Abstract
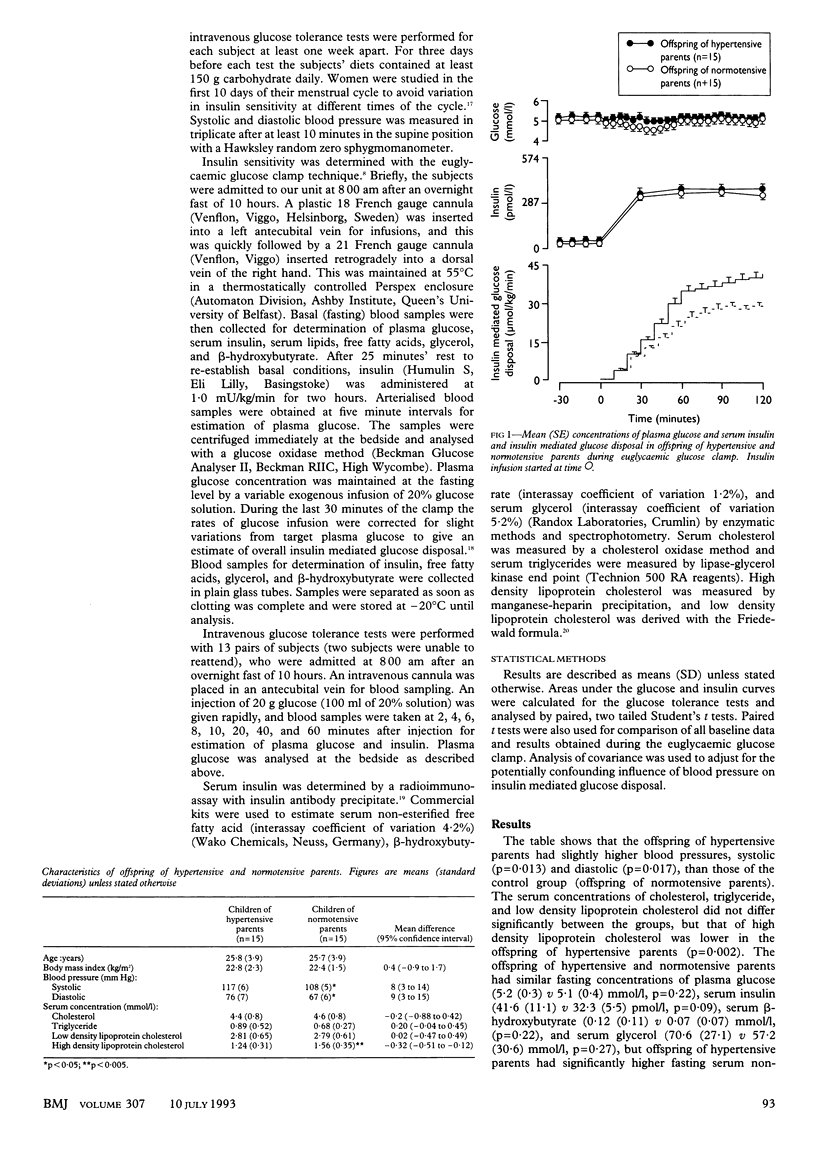
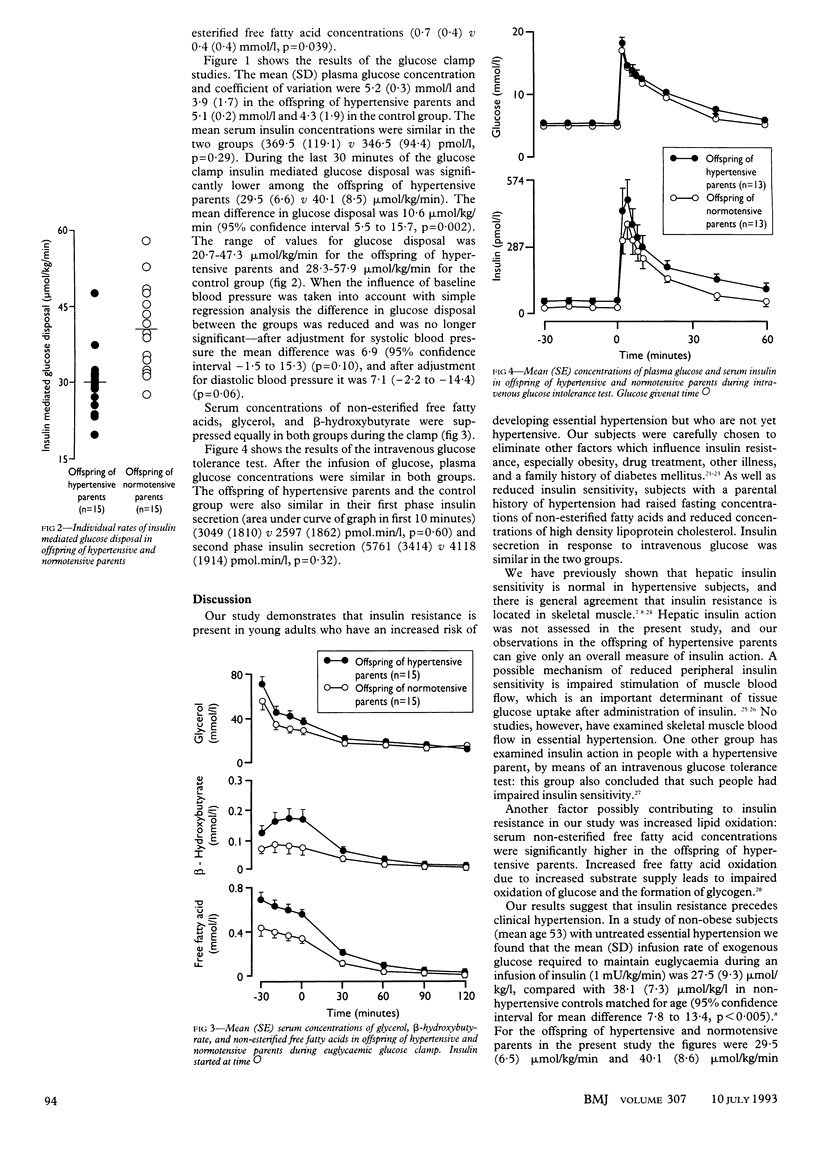
OBJECTIVE--To determine if insulin resistance is present in normotensive adults at increased risk of developing hypertension. DESIGN--Normotensive subjects with at least one hypertensive parent were paired with offspring of normotensive parents (controls), being matched for age, sex, social class, and physical activity. SETTING--Outpatient clinic. SUBJECTS--30 paired subjects (16 men and 14 women) with and without a family history of hypertension, aged 18-32, with a body mass index < 25 kg/m2, with blood pressure < 130/85 mm Hg, and not taking drugs. INTERVENTIONS--Euglycaemic glucose clamp (two hour infusion of insulin 1 mU/kg/min) and intravenous glucose tolerance test (injection of 100 ml 20% glucose). MAIN OUTCOME MEASURES--Insulin mediated glucose disposal and insulin secretion. RESULTS--The offspring of hypertensive parents had slightly higher blood pressure than did the controls (mean 117 (SD 6) v 108 (5) mm Hg systolic, p = 0.013; 76 (7) v 67 (6) mm Hg diastolic, p = 0.017). Their insulin mediated glucose disposal was lower than that of controls (29.5 (6.5) v 40.1 (8.6) mumol/kg/min, p = 0.002), but, after adjustment for blood pressure, the difference was not significant (difference 6.9 (95% confidence interval -1.5 to 15.3), p = 0.10). Insulin secretion in the first hour after injection of glucose was slightly but not significantly higher in the offspring of hypertensive patients (9320 (5484) v 6723 (3751) pmol.min/l). The two groups had similar concentrations of plasma glucose (5.2 (0.3) v 5.1 (0.4) mmol/l), serum cholesterol (4.4 (0.8) v 4.6 (0.8) mmol/l), serum triglyceride (0.89 (0.52) v 0.68 (0.27) mmol/l), and serum low density lipoprotein cholesterol (2.81 (0.65) v 2.79 (0.61) mmol/l). The offspring of hypertensive parents, however, had lower serum concentrations of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (1.24 (0.31) v 1.56 (0.35) mmol/l, p = 0.002) and higher serum concentrations of non-esterified fatty acids (0.7 (0.4) v 0.4 (0.4) mmol/l, p = 0.039). CONCLUSIONS--Young normotensive subjects who are at increased risk of developing hypertension are insulin resistant.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Howard B. V., Reaven G., Mott D. Relationships between insulin secretion, insulin action, and fasting plasma glucose concentration in nondiabetic and noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1238–1246. doi: 10.1172/JCI111533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogardus C., Lillioja S., Nyomba B. L., Zurlo F., Swinburn B., Esposito-Del Puente A., Knowler W. C., Ravussin E., Mott D. M., Bennett P. H. Distribution of in vivo insulin action in Pima Indians as mixture of three normal distributions. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1423–1432. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. Insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and obesity. Int J Obes. 1982;6 (Suppl 1):73–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A. The effect of insulin on renal sodium metabolism. A review with clinical implications. Diabetologia. 1981 Sep;21(3):165–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00252649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Buzzigoli G., Bonadonna R., Giorico M. A., Oleggini M., Graziadei L., Pedrinelli R., Brandi L., Bevilacqua S. Insulin resistance in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1987 Aug 6;317(6):350–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198708063170605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari P., Weidmann P., Shaw S., Giachino D., Riesen W., Allemann Y., Heynen G. Altered insulin sensitivity, hyperinsulinemia, and dyslipidemia in individuals with a hypertensive parent. Am J Med. 1991 Dec;91(6):589–596. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90211-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedewald W. T., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):499–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J. In defence of insulin: a critique of syndrome X. Lancet. 1992 Aug 22;340(8817):469–471. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)91781-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius S., Gudbrandsson T., Jamerson K., Tariq Shahab S., Andersson O. The hemodynamic link between insulin resistance and hypertension. J Hypertens. 1991 Nov;9(11):983–986. doi: 10.1097/00004872-199111000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolterman O. G., Insel J., Saekow M., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in human obesity: evidence for receptor and postreceptor defects. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1272–1284. doi: 10.1172/JCI109790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusari J., Verma U. S., Buse J. B., Henry R. R., Olefsky J. M. Analysis of the gene sequences of the insulin receptor and the insulin-sensitive glucose transporter (GLUT-4) in patients with common-type non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1323–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI115437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso M., Edelman S. V., Brechtel G., Baron A. D. Decreased effect of insulin to stimulate skeletal muscle blood flow in obese man. A novel mechanism for insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1844–1852. doi: 10.1172/JCI114644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Mott D. M., Zawadzki J. K., Young A. A., Abbott W. G., Knowler W. C., Bennett P. H., Moll P., Bogardus C. In vivo insulin action is familial characteristic in nondiabetic Pima Indians. Diabetes. 1987 Nov;36(11):1329–1335. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.11.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Effects of insulin upon ion transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):1–49. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger R. G., Prineas R. J., Gomez-Marin O. Persistent elevation of blood pressure among children with a family history of hypertension: the Minneapolis Children's Blood Pressure Study. J Hypertens. 1988 Aug;6(8):647–653. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198808000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali A., Santoro D., Palombo C., Cerri M., Ghione S., Ferrannini E. Impaired insulin action on skeletal muscle metabolism in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1991 Feb;17(2):170–178. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.17.2.170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelbaum R. S., Bouloux P. M., Li S. R., Baroni M. G., Stocks J., Galton D. J. Insulin receptor gene polymorphisms in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1991 Apr;34(4):260–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00405085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollare T., Lithell H., Berne C. A comparison of the effects of hydrochlorothiazide and captopril on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):868–873. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollare T., Lithell H., Selinus I., Berne C. Application of prazosin is associated with an increase of insulin sensitivity in obese patients with hypertension. Diabetologia. 1988 Jul;31(7):415–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00271585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollare T., Lithell H., Selinus I., Berne C. Sensitivity to insulin during treatment with atenolol and metoprolol: a randomised, double blind study of effects on carbohydrate and lipoprotein metabolism in hypertensive patients. BMJ. 1989 Apr 29;298(6681):1152–1157. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6681.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDLE P. J., GARLAND P. B., HALES C. N., NEWSHOLME E. A. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):785–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raben N., Barbetti F., Cama A., Lesniak M. A., Lillioja S., Zimmet P., Serjeantson S. W., Taylor S. I., Roth J. Normal coding sequence of insulin gene in Pima Indians and Nauruans, two groups with highest prevalence of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Jan;40(1):118–122. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.1.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G., Miller R. Study of the relationship between glucose and insulin responses to an oral glucose load in man. Diabetes. 1968 Sep;17(9):560–569. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.9.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R. A., Mandarino L. J., Gerich J. E. Mechanism and significance of insulin resistance in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):990–995. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney D. P., Edgar J. D., Sheridan B., Atkinson A. B., Bell P. M. The effects of low dose insulin infusions on the renin angiotensin and sympathetic nervous systems in normal man. Eur J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;21(4):430–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1991.tb01391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney D. P., Neely R. D., Ennis C. N., Bell N. P., Sheridan B., Atkinson A. B., Trimble E. R., Bell P. M. Insulin action and hepatic glucose cycling in essential hypertension. Metabolism. 1992 Mar;41(3):317–324. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90278-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Young J. B., Minaker K. L., Stevens A. L., Pallotta J., Landsberg L. Effect of insulin and glucose infusions on sympathetic nervous system activity in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):219–225. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen D. C., Shieh S. M., Fuh M. M., Wu D. A., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Resistance to insulin-stimulated-glucose uptake in patients with hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Mar;66(3):580–583. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-3-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler R., Stamler J., Riedlinger W. F., Algera G., Roberts R. H. Family (parental) history and prevalence of hypertension. Results of a nationwide screening program. JAMA. 1979 Jan 5;241(1):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swislocki A. L., Hoffman B. B., Reaven G. M. Insulin resistance, glucose intolerance and hyperinsulinemia in patients with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Jun;2(6 Pt 1):419–423. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.6.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes C. T., Elkind-Hirsch K. E. Intravenous glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity changes during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Mar;72(3):642–646. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-3-642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt G. Design and interpretation of studies comparing individuals with and without a family history of high blood pressure. J Hypertens. 1986 Feb;4(1):1–7. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198602000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. R., Hunt S. C., Hasstedt S. J., Hopkins P. N., Wu L. W., Berry T. D., Stults B. M., Barlow G. K., Schumacher M. C., Kuida H. Current knowledge regarding the genetics of human hypertension. J Hypertens Suppl. 1989 Dec;7(6):S8–13. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198900076-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. R., Hunt S. C., Hopkins P. N., Stults B. M., Wu L. L., Hasstedt S. J., Barlow G. K., Stephenson S. H., Lalouel J. M., Kuida H. Familial dyslipidemic hypertension. Evidence from 58 Utah families for a syndrome present in approximately 12% of patients with essential hypertension. JAMA. 1988 Jun 24;259(24):3579–3586. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.24.3579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


