Abstract
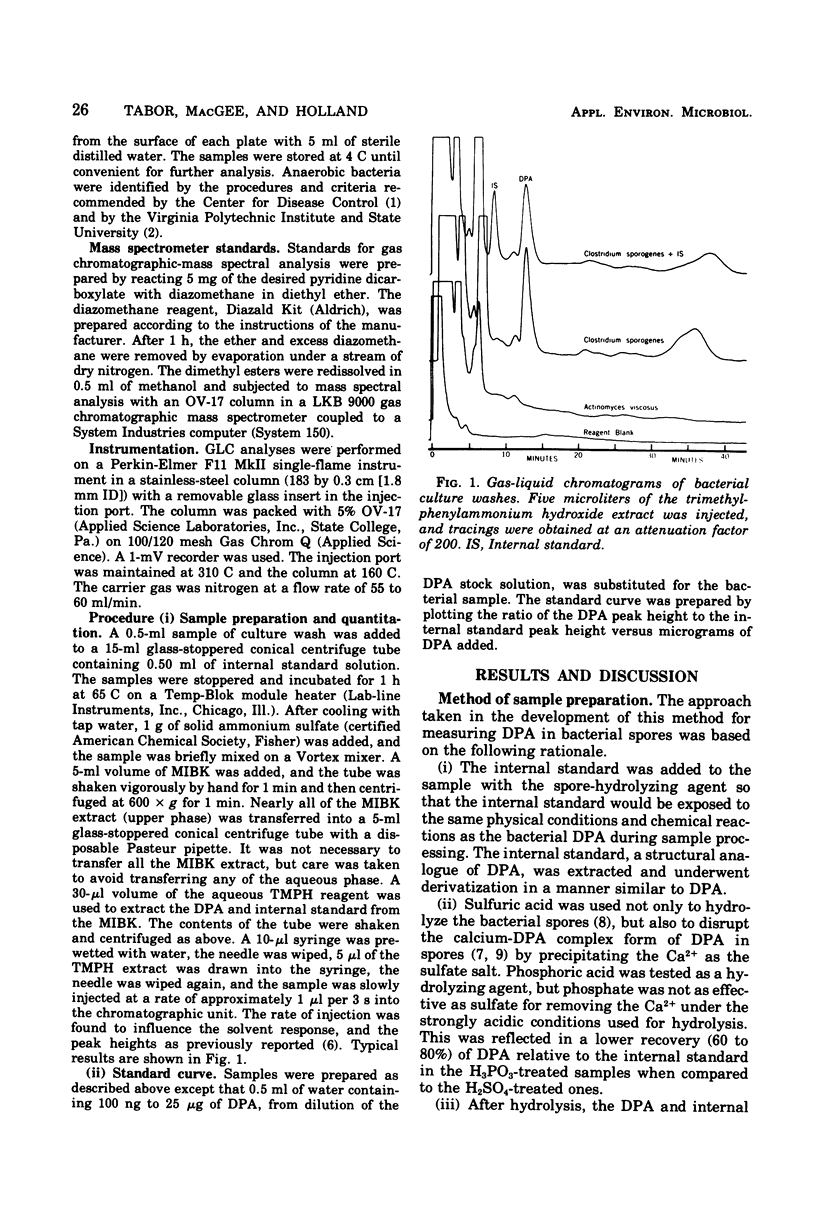
A gas-liquid chromatographic procedure has been developed to quantitate dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. The culture, washed from a plate, was hydrolyzed with acid containing the internal standard, pyridine-2,4-dicarboxylate, and then extracted into methyl isobutyl ketone. The internal standard and dipicolinic acid were then extracted into a small volume of trimethylphenylammonium hydroxide. Injection of the resultant quaternary ammonium salts into a gas chromatograph yielded, via thermal decomposition, the methyl ester derivatives of the dipicolinic acid and the internal standard. The amount of dipicolinic acid in the sample was determined from a standard curve. The method was sensitive to 100 ng of dipicolinic acid per sample and was 1,000 to 5,000 times more sensitive than the commonly used methods. Preparation of the sample required less than 1.5 h and less than 15 min of the analyst's time.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRISHNA MURTY G. G., HALVORON H. O. Effect of duration of heating, L-alanine and spore concentration on the oxidation of glucose by spores of Bacillus cereus var. terminalis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Feb;73(2):235–240. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.2.235-240.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. C. Determination of dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores by ultraviolet spectrometry of the calcium chelate. Anal Biochem. 1967 May;19(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90168-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERRY J. J., FOSTER J. W. Studies on the biosynthesis of dipicolinic acid in spores of Bacillus cereus var. mycoides. J Bacteriol. 1955 Mar;69(3):337–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.69.3.337-346.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POWELL J. F. Isolation of dipicolinic acid (pyridine-2:6-dicarboxylic acid) from spores of Bacillus megatherium. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):210–211. doi: 10.1042/bj0540210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


