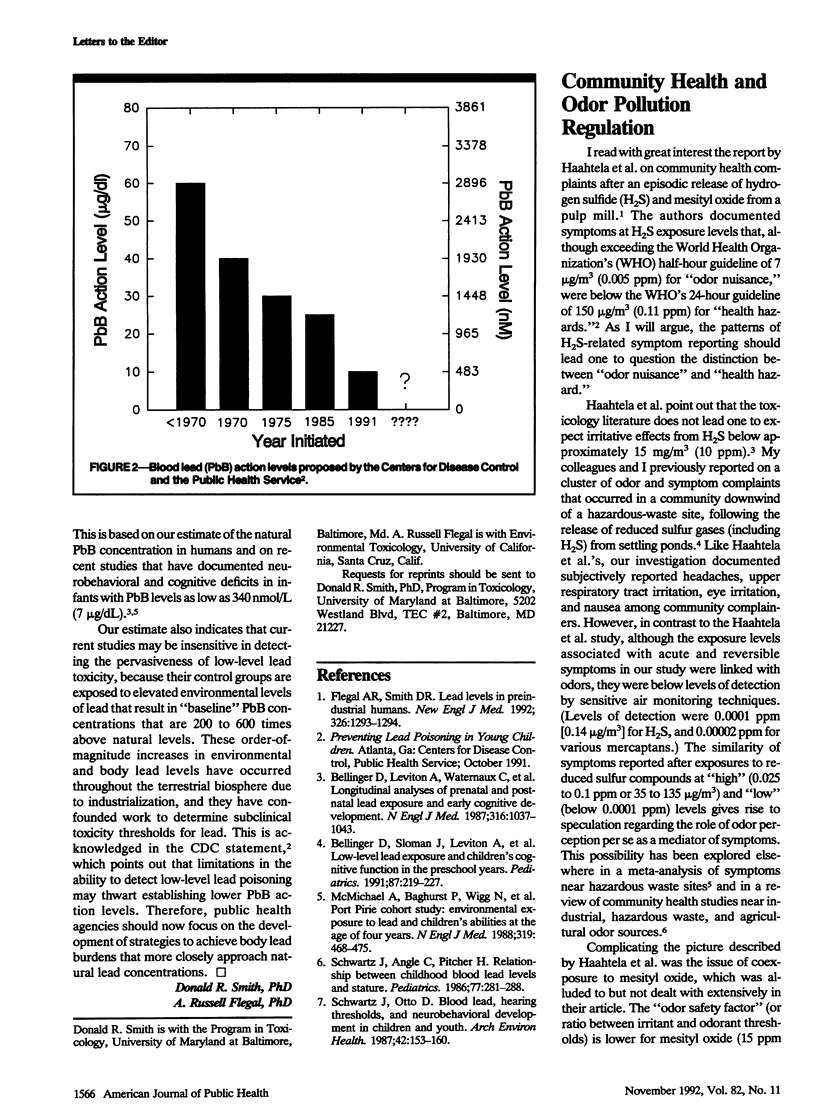
Full text
PDF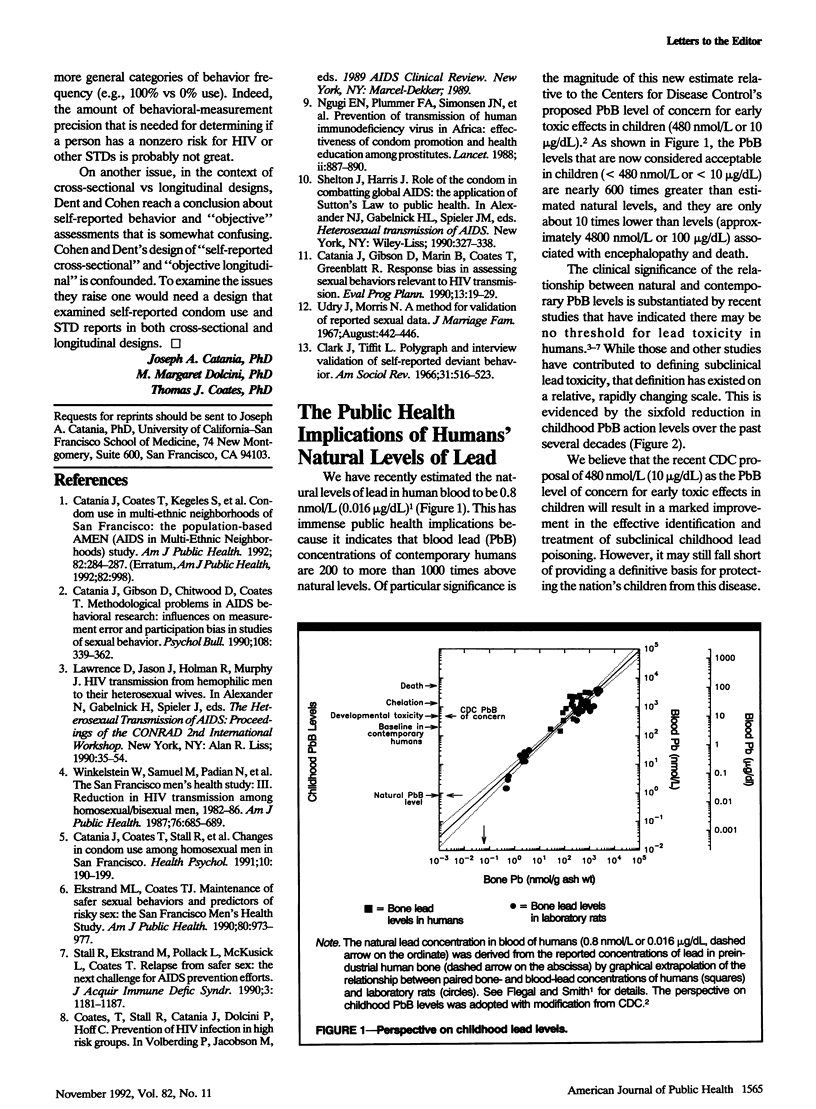
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellinger D., Leviton A., Waternaux C., Needleman H., Rabinowitz M. Longitudinal analyses of prenatal and postnatal lead exposure and early cognitive development. N Engl J Med. 1987 Apr 23;316(17):1037–1043. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198704233161701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellinger D., Sloman J., Leviton A., Rabinowitz M., Needleman H. L., Waternaux C. Low-level lead exposure and children's cognitive function in the preschool years. Pediatrics. 1991 Feb;87(2):219–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegal A. R., Smith D. R. Lead levels in preindustrial humans. N Engl J Med. 1992 May 7;326(19):1293–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Baghurst P. A., Wigg N. R., Vimpani G. V., Robertson E. F., Roberts R. J. Port Pirie Cohort Study: environmental exposure to lead and children's abilities at the age of four years. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 25;319(8):468–475. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808253190803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Angle C., Pitcher H. Relationship between childhood blood lead levels and stature. Pediatrics. 1986 Mar;77(3):281–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J., Otto D. Blood lead, hearing thresholds, and neurobehavioral development in children and youth. Arch Environ Health. 1987 May-Jun;42(3):153–160. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1987.9935814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


