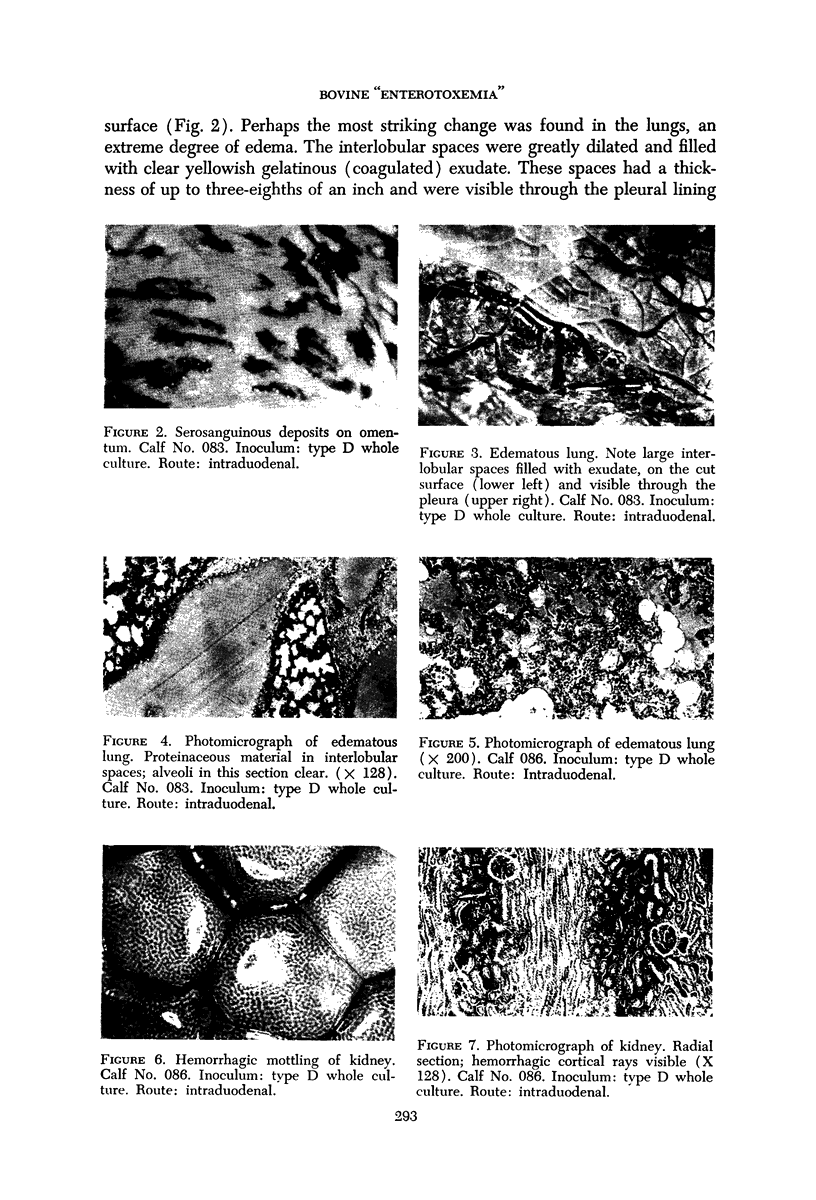
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BATTY I., BULLEN J. J. The effect of Clostridium welchii type D culture filtrates on the permeability of the mouse intestine. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1956 Apr;71(2):311–323. doi: 10.1002/path.1700710206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLEN J. J. Enterotoxaemia of sheep: Clostridium welchii type D in the alimentary tract of normal animals. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jan;64(1):201–206. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLEN J. J., SCARISBRICK R. Enterotoxaemia of sheep: the fate of washed suspensions of Clostridium welchii type D introduced into the rumen of normal sheep. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Jan;65(1):209–219. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLNER P. D. Fate of partially purified C-14-labeled toxin of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1961 Aug;82:275–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.2.275-283.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD H. I., GOODWIN R. F. The experimental reproduction of enterotoxaemia in piglets. J Hyg (Lond) 1959 Mar;57(1):81–91. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINER L. A., BRACKEN F. K. Clostridium perfringens (type C) in acute hemorrhagic enteritis of calves. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1953 Feb;122(911):99–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINER L. A., CARLSON W. D. Enterotoxemia of sheep. II. Distribution of I-131 radioiodinated serum albumin in brains of Clostridium perfringens type D intoxicated lambs. Am J Vet Res. 1961 May;22:443–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRINER L. A. Enterotoxemi of sheep. I. Effects of Clostridium perfringens type D toxin on the brains of sheep and mice. Am J Vet Res. 1961 May;22:429–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niilo L., Avery R. J. Bovine "Enterotoxemia" I. Clostridium Perfringens Types Isolated from Animal Sources in Alberta and Saskatchewan. Can Vet J. 1963 Feb;4(2):31–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLANS E. S., JONES V. E. Studies on some soluble antigens of Clostridium welchii types B, C and D. Immunology. 1958 Jul;1(3):268–290. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]