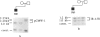Abstract
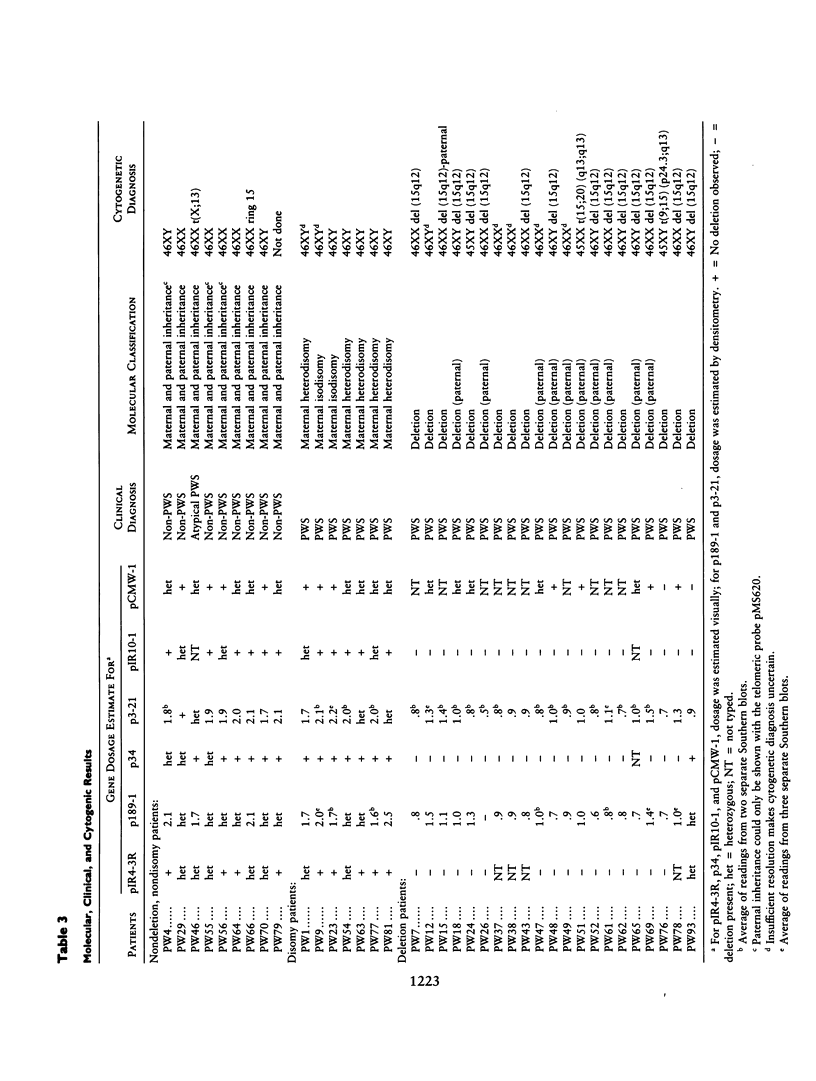
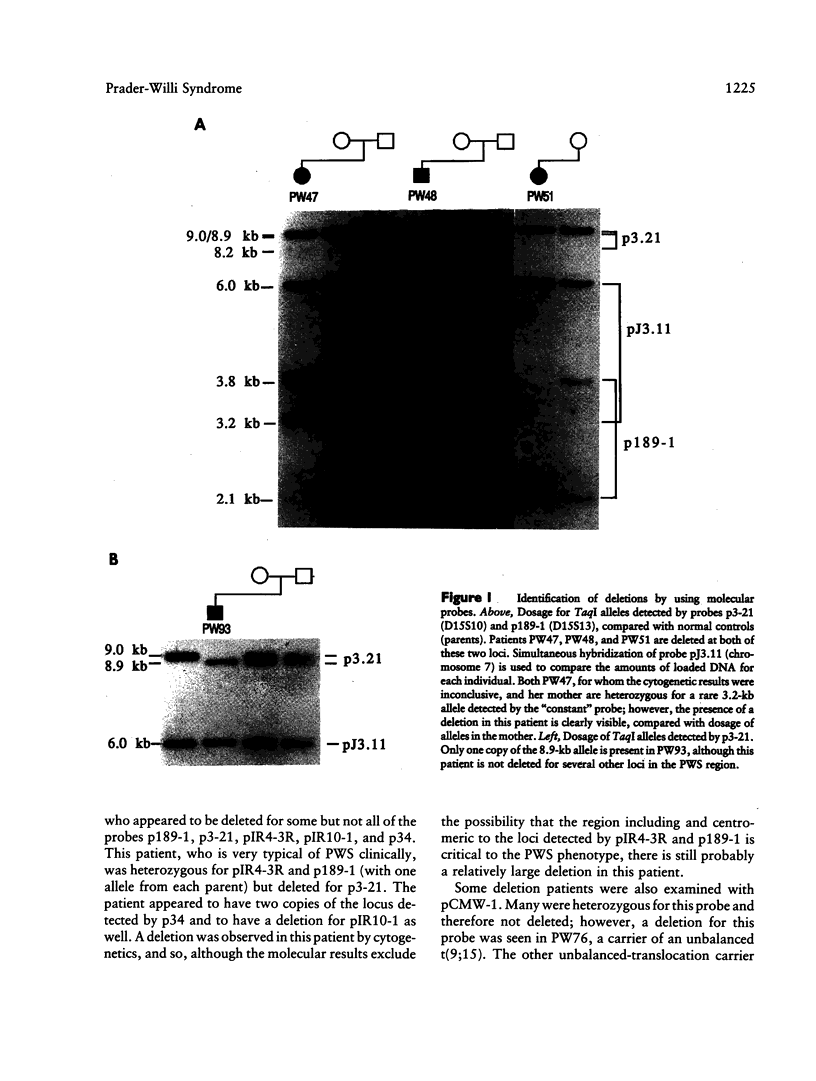
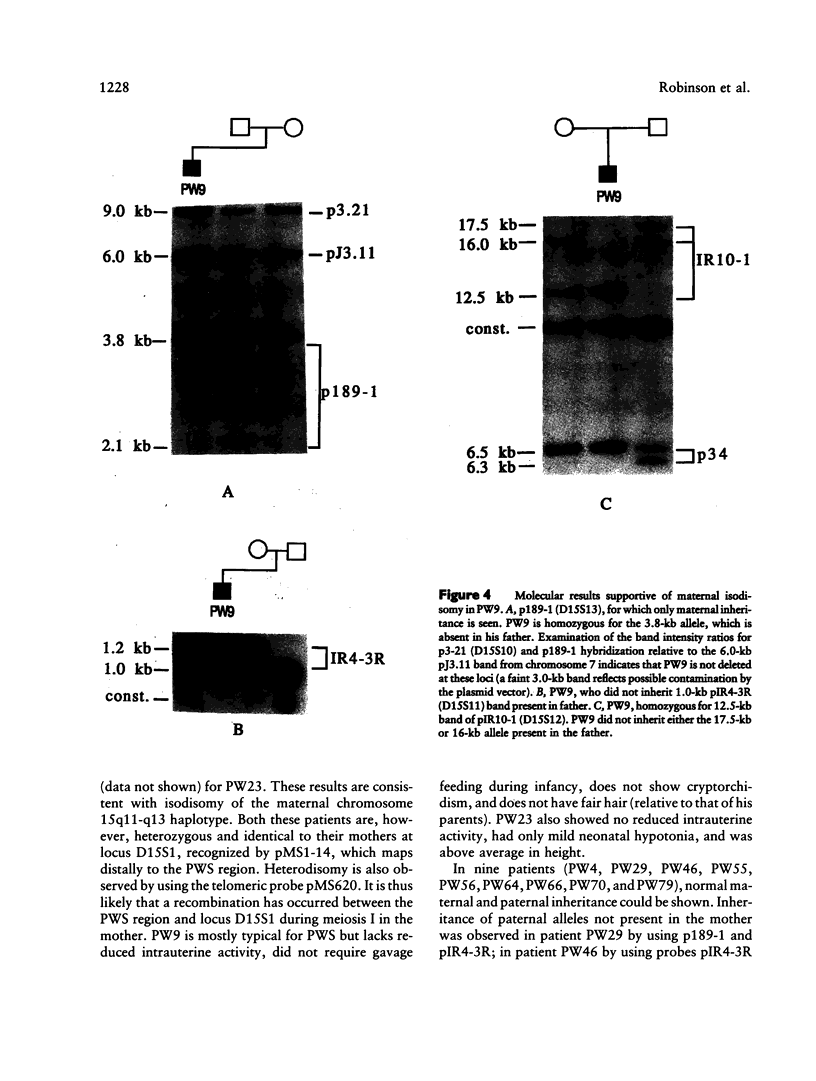
Thirty-seven patients presenting features of the Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) have been examined using cytogenetic and molecular techniques. Clinical evaluation showed that 29 of these patients fulfilled diagnostic criteria for PWS. A deletion of the 15q11.2-q12 region could be identified molecularly in 21 of these cases, including several cases where the cytogenetics results were inconclusive. One clinically typical patient is deleted at only two of five loci normally included in a PWS deletion. A patient carrying a de novo 13;X translocation was not deleted for the molecular markers tested but was clinically considered to be "atypical" PWS. In addition, five cases of maternal heterodisomy and two of isodisomy for 15q11-q13 were observed. All of the eight patients who did not fulfill clinical diagnosis of PWS showed normal maternal and paternal inheritance of chromosome 15 markers; however, one of these carried a ring-15 chromosome. A comparison of clinical features between deletion patients and disomy patients shows no significant differences between the two groups. The parental ages at birth of disomic patients were significantly higher than those for deletion patients. As all typical PWS cases showed either a deletion or disomy of 15q11.2-q12, molecular examination should provide a reliable diagnostic tool. As the disomy patients do not show either any additional or more severe features than typical deletion patients do, it is likely that there is only one imprinted region on chromosome 15 (within 15q11.2-q12).
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E. Parental origin of the extra chromosome in trisomy 21 as indicated by analysis of DNA polymorphisms. Down Syndrome Collaborative Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Mar 28;324(13):872–876. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199103283241302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armour J. A., Povey S., Jeremiah S., Jeffreys A. J. Systematic cloning of human minisatellites from ordered array charomid libraries. Genomics. 1990 Nov;8(3):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90037-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baas F., Bikker H., van Ommen G. J., de Vijlder J. J. Unusual scarcity of restriction site polymorphism in the human thyroglobulin gene. A linkage study suggesting autosomal dominance of a defective thyroglobulin allele. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):301–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00291357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. J., Lafreniere R. G., Powers V. E., Sebastio G., Ballabio A., Pettigrew A. L., Ledbetter D. H., Levy E., Craig I. W., Willard H. F. Localization of the X inactivation centre on the human X chromosome in Xq13. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):82–84. doi: 10.1038/349082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buiting K., Neumann M., Lüdecke H. J., Senger G., Claussen U., Antich J., Passarge E., Horsthemke B. Microdissection of the Prader-Willi syndrome chromosome region and identification of potential gene sequences. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):521–527. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90481-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G., Meaney F. J., Palmer C. G. Clinical and cytogenetic survey of 39 individuals with Prader-Labhart-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Mar;23(3):793–809. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy S. B. Prader-Willi syndrome. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984 Jan;14(1):1–55. doi: 10.1016/0045-9380(84)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon T. A., Lalande M., Wyman A., Bruns G., Latt S. A. Isolation of molecular probes associated with the chromosome 15 instability in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4408–4412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donlon T. A. Similar molecular deletions on chromosome 15q11.2 are encountered in both the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Hum Genet. 1988 Dec;80(4):322–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00273644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel E. A new genetic concept: uniparental disomy and its potential effect, isodisomy. Am J Med Genet. 1980;6(2):137–143. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320060207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryns J. P., Kleczkowska A., Buttiens M., Jonckheere P., Brouckmans-Buttiens K., van den Berghe H. Ring chromosome 15 syndrome. Further delineation of the adult phenotype. Ann Genet. 1986;29(1):45–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. A., Kirkilionis A. J., Greenberg C. R., Chudley A. E., Hamerton J. L. Detection of molecular rearrangements in Prader-Willi syndrome patients by using genomic probes recognizing four loci within the PWCR. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Apr;35(4):536–545. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassold T. J., Pettay D., Freeman S. B., Grantham M., Takaesu N. Molecular studies of non-disjunction in trisomy 16. J Med Genet. 1991 Mar;28(3):159–162. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.3.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson S. V., Barber J. C., Dowie A., Dubowitz V. A de novo X;13 translocation with abnormal phenotype. J Med Genet. 1986 Oct;23(5):477–478. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.5.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P. A., Betts P. R., Cockwell A. E., Crolla J. A., Mackenzie M. J., Robinson D. O., Youings S. A. A cytogenetic and molecular reappraisal of a series of patients with Turner's syndrome. Ann Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;54(Pt 3):209–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1990.tb00379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Thein S. L. Hypervariable 'minisatellite' regions in human DNA. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):67–73. doi: 10.1038/314067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. C., Wharton R., Elias E., Mandell F., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Clinical heterogeneity associated with deletions in the long arm of chromosome 15: report of 3 new cases and their possible genetic significance. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss P., Osztovics M. Ring chromosome 15. Acta Paediatr Acad Sci Hung. 1982;23(4):409–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Glatt K. A., Nicholls R. D., Malcolm S., Lalande M. Chromosome 15 uniparental disomy is not frequent in Angelman syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Jan;48(1):16–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Glatt K., Graham J. M., Jr, Kaplan L., Lalande M. Angelman syndrome: three molecular classes identified with chromosome 15q11q13-specific DNA markers. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):149–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll J. H., Nicholls R. D., Magenis R. E., Graham J. M., Jr, Lalande M., Latt S. A. Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes share a common chromosome 15 deletion but differ in parental origin of the deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;32(2):285–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo I., Hamabe J., Yamamoto K., Niikawa N. Exclusion mapping of the Cohen syndrome gene from the Prader-Willi syndrome locus. Clin Genet. 1990 Dec;38(6):422–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1990.tb03607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousseff B. G. Ring chromosome 15 and failure to thrive. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Aug;134(8):798–799. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130200066022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupke K. G., Müller U. Parental origin of the extra chromosome in trisomy 18. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):599–605. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Mascarello J. T., Riccardi V. M., Harper V. D., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J. Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: a follow-up report of 40 cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):278–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Riccardi V. M., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J., Keenan B. S., Crawford J. D. Deletions of chromosome 15 as a cause of the Prader-Willi syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 5;304(6):325–329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102053040604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Brown M. G., Lacy D. A., Budden S., LaFranchi S. Is Angelman syndrome an alternate result of del(15)(q11q13)? Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):829–838. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Toth-Fejel S., Allen L. J., Black M., Brown M. G., Budden S., Cohen R., Friedman J. M., Kalousek D., Zonana J. Comparison of the 15q deletions in Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes: specific regions, extent of deletions, parental origin, and clinical consequences. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):333–349. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm S., Clayton-Smith J., Nichols M., Robb S., Webb T., Armour J. A., Jeffreys A. J., Pembrey M. E. Uniparental paternal disomy in Angelman's syndrome. Lancet. 1991 Mar 23;337(8743):694–697. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90278-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. H., Rademaker A. The frequency of aneuploidy among individual chromosomes in 6,821 human sperm chromosome complements. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;53(2-3):103–107. doi: 10.1159/000132905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May K. M., Jacobs P. A., Lee M., Ratcliffe S., Robinson A., Nielsen J., Hassold T. J. The parental origin of the extra X chromosome in 47,XXX females. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):754–761. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau N., Teyssier M. Ring chromosome 15: report of a case in an infertile man. Clin Genet. 1982 Apr;21(4):272–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb00763.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., O'Connell P., Leppert M., Lalouel J. M., White R. A mapped set of DNA markers for human chromosome 15. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Butler M. G., Karam S., Lalande M. Genetic imprinting suggested by maternal heterodisomy in nondeletion Prader-Willi syndrome. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):281–285. doi: 10.1038/342281a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Knoll J. H., Glatt K., Hersh J. H., Brewster T. D., Graham J. M., Jr, Wurster-Hill D., Wharton R., Latt S. A. Restriction fragment length polymorphisms within proximal 15q and their use in molecular cytogenetics and the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 May;33(1):66–77. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pembrey M., Fennell S. J., van den Berghe J., Fitchett M., Summers D., Butler L., Clarke C., Griffiths M., Thompson E., Super M. The association of Angelman's syndrome with deletions within 15q11-13. J Med Genet. 1989 Feb;26(2):73–77. doi: 10.1136/jmg.26.2.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prader A., Largo R. H., Molinari L., Issler C. Physical growth of Swiss children from birth to 20 years of age. First Zurich longitudinal study of growth and development. Helv Paediatr Acta Suppl. 1989 Jun;52:1–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. F., Daniel A., FitzGerald J. Atypical phenotype associated with deletion (15) (pter----q11::q13----qter). Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):55–58. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. C., Witkowski C. M., Summers K. M., van Tuinen P., Ledbetter D. H. Highly polymorphic locus D15S24 (CMW-1) maps to 15pter-q13. [HGM9 provisional no. D15S24]. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8740–8740. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C. Sex-linked dosage-sensitive modifiers as imprinting genes. Dev Suppl. 1990:107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Max S. R., Panny S. R., Cohen M. M. Deletions of proximal 15q and non-classical Prader-Willi syndrome phenotypes. Am J Med Genet. 1985 Feb;20(2):255–263. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320200208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Second Annual Prader-Willi Syndrome Scientific Conference. Houston, June 17, 1987. Proceedings and abstracts. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):779–924. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tantravahi U., Nicholls R. D., Stroh H., Ringer S., Neve R. L., Kaplan L., Wharton R., Wurster-Hill D., Graham J. M., Jr, Cantú E. S. Quantitative calibration and use of DNA probes for investigating chromosome abnormalities in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1989 May;33(1):78–87. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320330110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesner G. L., Bendel C. M., Olds D. P., White J. G., Arthur D. C., Ball D. W., King R. A. Hypopigmentation in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 May;40(5):431–442. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Gray B. A., Hendrickson J. E., Stone J. W., Cantú E. S. Incidence of 15q deletions in the Angelman syndrome: a survey of twelve affected persons. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Mar;32(3):339–345. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Stone J. W., Gray B. A., Cantu E. S., Ostrer H. Maternal origin of 15q11-13 deletions in Angelman syndrome suggests a role for genomic imprinting. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):350–353. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis E., Leibovici M., Quintero L. Ring (15) chromosome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(2):207–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00282025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yunis J. J. High resolution of human chromosomes. Science. 1976 Mar 26;191(4233):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.1257746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]