Abstract
1. A method is described for studying the peristaltic reflex in the guinea-pig or cat isolated colon, using a graded localized intraluminal stimulus consisting of a solid bolus.
2. The method gives an easy evaluation of propulsive activity and makes it possible to record simultaneously the segmental activity of the circular muscle in relation to the site of stimulation and the contractions and relaxations of the longitudinal muscle coat.
3. The velocity of propulsion, which is a reliable measure of propulsive activity, is dependent on the degree of distension and is easily affected by physical agents and nervous stimulation. A solid bolus is propelled only when there is simultaneous ascending contraction and descending inhibition of the circular musculature.
4. Since the peristaltic reflex could not be elicited from areas from which the mucosal and submucosal layers had been removed, these layers are essential for the triggering of the peristaltic reflex and for the propulsion of solid contents in the colon.
Full text
PDF

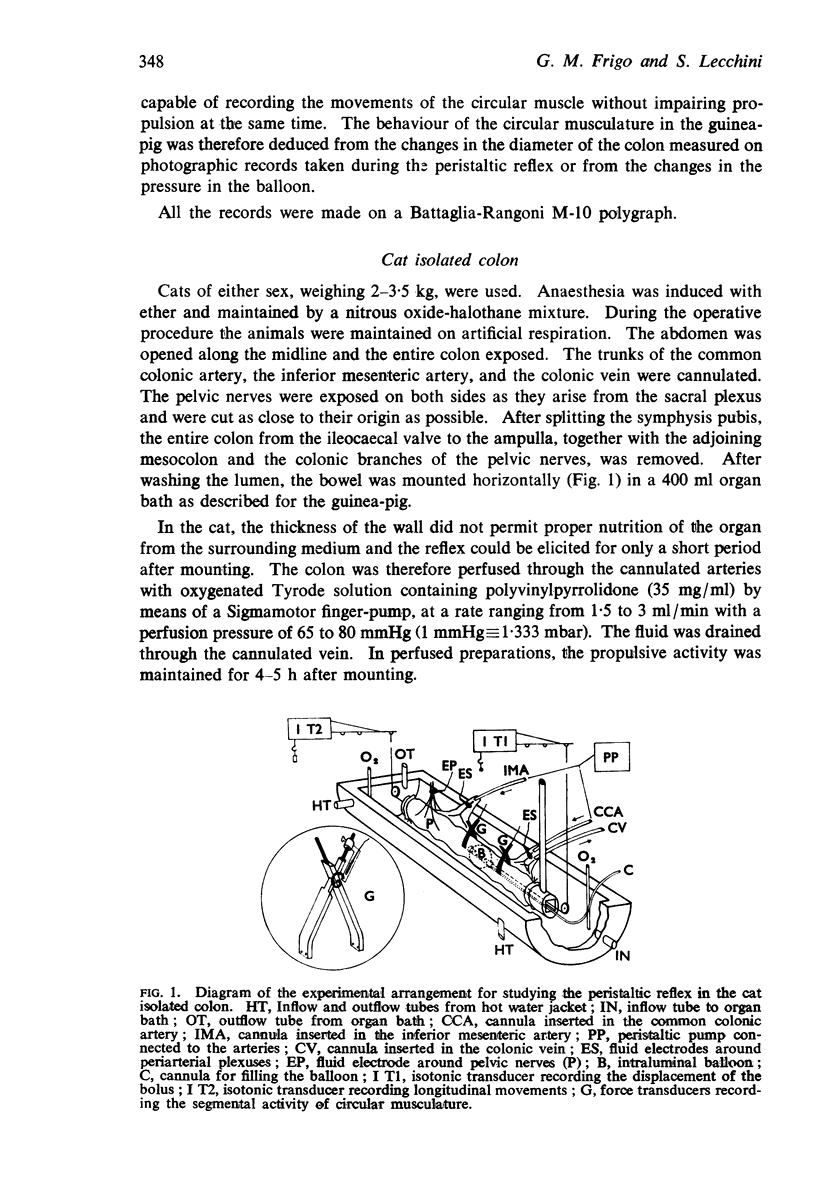

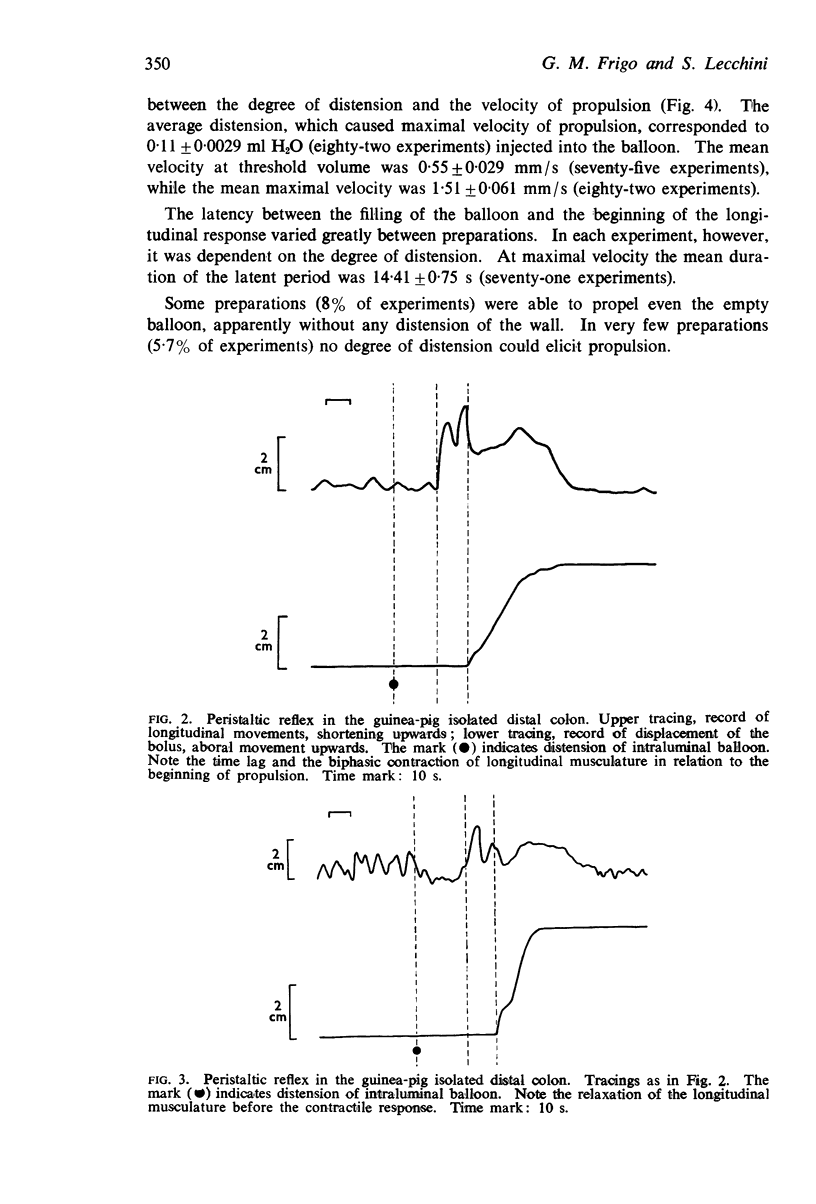






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELESLIN D., VARAGIC V. The effect of substance P on the peristaltic reflex of the isolated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Sep;13(3):321–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULBRING E., LIN R. C., SCHOFIELD G. An investigation of the peristaltic reflex in relation to anatomical observations. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Jan;43(1):26–37. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The movements and the innervation of the large intestine. J Physiol. 1900 Dec 31;26(1-2):107–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1900.sp000825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E., WACHTER B. T., HONOUR A. J., BOGOCH A. The relationship between electrical and mechanical activity of the small intestine of dog and man. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1960 Jul;38:777–802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIAMENT M. L., KOSTERLITZ H. W., McKENZIE J. Role of the mucous membrane in the peristaltic reflex in the isolated ileum of the guinea pig. Nature. 1961 Jun 24;190:1205–1206. doi: 10.1038/1901205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. R. Antiperistalsis and other muscular activities of the colon. J Physiol. 1904 Jun 30;31(3-4):272–304. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1904.sp001037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINZEL K. H. Are mucosal nerve fibres essential for the peristaltic reflex? Nature. 1959 Oct 17;184(Suppl 16):1235–1236. doi: 10.1038/1841235b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUKUHARA T., MIYAKE T. The intrinsic reflexes in the colon. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Mar 25;9(1):49–55. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUKUHARA T., NAKAYAMA S., NANBA R. The role of the intrinsic mucosal reflex in the fluid transport through the denervated colonic loop. Jpn J Physiol. 1961 Feb 15;11:71–79. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.11.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hukuhara T., Neya T. The movements of the colon of rats and guinea pigs. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Aug 15;18(4):551–562. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., LEES G. M. PHARMACOLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF INTRINSIC INTESTINAL REFLEXES. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Sep;16:301–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMBECK F. Die Beeinflussung der Darmmotilität durch Hydroxytryptamin. Pflugers Arch. 1958;265(6):567–574. doi: 10.1007/BF00416582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley J. N., Magnus R. Some observations of the movements of the intestine before and after degenerative section of the mesenteric nerves. J Physiol. 1905 Sep 8;33(1):34–51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1905.sp001108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varagić V., Kazić T. The effect of frequency of coaxial electrical stimulation on the peristaltic activity of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Aug;18(8):513–518. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


