Abstract
1. The isolation of human plasma prekallikrein was achieved by fractionating human plasma on diethylaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE) in the presence of heparin.
2. Heparin was shown to inhibit the activation of prekallikrein during the isolation procedure.
3. The isolated prekallikrein fraction had some kallikrein activity which could be inhibited by diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) without affecting the ability of prekallikrein to be activated.
4. The prekallikrein obtained was functionally pure in that it had no kallikrein inhibiting or activating activity. It was not physico-chemically pure, the major contaminant being the immunoglobulin IgG.
Full text
PDF



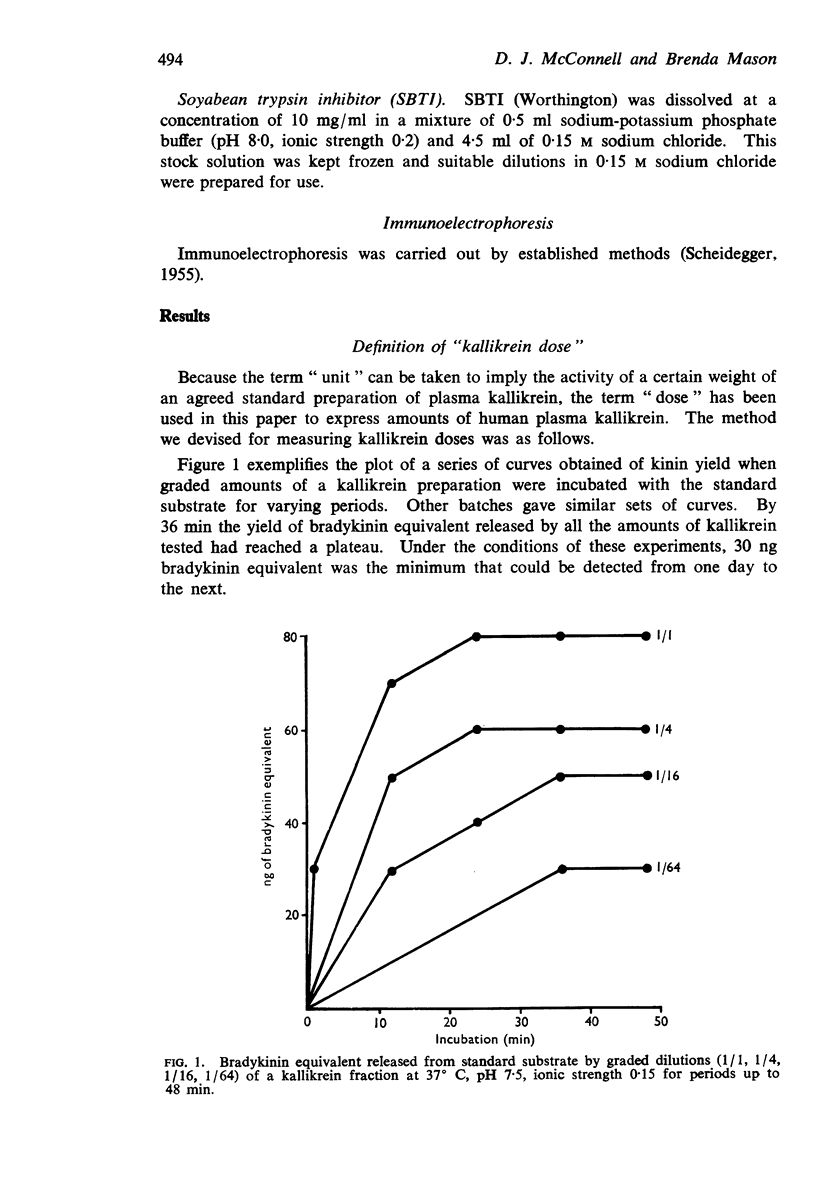
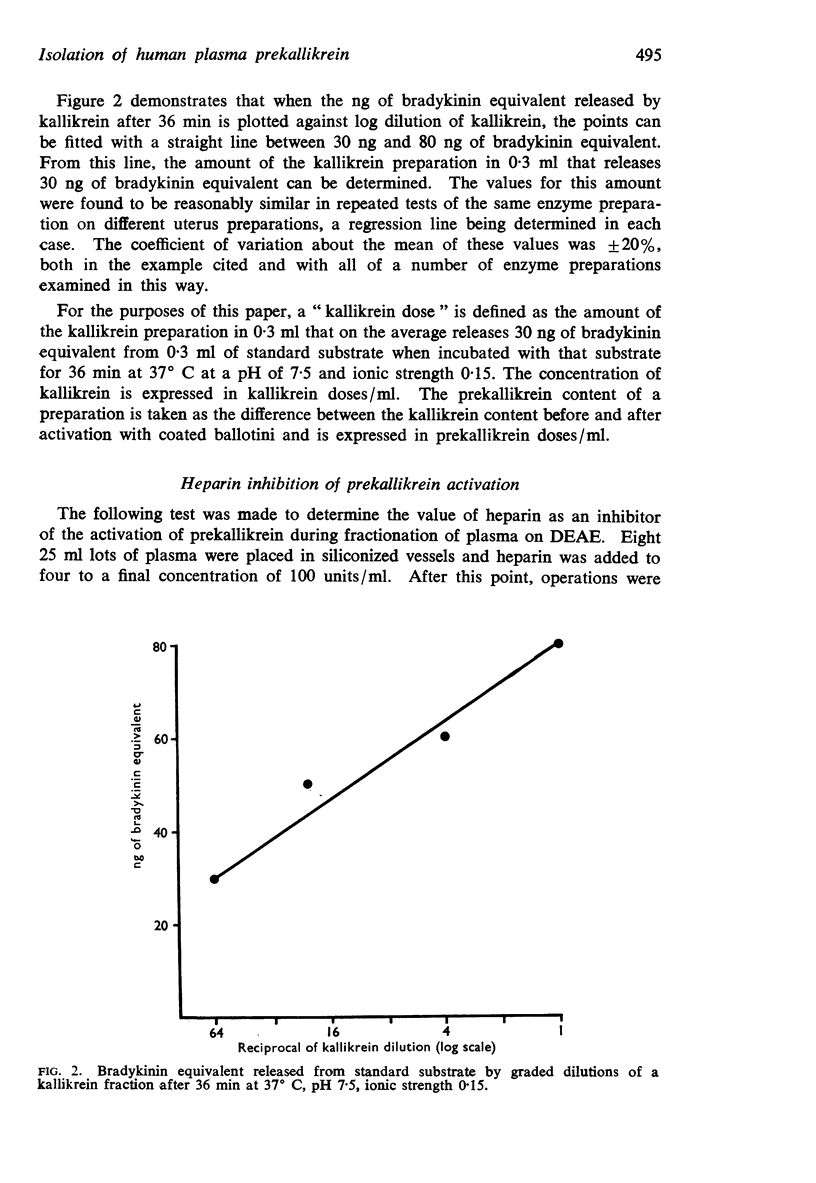

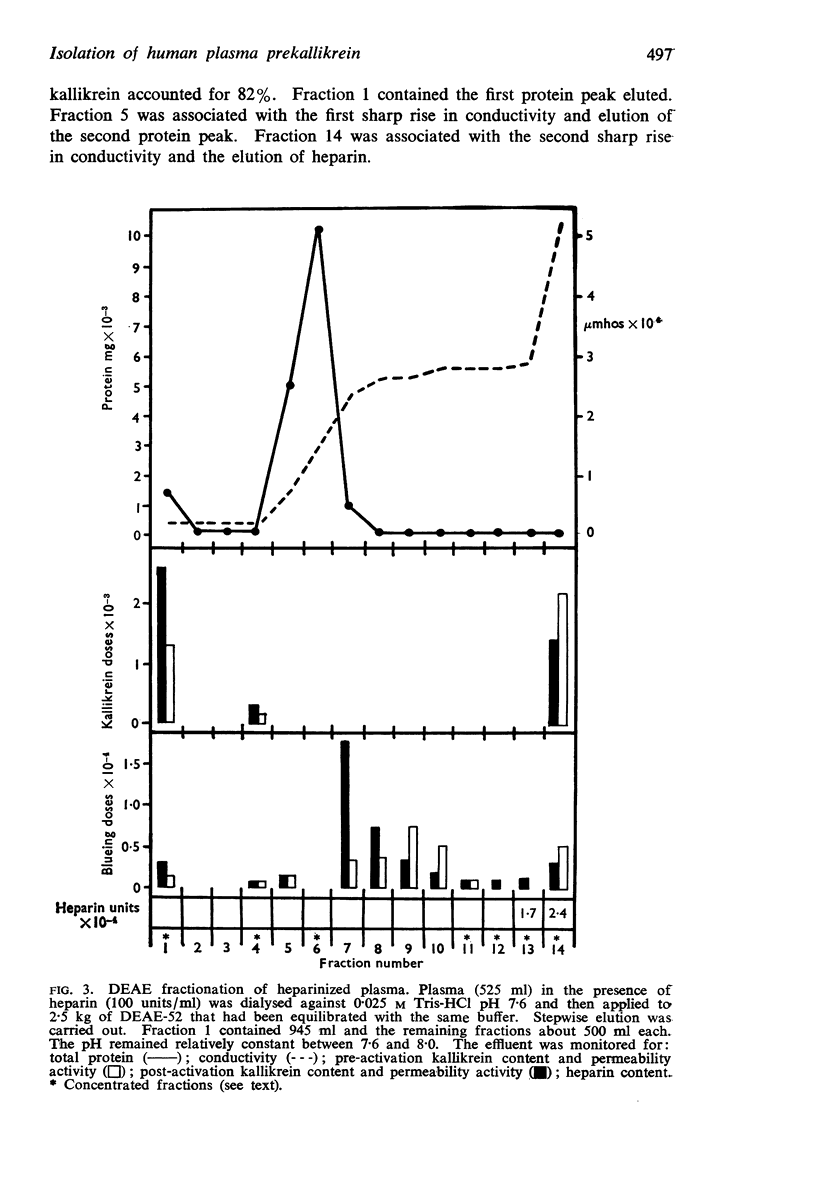





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTESCU E. J. A rapid turbidimetric method for heparin assay. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1963 Jul;15:488–489. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1963.tb12821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER E. L., KAGEN L. THE PERMEABILITY GLOBULINS OF HUMAN SERUM AND THE BIOCHEMICAL MECHANISM OF HEREDITARY ANGIONEUROTIC EDEMA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Aug 27;116:866–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb52552.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman R. W., Mattler L., Sherry S. Studies on the prekallikrein (kallikreinogen)--kallikrein enzyme system of human plasma. I. Isolation and purification of plasma kallikreins. J Clin Invest. 1969 Jan;48(1):11–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI105959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES G. E., LOWE J. S. PRESENCE OF KALLIKREIN IN THE GAMMA-GLOBULIN PERMEABILITY FACTOR OF GUINEA-PIG SERUM. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Dec;21:491–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb02017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN V. EFFECT OF HEXADIMETHRINE BROMIDE ON PLASMA KININ FORMATION, HYDROLYSIS OF P-TOSYL-L-ARGININE METHYL ESTER AND FIBRINOLYSIS. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Feb;22:87–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELDER J. M., WILHELM D. L. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. V. Activable permeability factor in human serum. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Aug;39(4):335–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen V. Observations on intrinsic kinin-forming factors in human plasma: the effect of acid, acetone, chloroform, heat and euglobulin separation on kinin formation. J Physiol. 1963 May;166(3):496–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOCH W. Relationship between air temperature and mean radiant temperature in thermal comfort. Nature. 1962 Nov 10;196:587–587. doi: 10.1038/196587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIS J. The mode of action of Hageman factor in the release of plasma kinin. J Physiol. 1960 May;151:238–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONNELL D. J., KAGEN L. J., BECKER E. L. USE OF HEPARIN IN DISTINGUISHING PLASMA KALLIKREIN FROM PF/DIL. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jul;119:652–656. doi: 10.3181/00379727-119-30262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell D. J., Becker E. L. The development of permeability activity by undiluted plasma on exposure to glass. Br J Exp Pathol. 1966 Apr;47(2):135–143. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa S., Takahashi H., Koida M., Suzuki T., Schoenmakers J. G. Partial purification of bovine plasma kallikreinogen, its activation by the Hageman factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 21;32(4):644–649. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90287-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RATNOFF O. D., MILES A. A. THE INDUCTION OF PERMEABILITY-INCREASING ACTIVITY IN HUMAN PLASMA BY ACTIVATED HAGEMAN FACTOR. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Jun;45:328–345. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH R. T., VON KORFF R. W. A heparin-precipitable fraction of human plasma. I. Isolation and characterization of the fraction. J Clin Invest. 1957 Apr;36(4):596–604. doi: 10.1172/JCI103459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT W. KININ FORMATION BY PLASMIN, AN INDIRECT PROCESS MEDIATED BY ACTIVATION OF KALLIKREIN. J Physiol. 1964 Jan;170:153–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILHELM D. L., MILL P. J., SPARROW E. M., MACKAY M. E., MILES A. A. Enzyme-like globulins from serum reproducing the vascular phenomena of inflammation. IV. Activable permeability factor and its inhibitor in the serum of the rat and the rabbit. Br J Exp Pathol. 1958 Jun;39(3):228–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


