Abstract
1. The effects of strychnine on the degree of depression of neuronal firing induced by glycine, γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) have been examined quantitatively. All drugs were applied by iontophoresis to spontaneously active cerebral cortical neurones in the anaesthetized cat. The application of these drugs was continued until a plateau or equilibrium depression was reached. The time taken to reach this steady state was noted. Dose-response curves were then constructed for those currents giving less than complete depression.
2. Glycine was less potent than GABA and about 7-fold larger currents were needed to achieve comparable depression. 5-HT was also a weak depressant compared with GABA and had 0·6 the potency of glycine on a current basis.
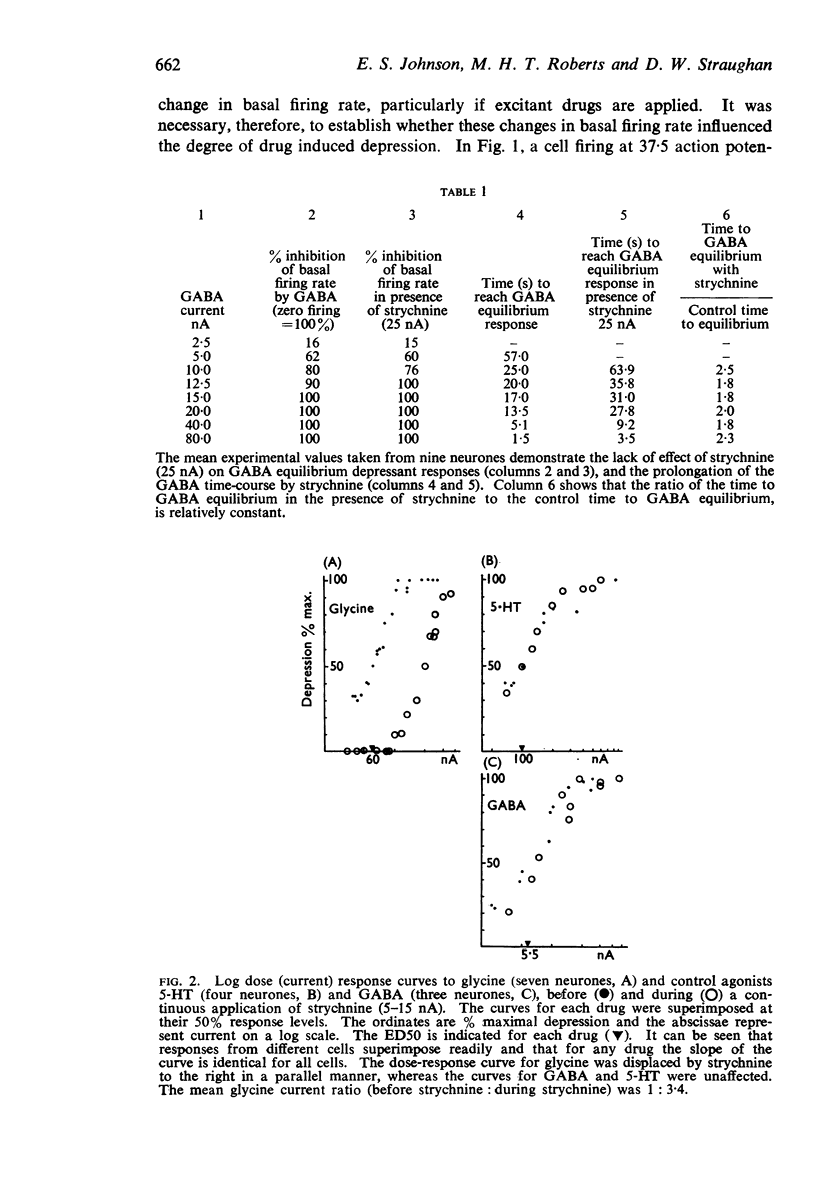
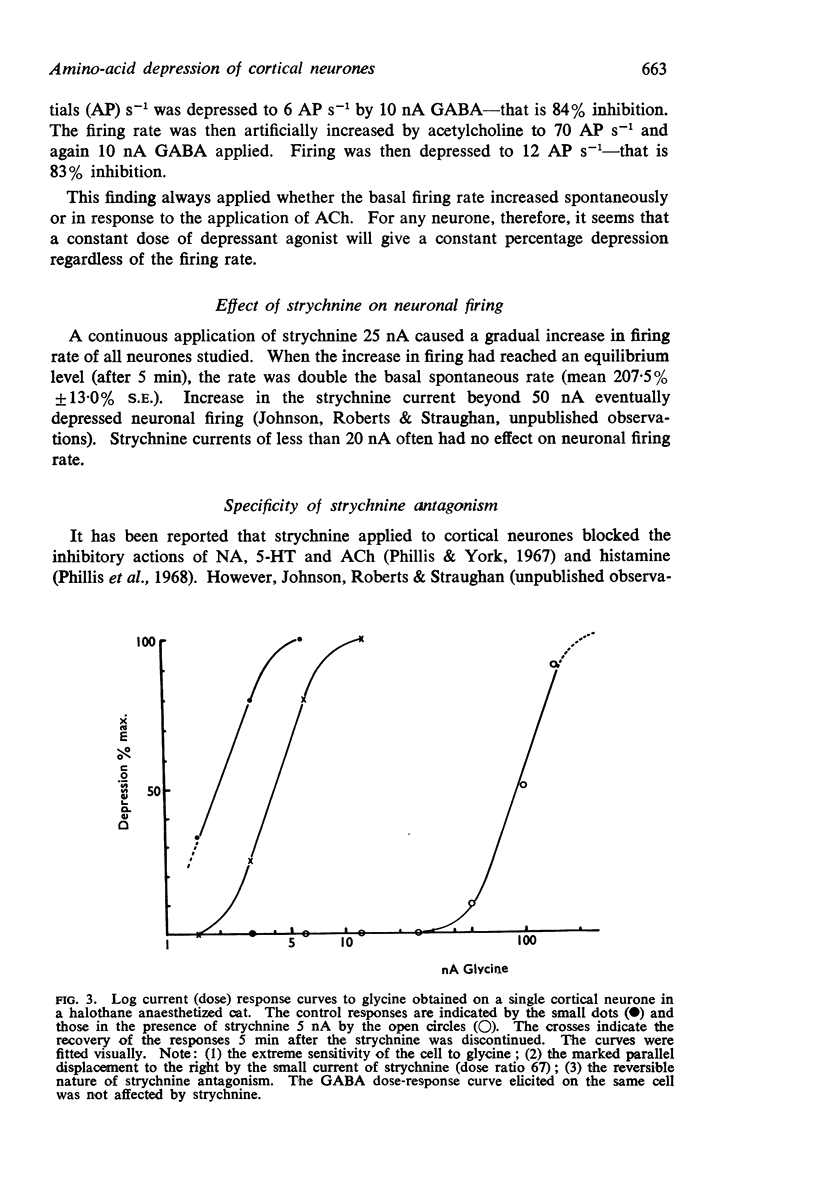
3. Strychnine in currents up to 25 nA shifted the dose-response curve of glycine to the right at a time when equilibrium depression in the same cells induced by the control agonists GABA or 5-HT was unaffected. These currents of strychnine did, however, prolong the time-course of onset of GABA and 5-HT depression.
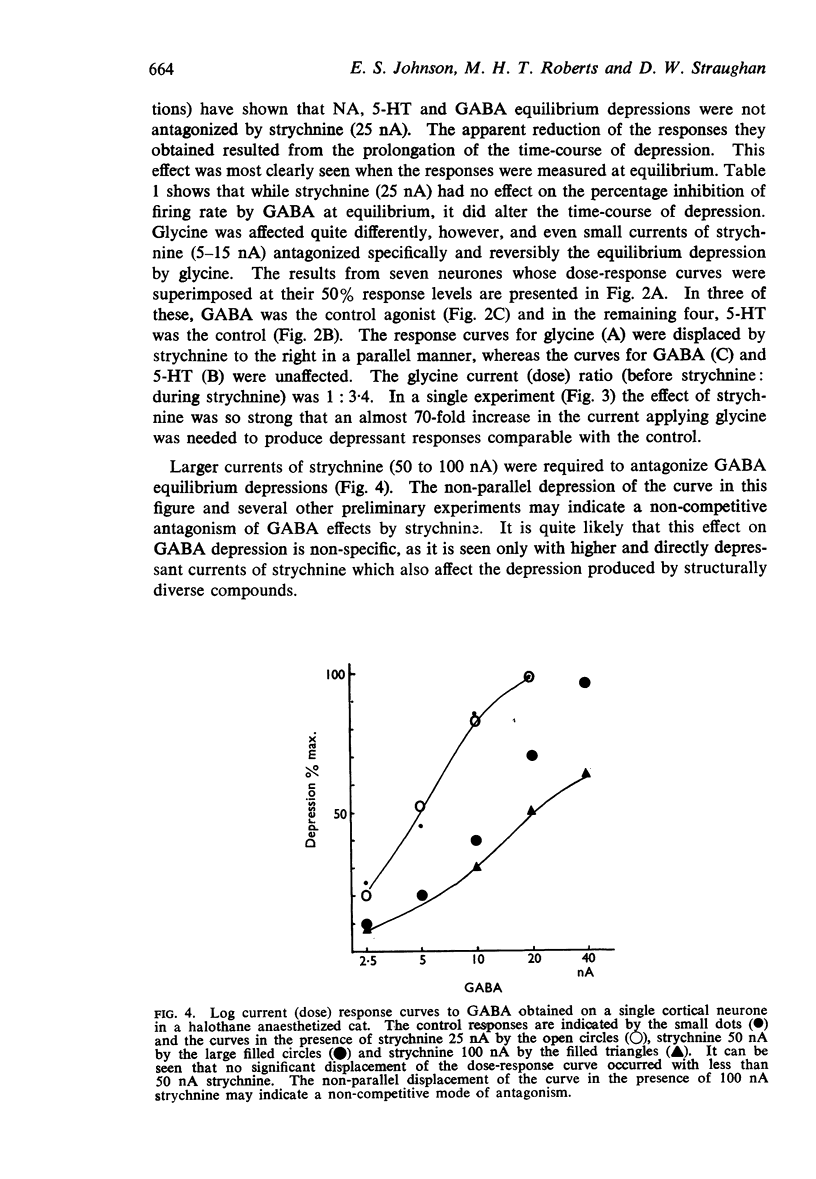
4. In larger currents strychnine reduced GABA equilibrium depression, but the dose-response curve was not shifted in a parallel fashion.
5. It is concluded that strychnine can specifically and competitively antagonize the effect of glycine on cortical neurones.
Full text
PDF

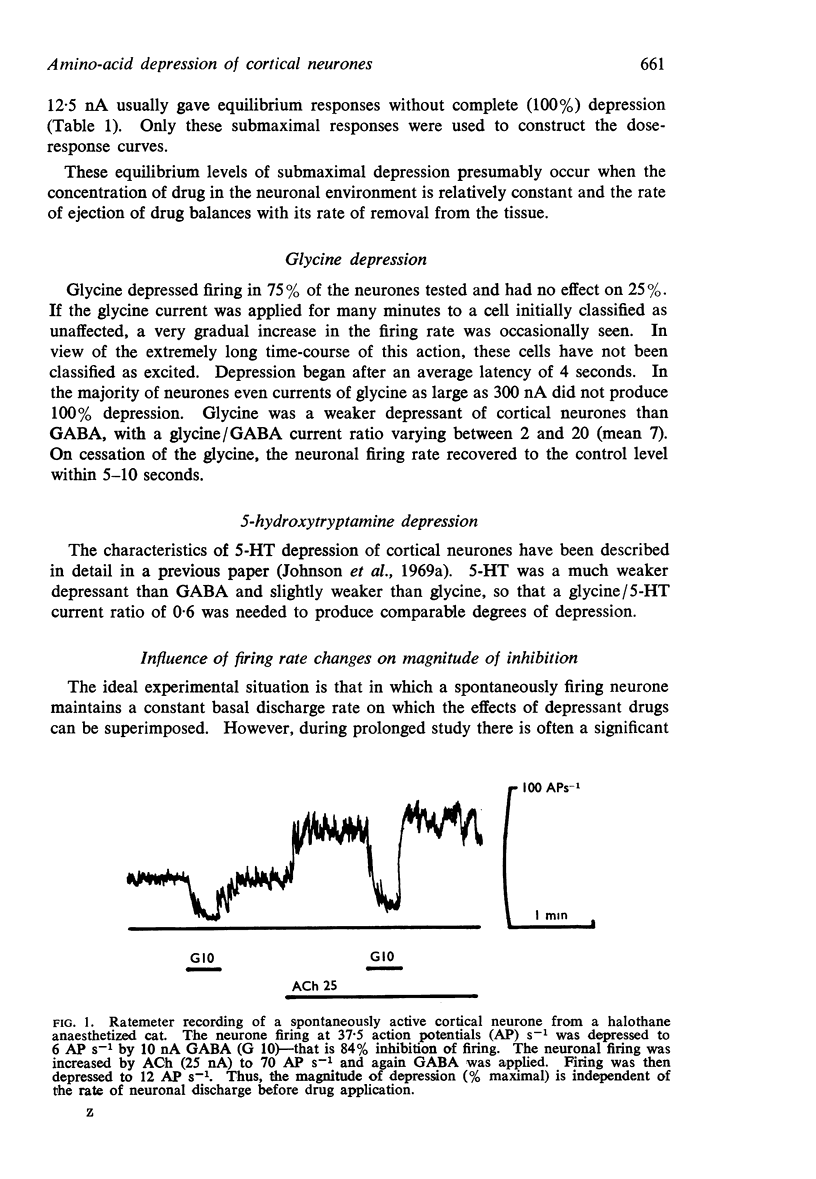


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Curtis D. R., Hösli L., Johnston G. A. A pharmacological study of the depression of spinal neurones by glycine and related amino acids. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00235443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A., Aprison M. H., Werman R. The effects of strychnine on the inhibition of interneurons by glycine and gamma-aminobutyric acid. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Mar;8(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florey E. Neurotransmitters and modulators in the animal kingdom. Fed Proc. 1967 Jul-Aug;26(4):1164–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hösli L., Tebècis A. K., Filias N. Effects of glycine, beta-alanine and GABA, and their interaction with strychnine, on brain stem neurones. Brain Res. 1969 Nov;16(1):293–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90106-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Sobieszek A., Straughan D. W. Noradrenaline sensitive cells in cat cerebral cortex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1969 Dec;8(6):549–566. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(69)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. S., Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. The responses of cortical neurones to monoamines under differing anaesthetic conditions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):261–280. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. S., Krnjević K. The action of glycine on cortical neurones. Exp Brain Res. 1969;9(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00238328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Randić M., Straughan D. W. Pharmacology of cortical inhibition. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(1):78–105. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Tebecis A. K., York D. H. Histamine and some antihistamines: their actions on cerebral cortical neurones. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jul;33(3):426–440. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., York D. H. Strychnine block of neural and drug-induced inhibition in the cerebral cortex. Nature. 1967 Dec 2;216(5118):922–923. doi: 10.1038/216922a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M. H., Straughan D. W. Excitation and depression of cortical neurones by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):269–294. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Bruggencate G., Engberg I. The effect of strychnine on inhibition in Deiters' nucleus induced by GABA and glycine. Brain Res. 1969 Jul;14(2):536–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(69)90133-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


