Abstract
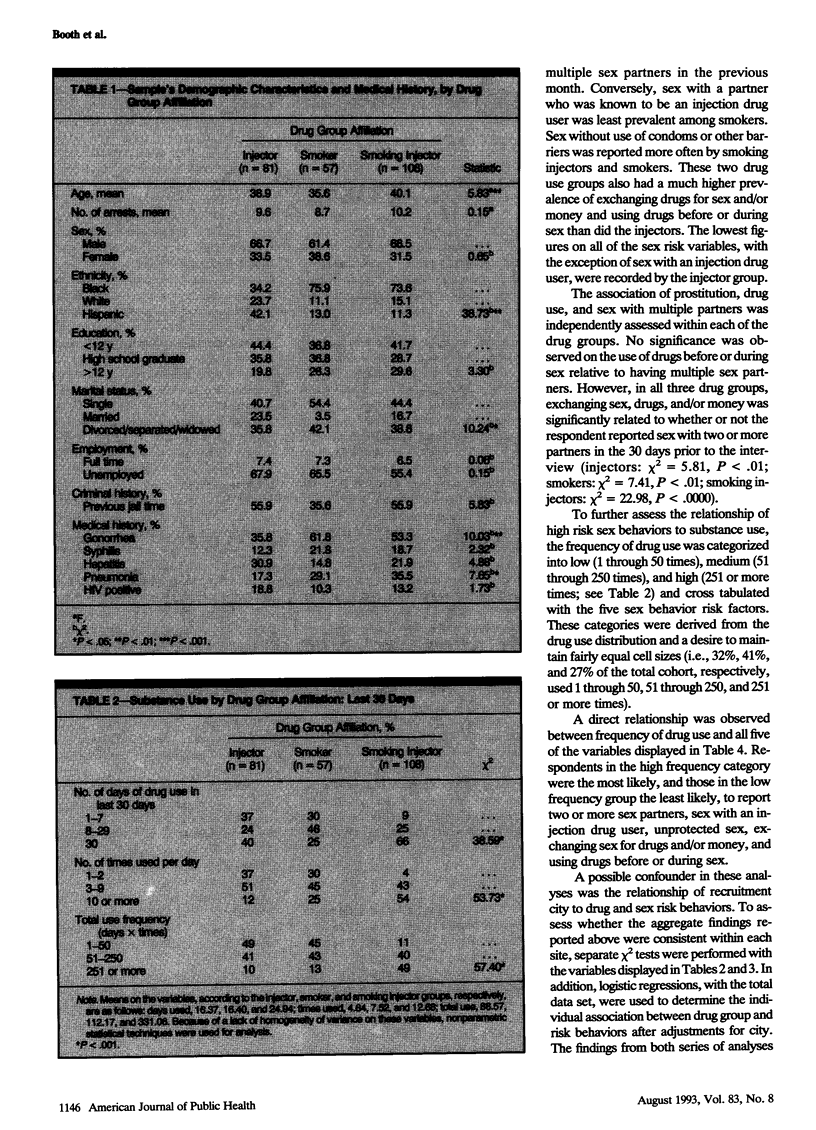
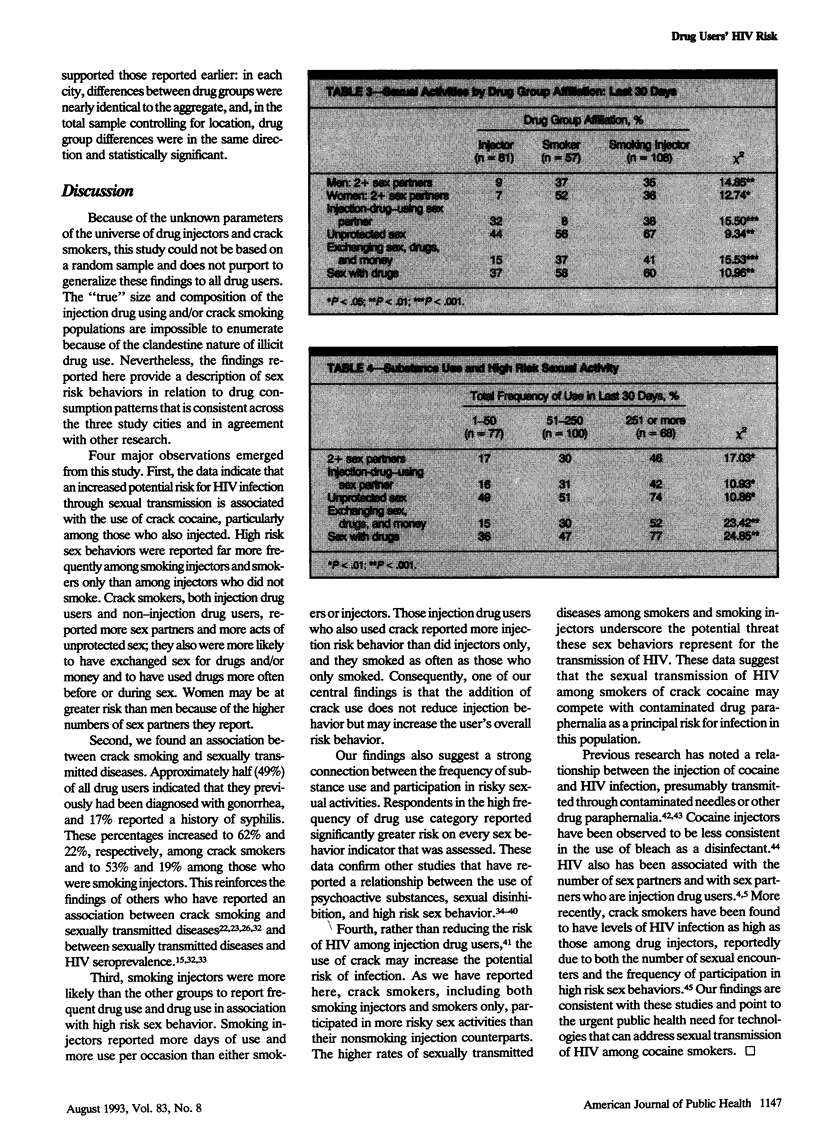
OBJECTIVES. This study was designed to assess and compare sex risk behaviors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transmission of three drug user groups: injectors who do not smoke crack, crack smokers who do not inject, and injectors who also smoke crack. METHODS. Sexual risk behaviors for HIV were assessed among 246 drug users from Denver, Miami, and San Francisco. Respondents were classified into the three drug groups based on self-report and verified through urinalysis and physical inspection. RESULTS. An increased risk for HIV through sexual transmission was associated with crack cocaine use, particularly among those who also injected. Crack smoking injectors were more likely to report sex with an injector, exchanging sex for drugs and/or money, drug use before or during sex, and unprotected sexual intercourse. They also injected more than injectors only, smoked crack as often as smokers only, and reported higher overall frequencies of drug use. CONCLUSIONS. These findings, together with the higher rates of gonorrhea and syphilis reported by smokers and injectors/smokers, are indicators of the risk crack poses for the heterosexual transmission of HIV.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aral S. O., Holmes K. K. Sexually transmitted diseases in the AIDS era. Sci Am. 1991 Feb;264(2):62–69. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0291-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth R., Koester S., Brewster J. T., Weibel W. W., Fritz R. B. Intravenous drug users and AIDS: risk behaviors. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 1991 Sep;17(3):337–353. doi: 10.3109/00952999109027557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Congenital syphilis--New York City, 1986-1988. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1989 Dec 8;38(48):825–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Bacchetti P., Osmond D., Brodie B., Sande M. A., Moss A. R. Cocaine use and HIV infection in intravenous drug users in San Francisco. JAMA. 1989 Jan 27;261(4):561–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaisson R. E., Moss A. R., Onishi R., Osmond D., Carlson J. R. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in heterosexual intravenous drug users in San Francisco. Am J Public Health. 1987 Feb;77(2):169–172. doi: 10.2105/ajph.77.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson M. A., Stoneburner R. L., Hildebrandt D. S., Ewing W. E., Telzak E. E., Jaffe H. W. Heterosexual transmission of HIV-1 associated with the use of smokable freebase cocaine (crack). AIDS. 1991 Sep;5(9):1121–1126. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199109000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin K., DeHovitz J. A., Dillon S., McCormack W. M. HIV infection, genital ulcer disease, and crack cocaine use among patients attending a clinic for sexually transmitted diseases. Am J Public Health. 1991 Dec;81(12):1576–1579. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.12.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J. W., Jaffe H. W., Hardy A. M., Morgan W. M., Selik R. M., Dondero T. J. Epidemiology of HIV infection and AIDS in the United States. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):610–616. doi: 10.1126/science.3340847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Chamberland M. E., Yancovitz S. R., Weinberg P., Friedman S. R. Heterosexual partners: a large risk group for AIDS. Lancet. 1984 Dec 8;2(8415):1346–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90861-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R. HIV infection among intravenous drug users: epidemiology and risk reduction. AIDS. 1987 Jul;1(2):67–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Des Jarlais D. C., Friedman S. R. Intravenous cocaine, crack, and HIV infection. JAMA. 1988 Apr 1;259(13):1945–1946. doi: 10.1001/jama.1988.03720130023017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland G. H., Klein R. S. Transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 29;317(18):1125–1135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710293171806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. R., Sterk C., Sufian M., Des Jarlais D. C. Will bleach decontaminate needles during cocaine binges in shooting galleries? JAMA. 1989 Sep 15;262(11):1467–1467. doi: 10.1001/jama.1989.03430110057012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginzburg H. M. Intravenous drug users and the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Public Health Rep. 1984 Mar-Apr;99(2):206–212. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. S., Singh T., Htoo M., Schultz S. The association between congenital syphilis and cocaine/crack use in New York City: a case-control study. Am J Public Health. 1991 Oct;81(10):1316–1318. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.10.1316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinan M. E., Hardy A. Epidemiology of AIDS in women in the United States. 1981 through 1986. JAMA. 1987 Apr 17;257(15):2039–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmor M., Des Jarlais D. C., Cohen H., Friedman S. R., Beatrice S. T., Dubin N., el-Sadr W., Mildvan D., Yancovitz S., Mathur U. Risk factors for infection with human immunodeficiency virus among intravenous drug abusers in New York City. AIDS. 1987 May;1(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L. Drug use and unprotected anal intercourse among gay men. Health Psychol. 1990;9(4):450–465. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.9.4.450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. R., Osmond D., Bacchetti P., Chermann J. C., Barre-Sinoussi F., Carlson J. Risk factors for AIDS and HIV seropositivity in homosexual men. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Jun;125(6):1035–1047. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrow D. G., VanRaden M. J., Fox R., Kingsley L. A., Dudley J., Kaslow R. A. Recreational drug use and sexual behavior change in a cohort of homosexual men. The Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). AIDS. 1990 Aug;4(8):759–765. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199008000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penkower L., Dew M. A., Kingsley L., Becker J. T., Satz P., Schaerf F. W., Sheridan K. Behavioral, health and psychosocial factors and risk for HIV infection among sexually active homosexual men: the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study. Am J Public Health. 1991 Feb;81(2):194–196. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenbaum E. E., Hartel D., Selwyn P. A., Klein R. S., Davenny K., Rogers M., Feiner C., Friedland G. Risk factors for human immunodeficiency virus infection in intravenous drug users. N Engl J Med. 1989 Sep 28;321(13):874–879. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198909283211306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stall R., McKusick L., Wiley J., Coates T. J., Ostrow D. G. Alcohol and drug use during sexual activity and compliance with safe sex guidelines for AIDS: the AIDS Behavioral Research Project. Health Educ Q. 1986 Winter;13(4):359–371. doi: 10.1177/109019818601300407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterk C. Cocaine and HIV seropositivity. Lancet. 1988 May 7;1(8593):1052–1053. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91868-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washton A. M., Gold M. S., Pottash A. C. 'Crack'. Early report on a new drug epidemic. Postgrad Med. 1986 Oct;80(5):52-4, 57-8. doi: 10.1080/00325481.1986.11699554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


