Abstract
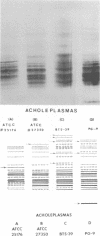
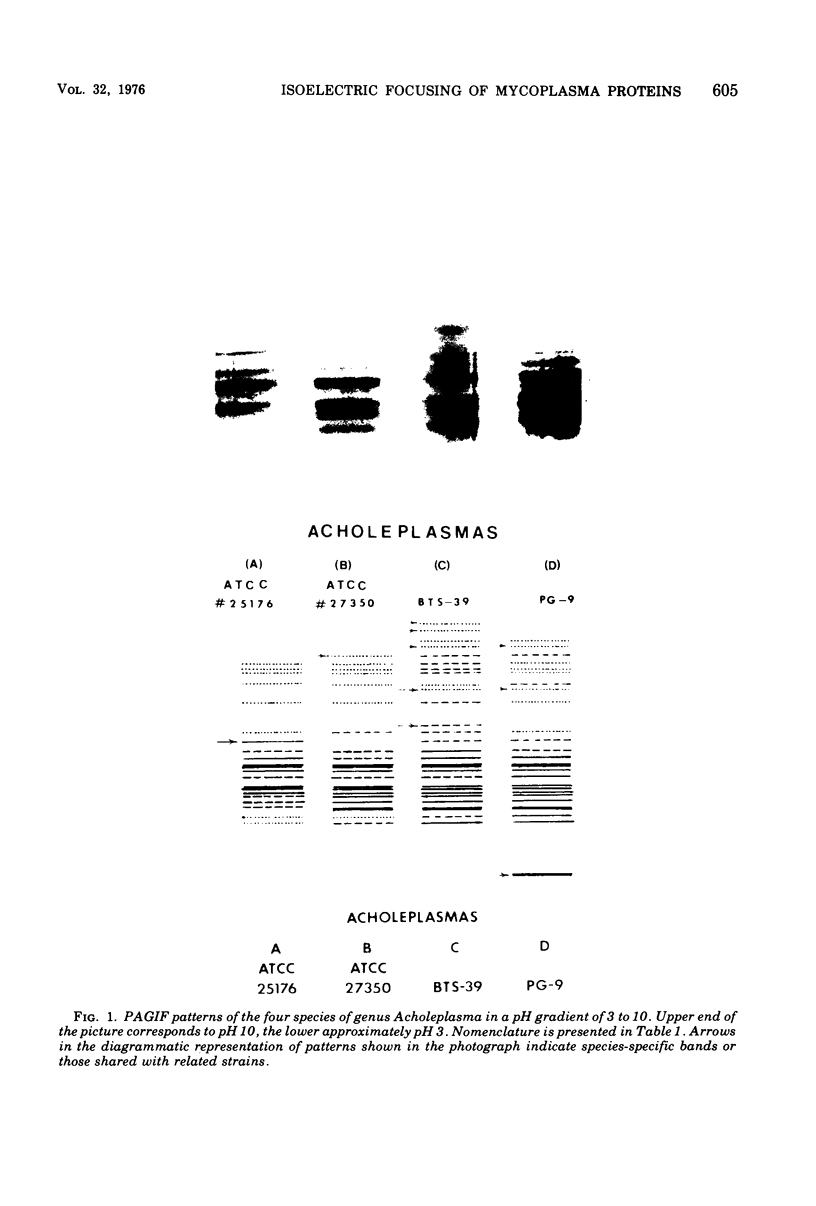
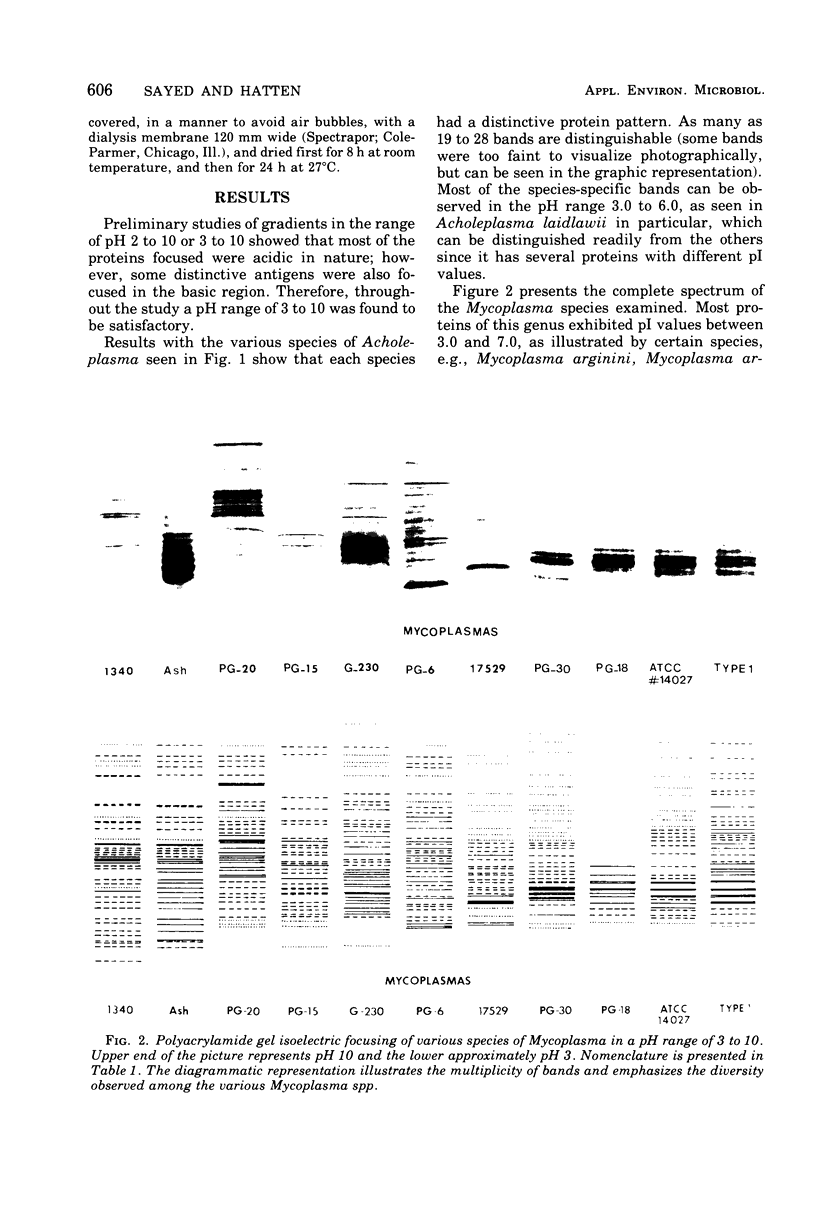
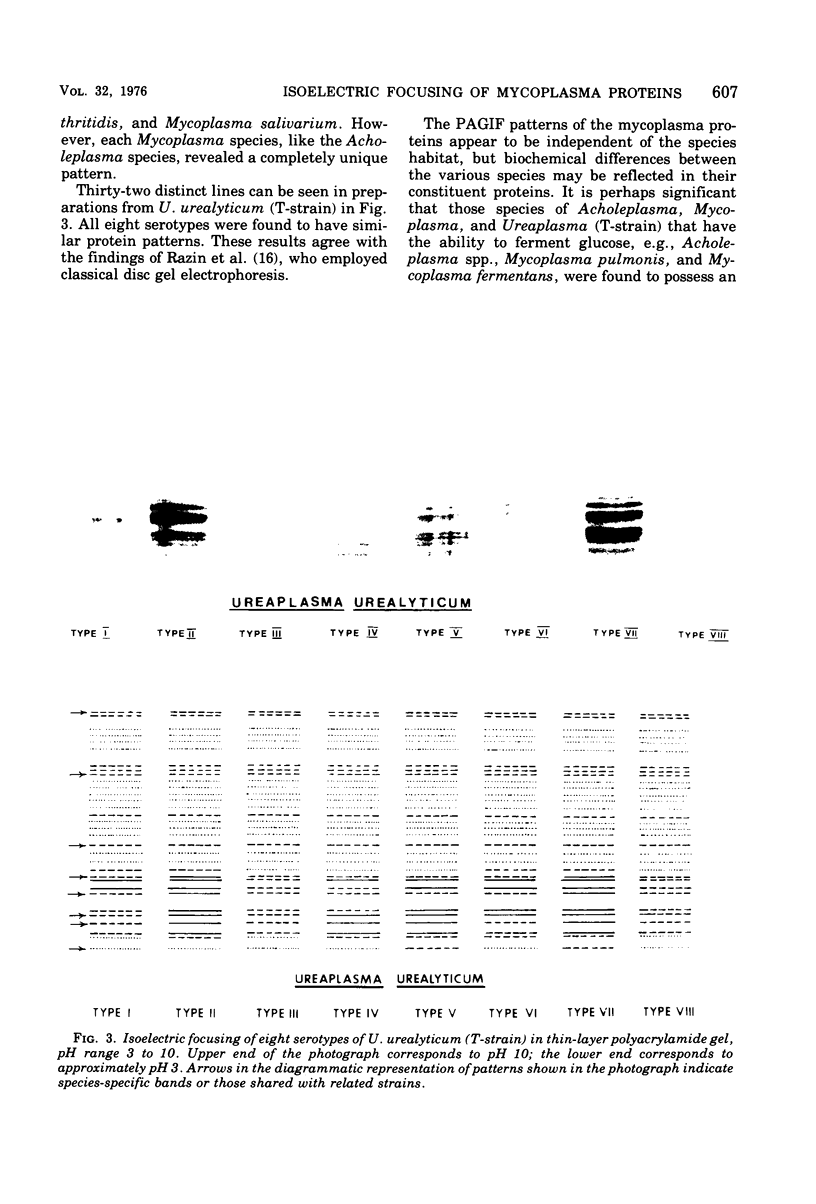
Polyacrylamide gel isoelectric focusing (PAGIF) in thin layer was used to resolve proteins of Mycoplasma spp., Acholeplasma spp., and eight strains of Ureaplasma urealyticum (T-strain). A mixture of urea, Triton X-100, and dithioerythritol was used to solubilize sonically disrupted cells. PAGIF was performed in the range of pH 3 to 10. Protein patterns were carefully compared, demonstrating resolved and distinguishable species-specific protein bands. The eight serotypes of U. urealyticum (T-strain) gave identical protein patterns in the pH 3 to 10 range. The characteristic "fingerprints" of a species appeared to correlate with the biochemical nature and not the habitat in each case. Arginine-hydrolyzing species seemed to show more diverse focusing than those that ferment glucose, or prefer an acid environment. Characterization and identification of highly resolved species-specific proteins, ease of performance, and reproducibility of this method suggest that PAGIF might be employed as a taxonomic aid.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Yu B. Characterization of canine mycoplasmas by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunodiffusion. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.295-299.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Williamson A. R., Askonas B. A. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gel and its application to immunoglobulins. Nature. 1968 Jul 6;219(5149):66–67. doi: 10.1038/219066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black F. T., Krogsgaard-Jensen A. Application of indirect immunofluorescence, indirect haemagglutination and polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis to human T-mycoplasmas. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Jun;82(3):345–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02336.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale G., Latner A. L. Isoelectric focusing in polyacrylamide gels. Lancet. 1968 Apr 20;1(7547):847–848. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels M. J., Meddins B. M. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of mycoplasma proteins in sodium dodecyl sulphate. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 May;76(1):239–242. doi: 10.1099/00221287-76-1-239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellinger J. D., Jasper D. E. Polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins of mycoplasma isolated from cattle and horses. Am J Vet Res. 1972 Apr;33(4):769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWLER R. C., COBLE D. W., KRAMER N. C., BROWN T. M. STARCH GEL ELECTROPHORESIS OF A FRACTION OF CERTAIN OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE GROUP OF MICROORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1145–1151. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1145-1151.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forshaw K. A. Electrophoretic patterns of strains of Mycoplasma pulmonis. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):493–499. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaback D. H., Rutter A. C. Polyacrylamide-isoelectric-focusing. A new technique for the electrophoresis of proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Aug 13;32(3):447–453. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90682-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasma taxonomy studiedy electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.687-694.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Rottem S. Identification of Mycoplasma and other microorganisms by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1807–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1807-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Valdesuso J., Purcell R. H., Chanock R. M. Electrophoretic analysis of cell proteins of T-strain mycoplasmas isolated from man. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):702–706. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.702-706.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoades K. R., Phillips M., Yoder H. W., Jr Comparison of strains of Mycoplasma gallisepticum by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Avian Dis. 1974 Jan-Mar;18(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Righetti P. G., Drysdale J. W. Isoelectric focusing in gels. J Chromatogr. 1974 Sep 25;98(2):271–321. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)92076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendal S. Analysis of the electrophoretic pattern of mycoplasma proteins for the identification of canine mycoplasma strains. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Jun;81(3):273–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1973.tb02204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Razin S. Electrophoretic patterns of membrane proteins of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):359–364. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.359-364.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wreghitt T. G., Windsor G. D., Butler M. Flat gel polyacrylamide electrophoresis of porcine mycoplasmas. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):530–533. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.530-533.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., Baxendale W., Sayer L. J. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of lysates of mycoplasmas. Res Vet Sci. 1970 Jul;11(4):397–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]