Abstract
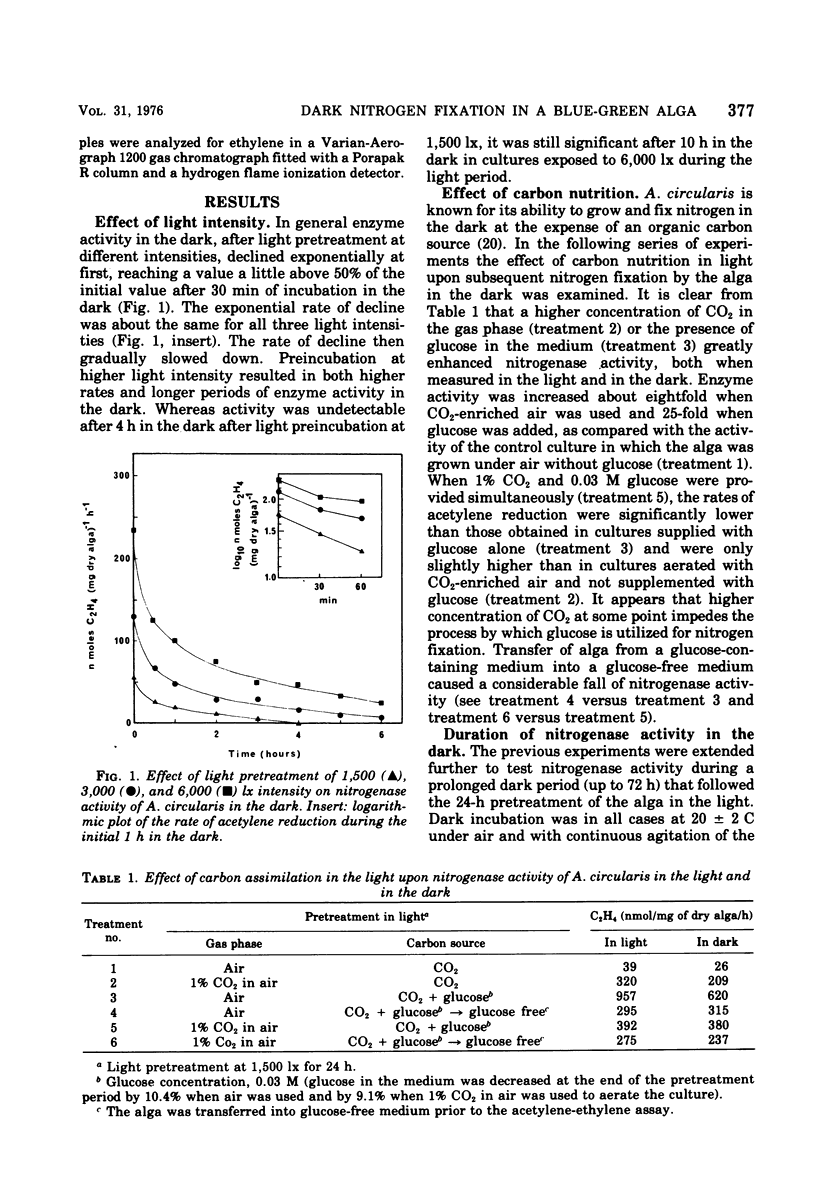
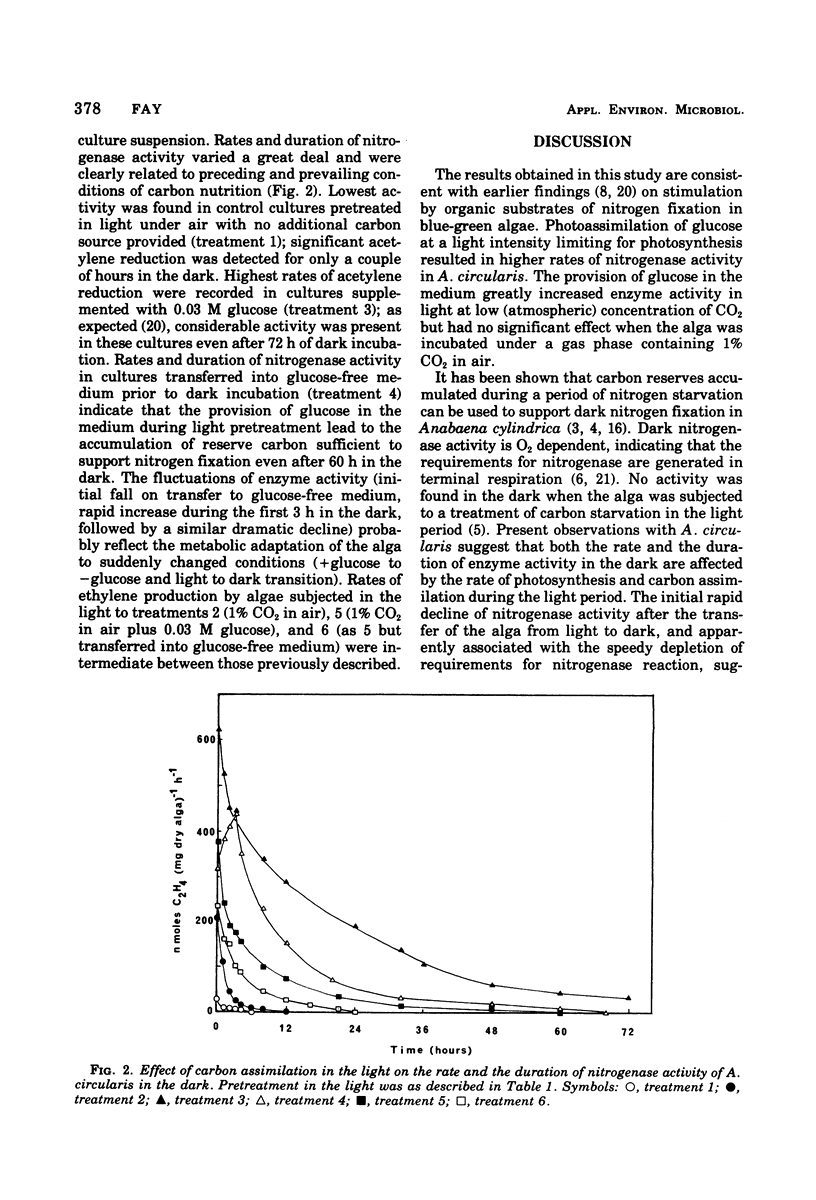
Nitrogen-fixing activity declines first rapidly and then more gradually when Anabaenopsis circularis is transferred from light into dark conditions. The rate and duration of dark acetylene reduction (nitrogen fixation) depend upon conditions prevailing during the preceding light period. Factors (such as light intensity, CO2 concentration, and supply of glucose), which in the light affect photosynthesis and the accumulation of reserve carbon, have a profound effect on dark nitrogen fixation. Glucose greatly promotes nitrogen fixation in the light and supports prolonged nitrogenase activity in the dark. The results suggest that heterotrophic nitrogen fixation by blue-green algae in the field may be important both under light and dark conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. M., Fay P. Special aspects of nitrogen fixation by blue-green algae. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1969 Apr 1;172(1029):357–366. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1969.0026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. M. Physiological studies on nitrogen fixation in the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Arch Mikrobiol. 1966 Mar 31;53(3):263–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00446673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAY P., FOGG G. E. Studies on nitrogen fixation by bluegreen algae. III. Growth and nitrogen fixation in Chlorogloea fritschii Mitra. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;42:310–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00422048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAY P. HETEROTROPHY AND NITROGEN FIXATION IN CHLOROGLOEA FRITSCHII. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Apr;39:11–20. doi: 10.1099/00221287-39-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lex M., Stewart W. D. Algal nitrogenase, reductant pools and photosystem I activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. S., Tulpule P. G. Varietal differences of groundnut in the production of aflatoxin. Nature. 1967 May 13;214(5089):738–739. doi: 10.1038/214738b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. D., Fitzgerald G. P., Burris R. H. In situ studies on N2 fixation using the acetylene reduction technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):2071–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


