Abstract
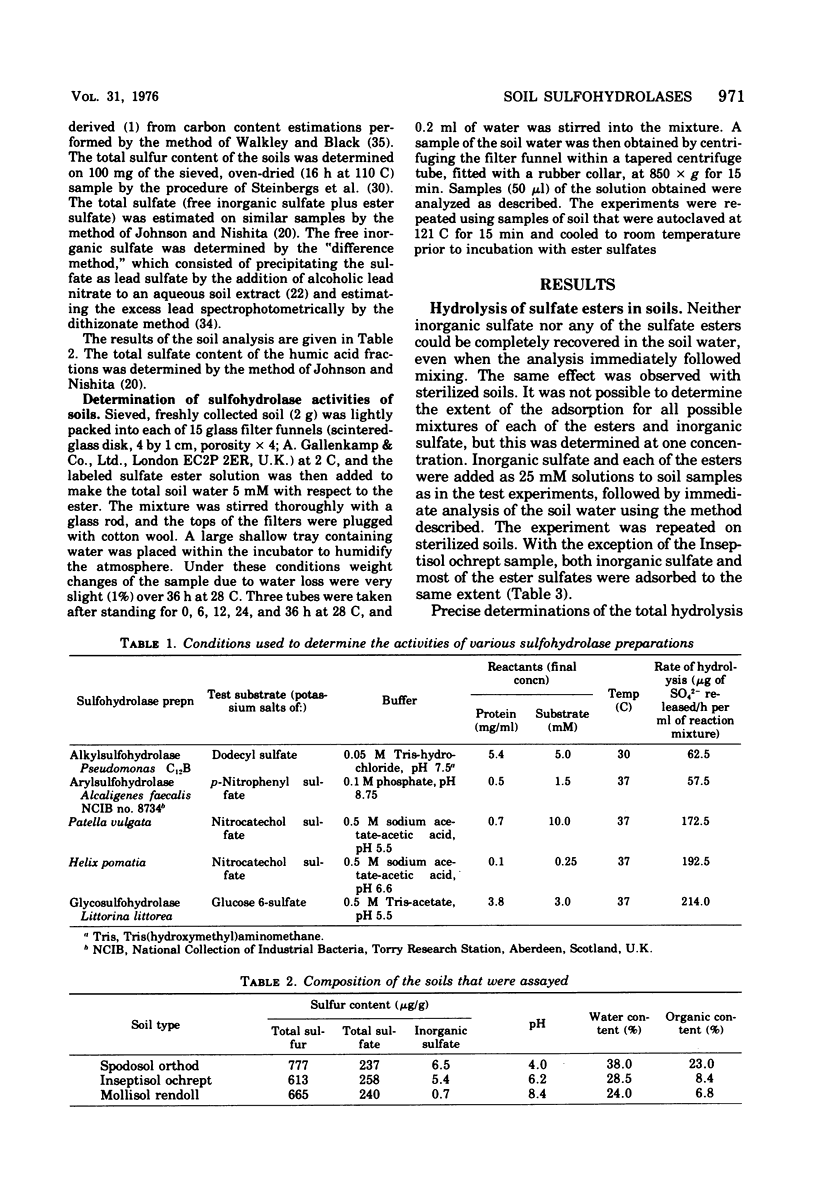
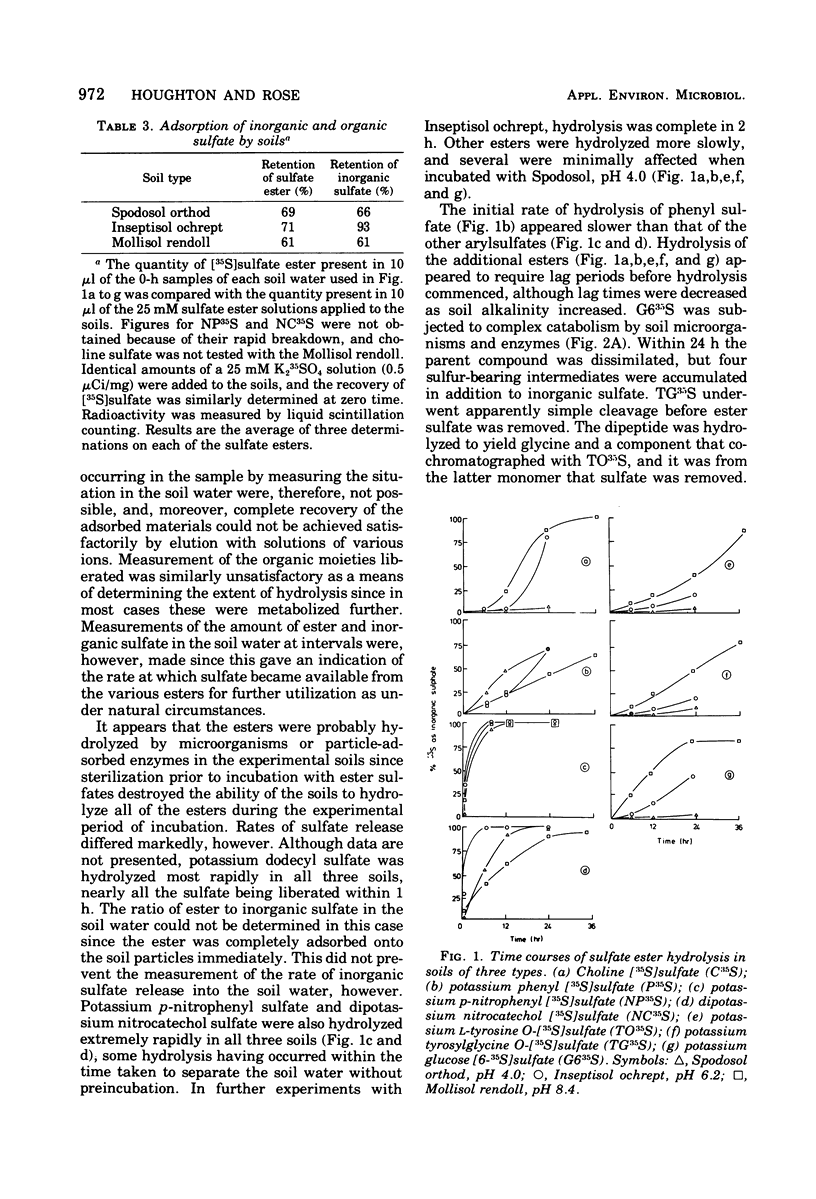
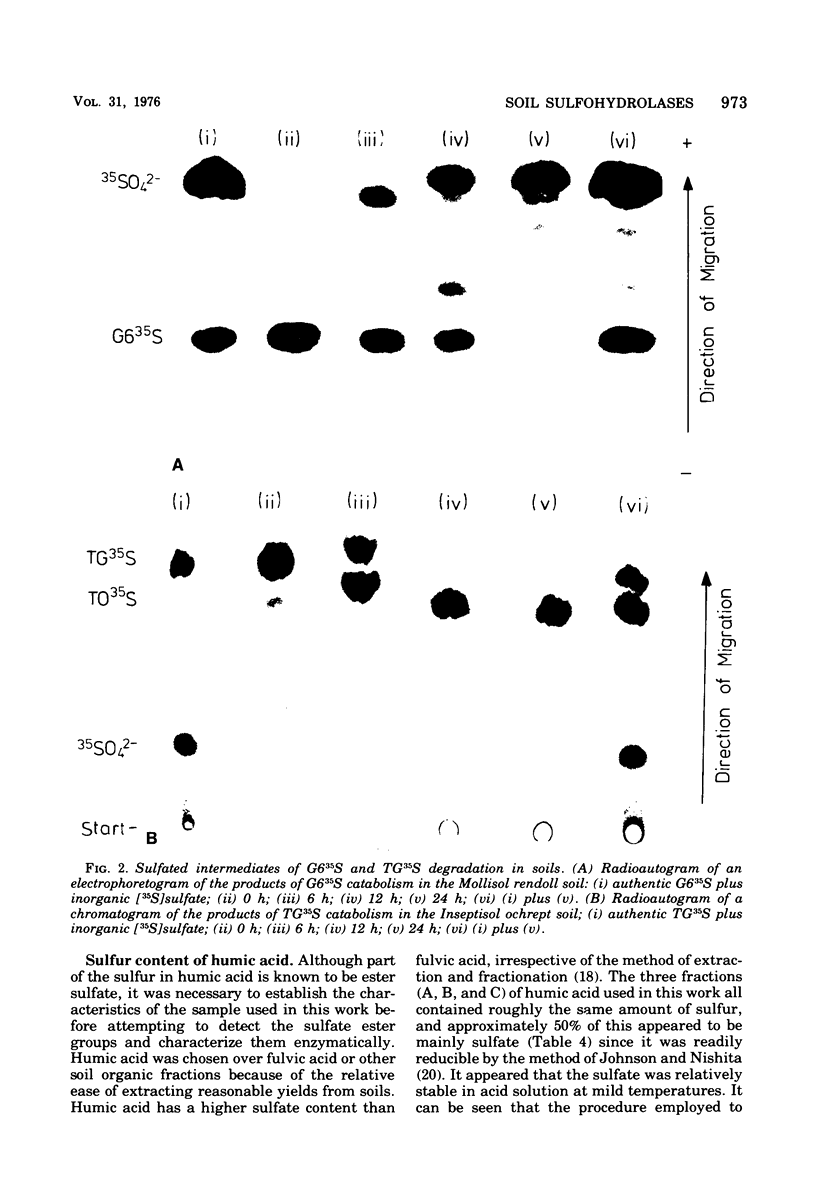
When incubated with acid, alkaline, and neutral soils, a variety of synthetic sulfate esters representing the various classes of these compounds was hydrolyzed by enzymes, probably of microbial origin. The appearance of sulfate in the soil water occurred immediately after introduction into the soils with some esters, whereas with others it occurred only after lag periods. Heat treatment destroyed the hydrolytic acitivity in the soils. The ester sulfate groups present in humic acid extracted from the soil appeared to be resistant to hydrolysis by a variety of sulfohydrolases extracted from bacteria and other organisms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DODGSON K. S. Determination of inorganic sulphate in studies on the enzymic and non-enzymic hydrolysis of carbohydrate and other sulphate esters. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:312–319. doi: 10.1042/bj0780312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., POWELL G. M., ROSE F. A., TUDBALL N. Observations on the metabolism of tyrosine O[35S]-sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1961 May;79:209–213. doi: 10.1042/bj0790209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., POWELL G. M. Studies on sulphatases. 27. The purification and properties of the arylsulphatase of the digestive gland of Helix pomatia. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:672–679. doi: 10.1042/bj0730672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B. Assay of sulfatases. Methods Biochem Anal. 1957;4:211–255. doi: 10.1002/9780470110201.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., SPENCER B. Studies on sulphatases. 4. Arylsulphatase and beta-glucuronidase concentrates from limpets. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):315–320. doi: 10.1042/bj0550315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGSON K. S., TUDBALL N. The metabolic fate of the ester sulphate group of potassium p-nitrophenyl [35S]sulphate. Biochem J. 1960 Jan;74:154–159. doi: 10.1042/bj0740154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner W. H., Olavesen A. H., Powell G. M., Dodgson K. S. The metabolism of potassium dodecyl [35-S]sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1969 Jan;111(1):43–51. doi: 10.1042/bj1110043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson K. S., Tudball N. Enzymic desulphation of l-serine O[S]-sulphate: the intracellular localization of the enzyme. Biochem J. 1961 Oct;81(1):68–71. doi: 10.1042/bj0810068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolly J. O., Curtis C. G., Dodgson K. S., Rose F. A. Metabolism of sodium oestrone ( 35 S)sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):261–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1230261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald J. W., Payne W. J. Induction in a Pseudomonas species of sulphatases active on short chain alkylsulphates. Microbios. 1972 Mar-Apr;5(18):87–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. G., Dodgson K. S., Powell G. M., Rose F. A. The metabolism of dipotassium 2-hydroxy-5-nitrophenyl [S]sulphate, a substrate for lysosomal arylsulphatases A and B. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1003–1012. doi: 10.1042/bj1051003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWKINS J. B., YOUNG L. Biochemical studies of toxic agents. V. Observations on the fate of 35S-labelled arylsulphuric acids following their administration of the rat. Biochem J. 1954 Jan;56(1):166–170. doi: 10.1042/bj0560166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. G., Large P. J., Davies M., Olavesen A. H., Dodgson K. S. The glycosulphatase of Trichoderma viride. Biochem J. 1968 Jul;108(3):393–399. doi: 10.1042/bj1080393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathur S. P., Paul E. A. Partial characterization of soil humic acids through biodegradation. Can J Microbiol. 1967 May;13(5):581–586. doi: 10.1139/m67-075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIPSON R. S. Sulfonic esters of carbohydrates. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1953;8:107–215. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Edson M., McCarter J. A. The measurement of radioactive sulphur (S) in biological material. Biochem J. 1949;44(2):179–185. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]