Abstract
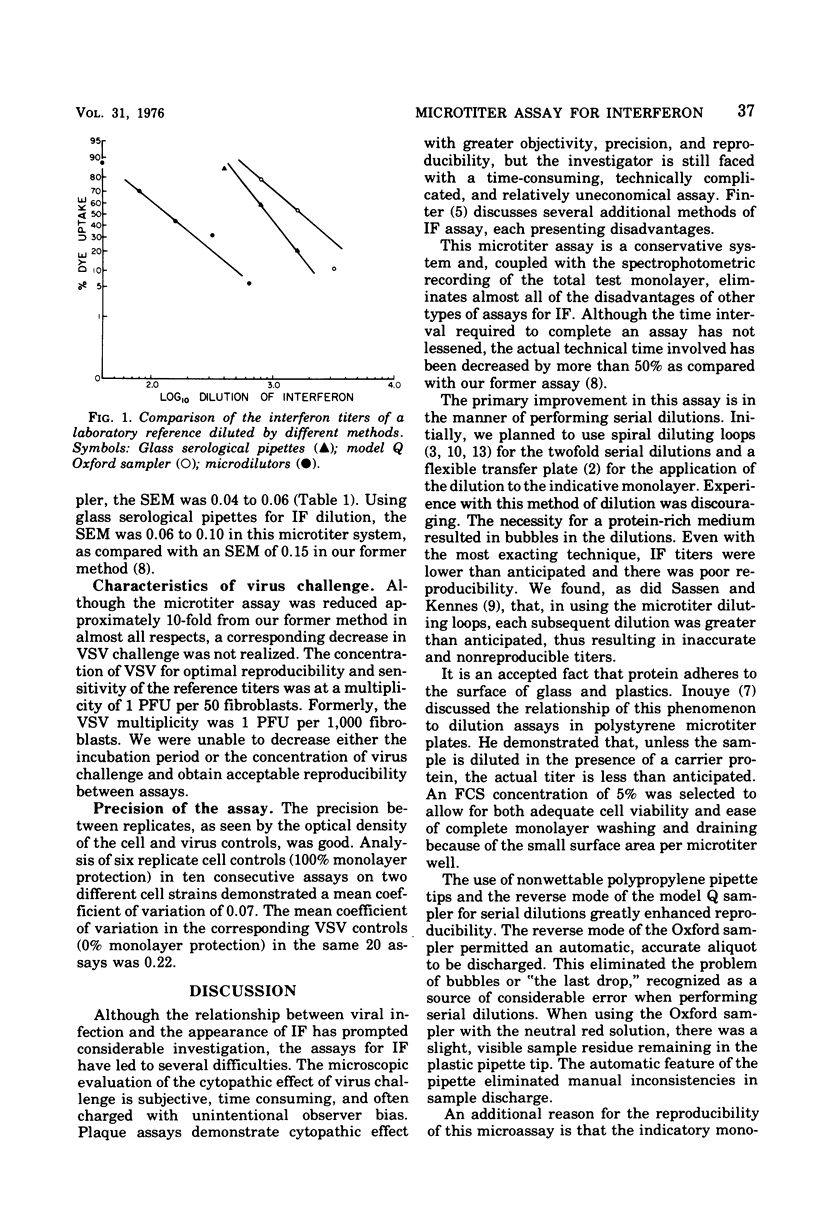
This report describes an accurate, reproducible, and efficient microassay for human interferon, using a dye-uptake method to quantitate cytopathogenicity. The antiviral activity was measured by using a Gilford 300-N microsepctrophotometer, with the automatic programmer, sampler, and data lister. Two hundred interferon samples, each in a final volume of 1.0 ml, may be analyzed and recorded in 45 min. The reproducibility of a laboratory reference interferon and the human international reference B 69/19 on two different cell lines, using the model Q Oxford sampler, was found to be excellent, with the standard error of the log10 geometric mean of both references +/- 0.04 to 0.06.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A. Semi-micro, dye-binding assay for rabbit interferon. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):723–725. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.723-725.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano L. W., Jr, Fuccillo D. A., Sever J. L. Piggy-back microtransfer technique. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Dec;18(6):1094–1095. doi: 10.1128/am.18.6.1094-1095.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H., Degré M. A micro assay for mouse and human interferon. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1972;80(6):863–870. doi: 10.1111/j.0365-5563.1973.tb00012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuccillo D. A., Catalano L. W., Jr, Moder F. L., Debus D. A., Sever J. L. Minicultures of mammalian cells in a new plastic plate. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):619–622. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.619-622.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. Nonspecific adsorption of proteins to microplates. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Feb;25(2):279–283. doi: 10.1128/am.25.2.279-283.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pidot A. L. Dye uptake assay: an efficient and sensitive method for human interferon titration. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Oct;22(4):671–677. doi: 10.1128/am.22.4.671-677.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassen A., Kennes F. Influence of mixing on dilutions obtained with the microtiter technique. J Immunol Methods. 1972 May;1(3):313–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spin C. A., Chang R. S., Mishra L., Golden H. D. Interferon production by human cells in vitro. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Nov;24(5):735–741. doi: 10.1128/am.24.5.735-741.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilles J. G., Finland M. Microassay for human and chick cell interferons. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Nov;16(11):1706–1707. doi: 10.1128/am.16.11.1706-1707.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. C., Lieberman L., Gerlach E. H. Microdilution antibiotic susceptibility test: examination of certain variables. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):658–665. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.658-665.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


