Abstract
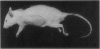
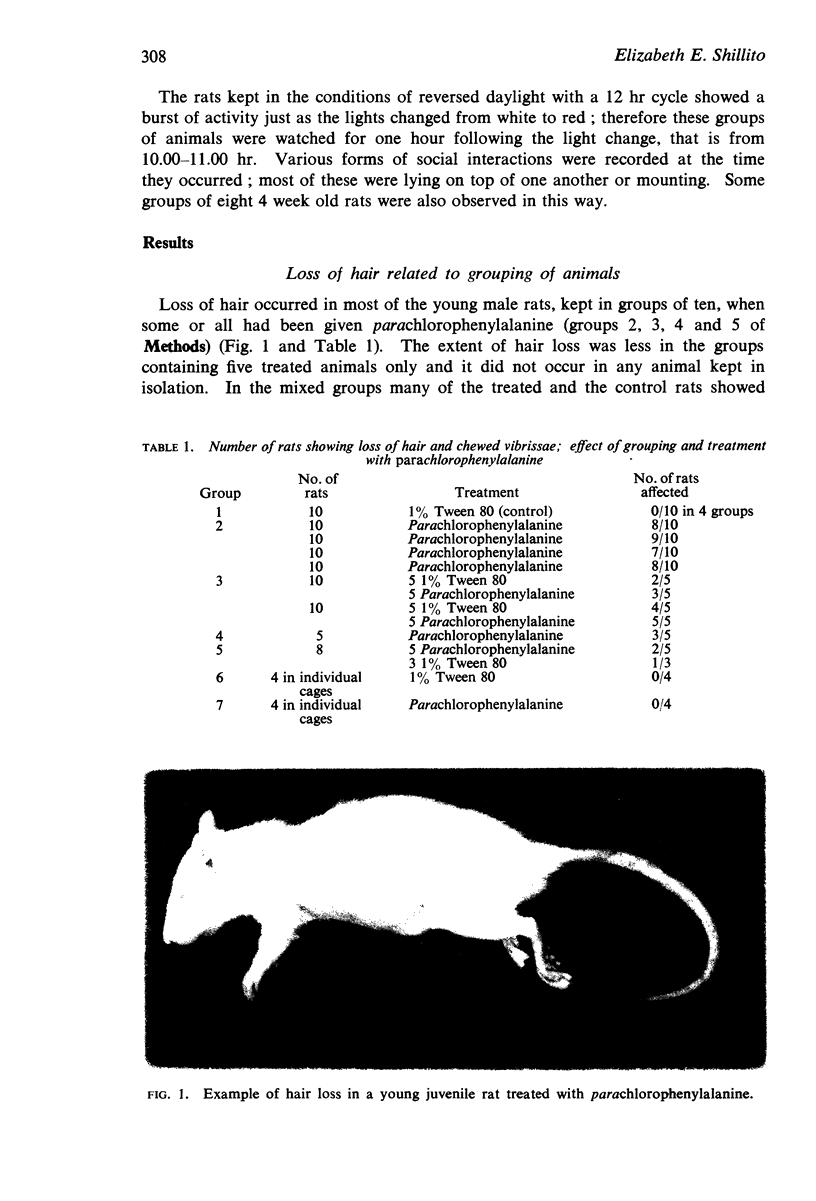
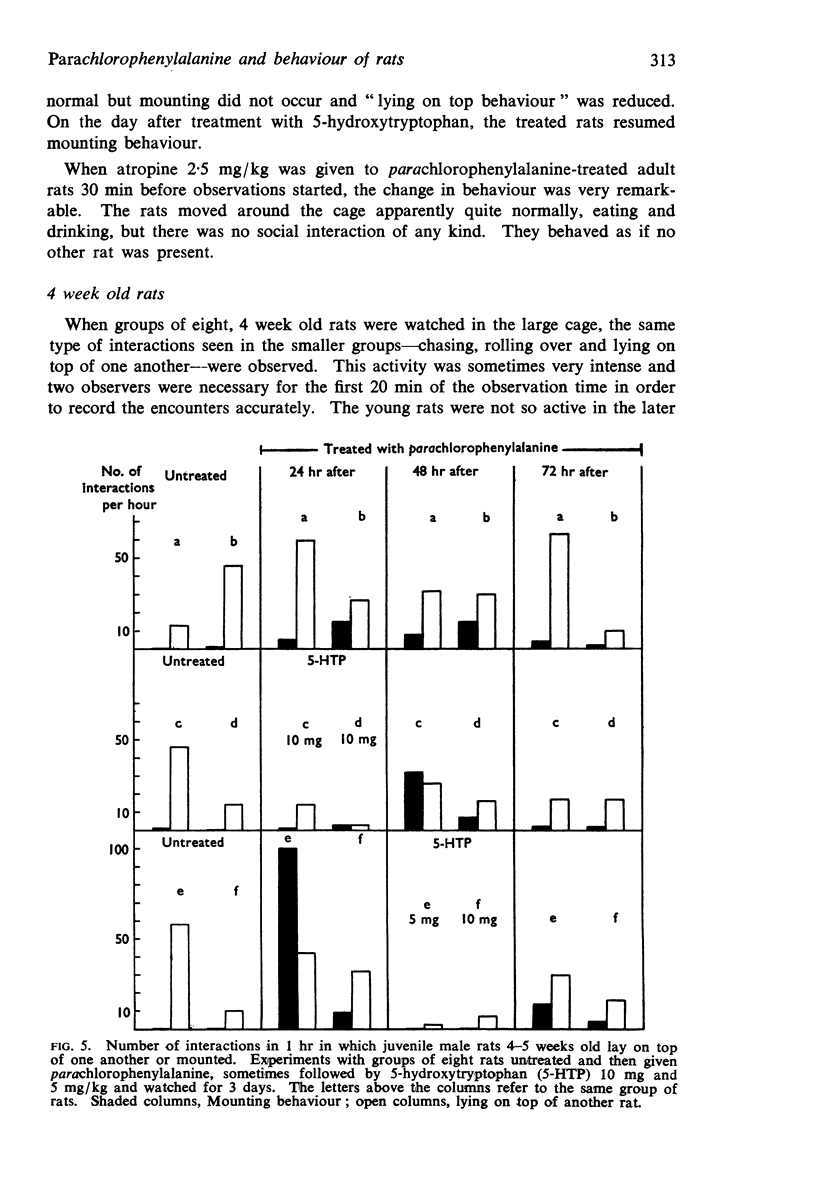
1. Juvenile male rats treated with parachlorophenylalanine showed hair loss round the head and neck extending down the chest and abdomen.
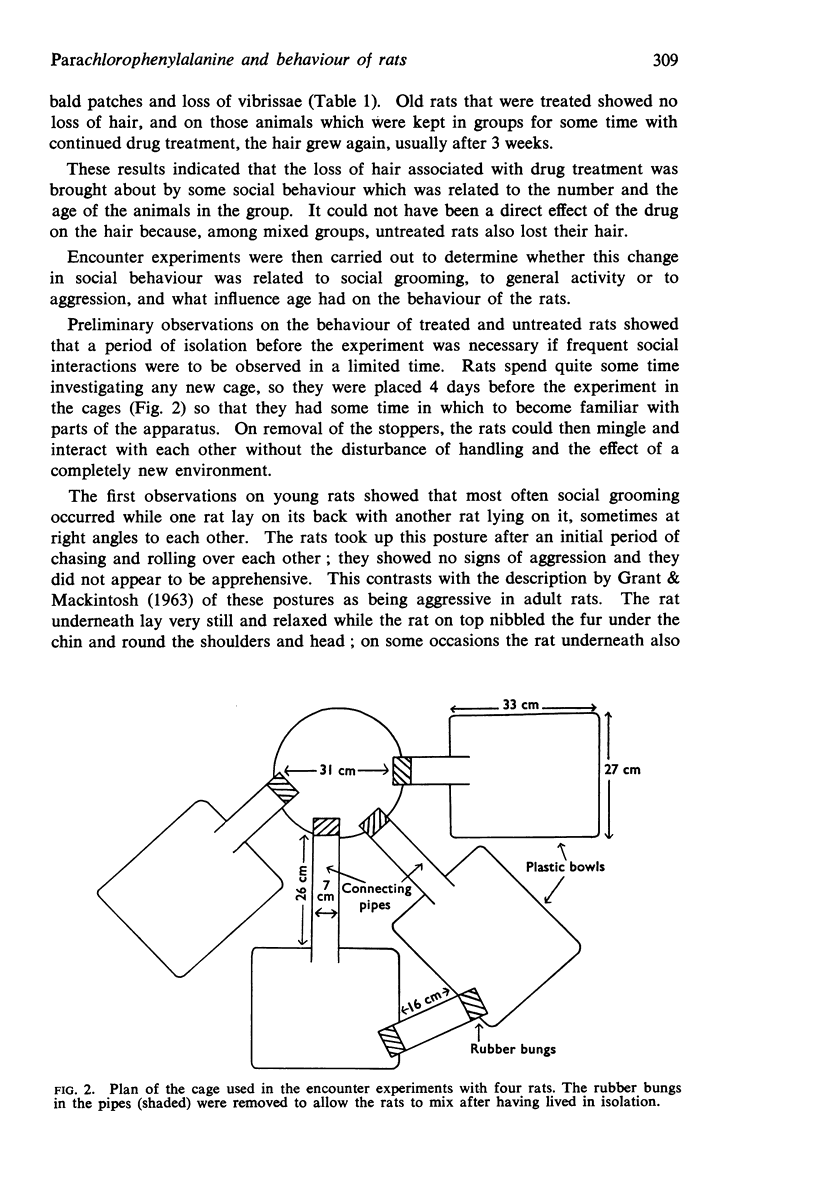
2. Treated isolated rats did not have this loss of hair, while untreated animals living in the same cage as treated rats lost their hair. The loss therefore seems to be caused by increased social behaviour. This consists of a greater frequency of chasing each other, rolling over and social grooming.
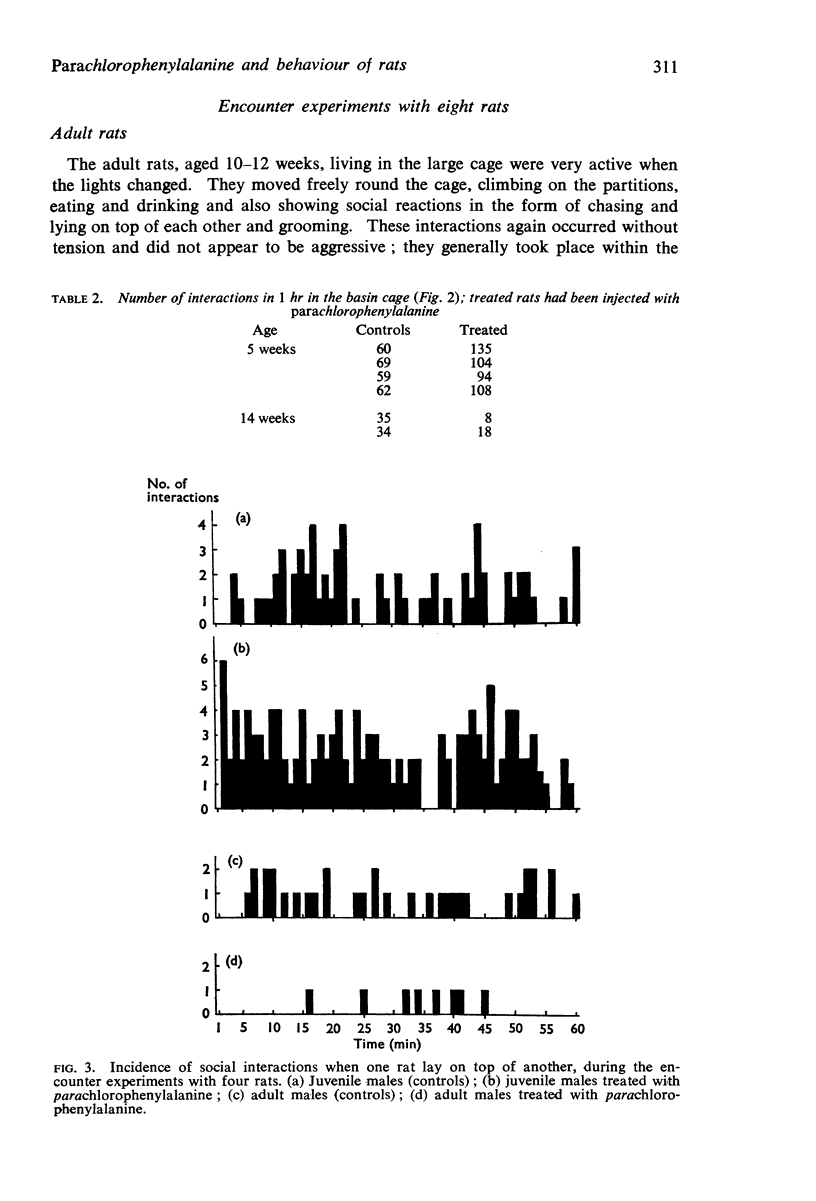
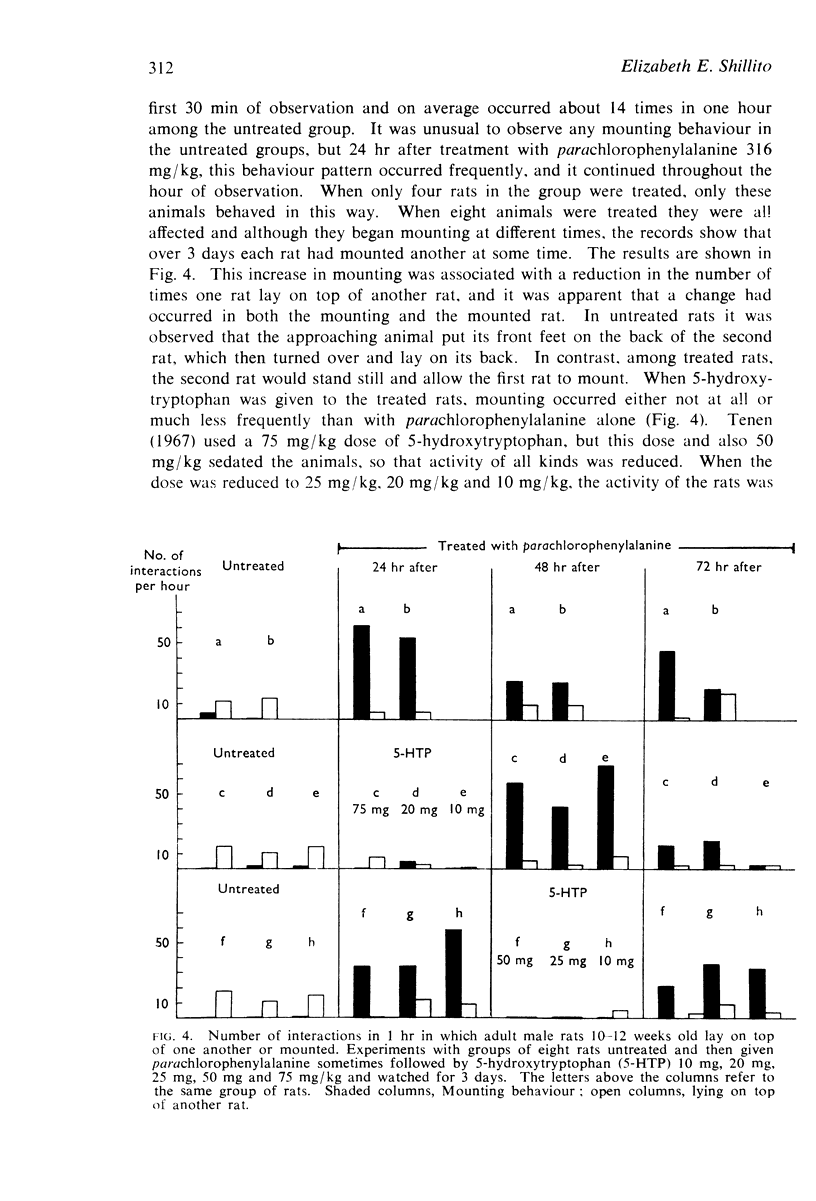
3. Adult male rats show an increase in mounting after treatment with parachlorophenylalanine, and this change in behaviour was counteracted by treatment with 5-hydroxytryptophan.
4. It is concluded that 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibits sexual behaviour in male rats. The increase in social interaction seen in juvenile rats may be the behavioural precursor of adult sexual behaviour.
5. Atropine 2·5 mg/kg blocked all forms of social interaction in adult male rats, although other activity was not altered.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jéquier E., Lovenberg W., Sjoerdsma A. Tryptophan hydroxylase inhibition: the mechanism by which p-chlorophenylalanine depletes rat brain serotonin. Mol Pharmacol. 1967 May;3(3):274–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koe B. K., Weissman A. p-Chlorophenylalanine: a specific depletor of brain serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Dec;154(3):499–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSUMOTO J., JOUVET M. EFFETS DE R'ESERPINE, DOPA ET 5 HTP SUR LES DEUX 'ETATS DE SOMMEIL. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1964;158:2137–2140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouret J., Bobillier P., Jouvet M. Effets de la parachlorophénylalanine sur le sommeil du Rat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1967;161(7):1600–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen S. S. Antagonism of the analgesic effect of morphine and other drugs by p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;12(4):278–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00401407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen S. S. The effects of p-chlorophenylalanine, a serotonin depletor, on avoidance acquisition, pain sensitivity and related behavior in the rat. Psychopharmacologia. 1967;10(3):204–219. doi: 10.1007/BF00401382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torda C. Effect of brain serotonin depletion on sleep in rats. Brain Res. 1967 Oct;6(2):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(67)90204-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzman E. D., Rapport M. M., McGregor P., Jacoby J. Sleep patterns of the monkey and brain serotonin concentration: effect of p-chlorophenylalanine. Science. 1968 Jun 21;160(3834):1361–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3834.1361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley D. W., van der Hoeven T. Alteration in Learning Ability Caused by Changes in Cerebral Serotonin and Catechol Amines. Science. 1963 Feb 15;139(3555):610–611. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3555.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]