Abstract
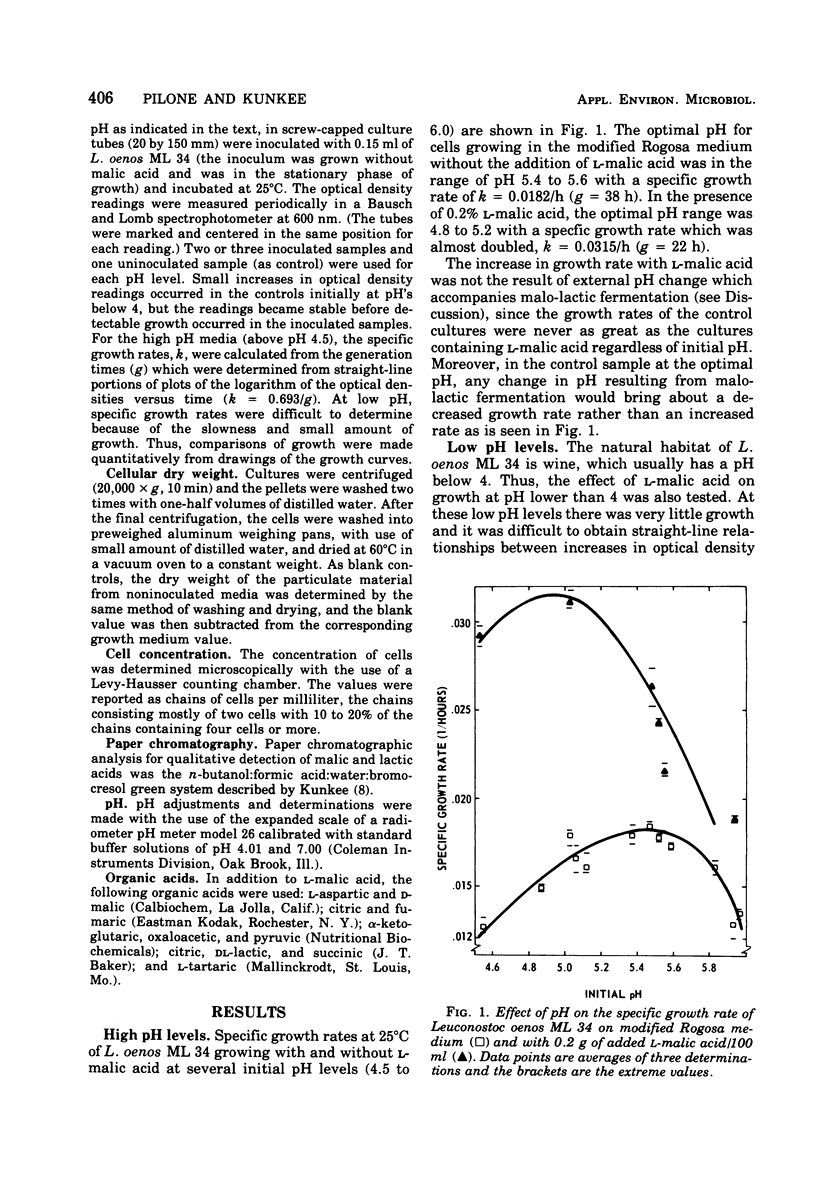
Although l-malic acid is not an energy source for the malo-lactic organism Leuconostoc oenos (L. citrovorum) ML 34, the growth rate of the organism was found to be greatly increased by malo-lactic fermentation (the decarboxylation of l-malic acid to l-lactic acid). The stimulation was especially striking at the low pH (below pH 4) of wine, the natural habitat of this bacterium. The stimulation of growth did not result from changes in pH that accompany malo-lactic fermentation. Thus, these results suggest a biological function of malo-lactic fermentation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins E. B., Bruhn J. C. Roles of acetate and pyruvate in the metabolism of Streptococcus diacetilactis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):541–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.541-546.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. J., COLLINS E. B. ROLES OF CITRATE AND ACETOIN IN THE METABOLISM OF STREPTOCOCCUS DIACETILACTIS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1301–1307. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1301-1307.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S., KORKES S., DEL CAMPILLO A. Biosynthesis of dicarboxylic acids by carbon dioxide fixation. V. Further study of the "malic" enzyme of Lactobacillus arabinosus. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):301–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORKES S., DEL CAMPILLO A., OCHOA S. Biosynthesis of dicarboxylic acids by carbon dioxide fixation. IV. Isolation and properties of an adaptive "malic" enzyme from Lactobacillus arabinosus. J Biol Chem. 1950 Dec;187(2):891–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkee R. E. Malo-lactic fermentation. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1967;9:235–279. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilone G. J., Kunkee R. E. Carbonic acid from decarboxylation by "malic" enzyme in lactic acid bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):404–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.404-409.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radler F. Die mikrobiologischen Grundlagen des Säureabbaus im Wein. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Infektionskr Hyg. 1966;120(3):237–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


