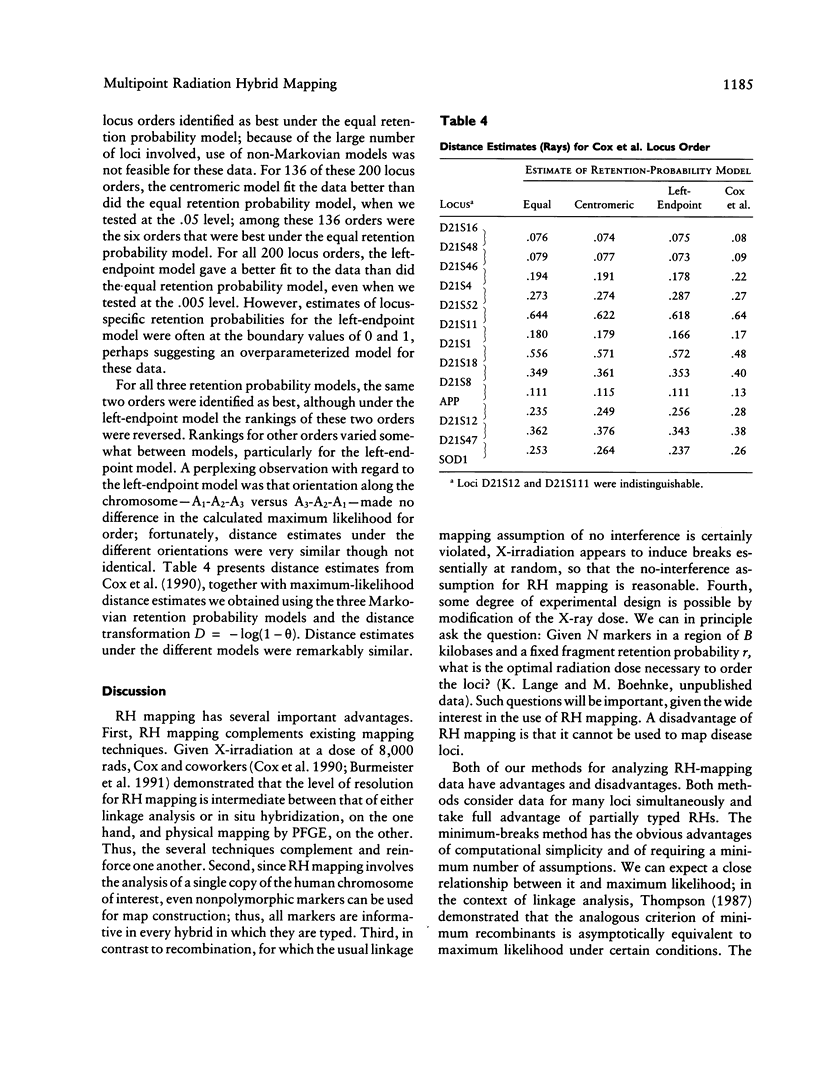
On the basis of the earlier work of Goss and Harris, Cox et al. introduced radiation hybrid (RH) mapping, a somatic cell genetic technique for constructing fine-structure maps of human chromosomes. Radiation hybrid mapping uses X-ray breakage of chromosomes to order a set of genetic loci and to estimate distances between them. To analyze RH mapping data Cox et al. derived statistical methods that employ information on sets of two and four loci, to build an overall locus order. Here we describe alternative nonparametric and maximum-likelihood methods for the analysis of RHs that use information on many loci simultaneously, including information on partially typed hybrids. Combination of these multipoint methods provides a statistically more efficient solution to the locus-ordering problem. We illustrate our approach by applying it to RH mapping data on 14 markers in 99 radiation hybrids for the proximal long arm of human chromosome 21.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D., Green P., Knowlton R., Schumm J., Lander E., Oliphant A., Willard H., Akots G., Brown V., Gravius T. Genetic linkage map of human chromosome 7 with 63 DNA markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8006–8010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benham F., Hart K., Crolla J., Bobrow M., Francavilla M., Goodfellow P. N. A method for generating hybrids containing nonselected fragments of human chromosomes. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Kim S., Price E. R., de Lange T., Tantravahi U., Myers R. M., Cox D. R. A map of the distal region of the long arm of human chromosome 21 constructed by radiation hybrid mapping and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. R., Burmeister M., Price E. R., Kim S., Myers R. M. Radiation hybrid mapping: a somatic cell genetic method for constructing high-resolution maps of mammalian chromosomes. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):245–250. doi: 10.1126/science.2218528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk C. T. A simple method for ordering loci using data from radiation hybrids. Genomics. 1991 Jan;9(1):120–123. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick S., Gelatt C. D., Jr, Vecchi M. P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):671–680. doi: 10.1126/science.220.4598.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange K., Weeks D., Boehnke M. Programs for Pedigree Analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dGENE. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5(6):471–472. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370050611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. A. Crossover counts and likelihood in multipoint linkage analysis. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol. 1987;4(2):93–108. doi: 10.1093/imammb/4.2.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. E., Lange K. Trials, tribulations, and triumphs of the EM algorithm in pedigree analysis. IMA J Math Appl Med Biol. 1989;6(4):209–232. doi: 10.1093/imammb/6.4.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


