Abstract
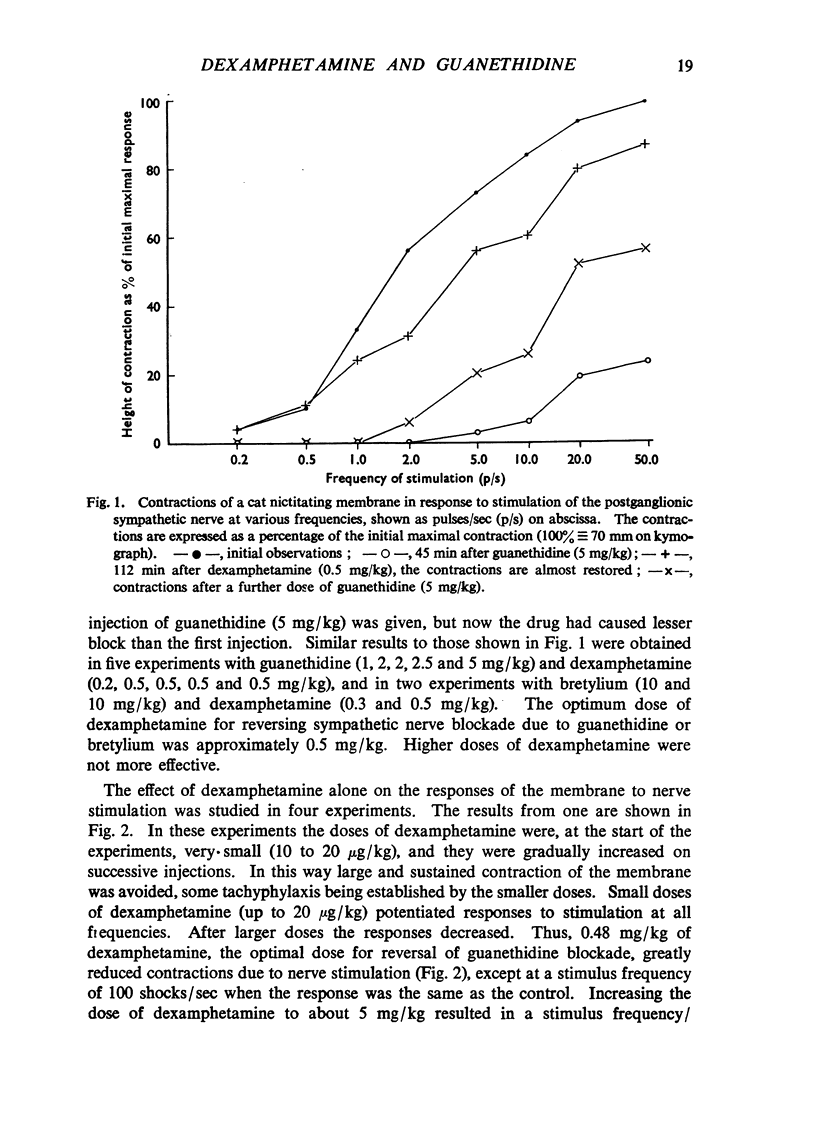
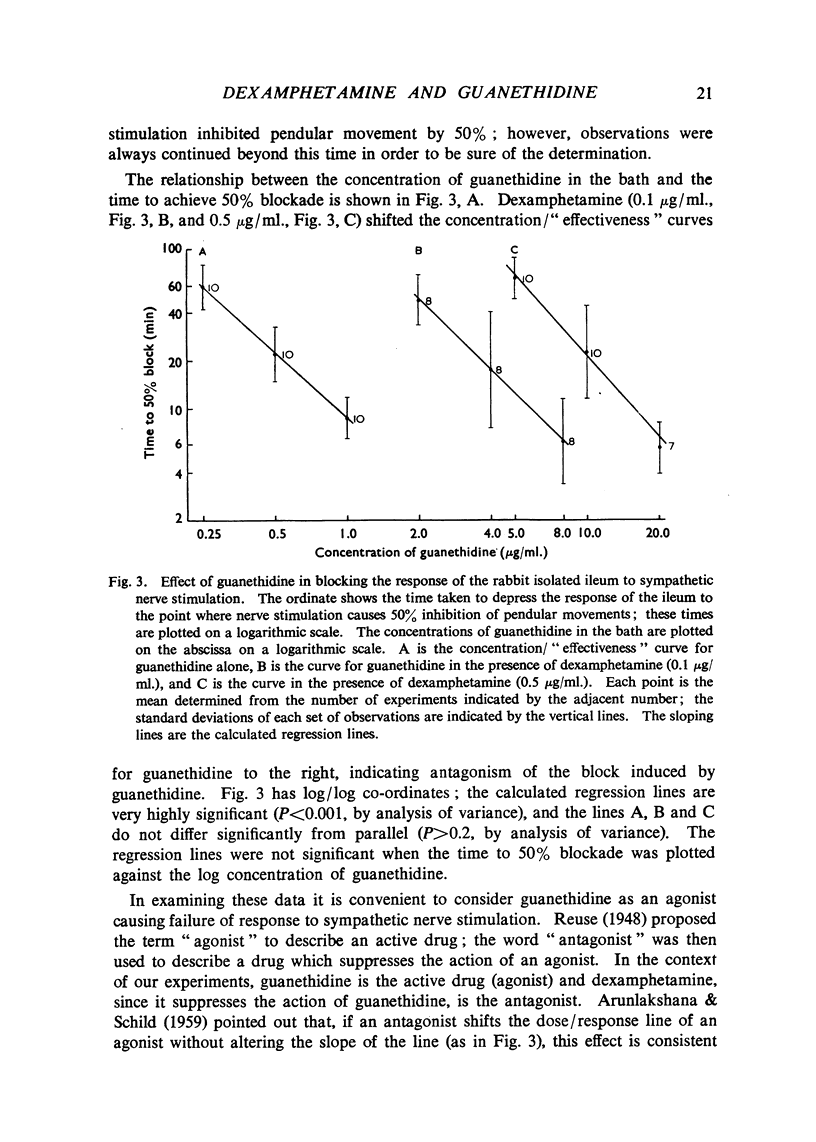
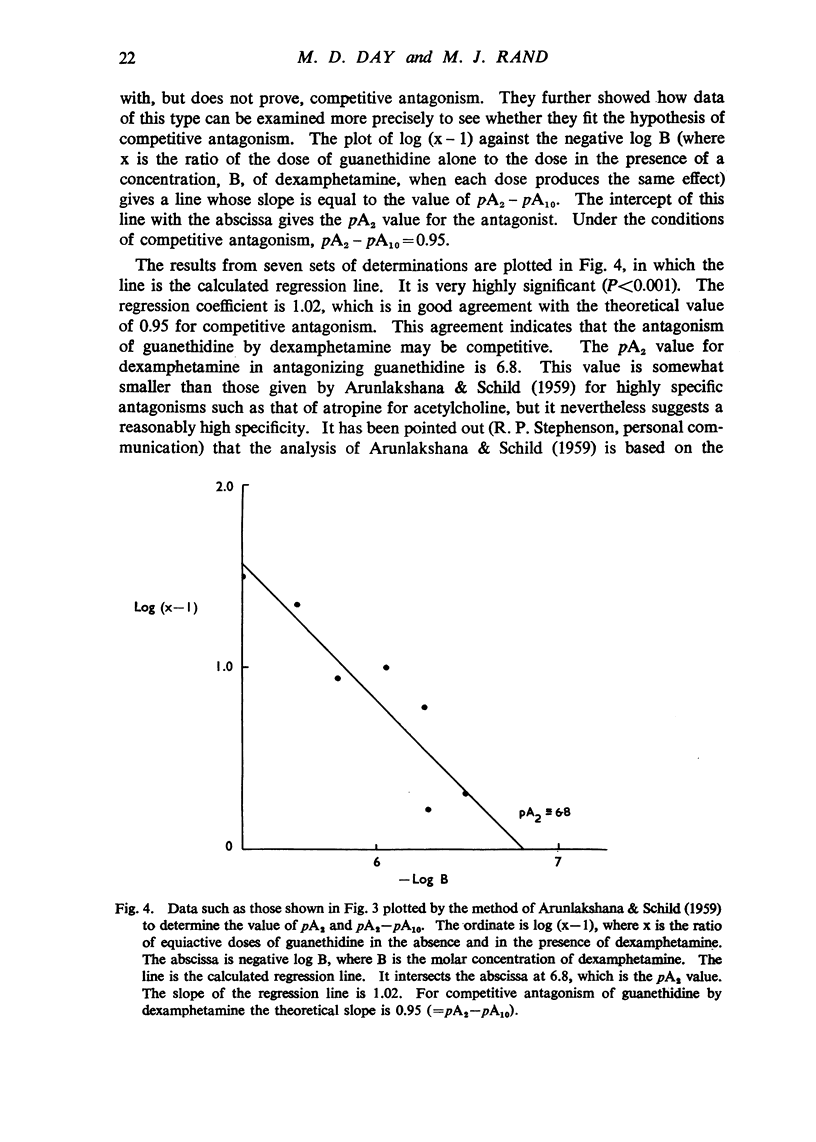
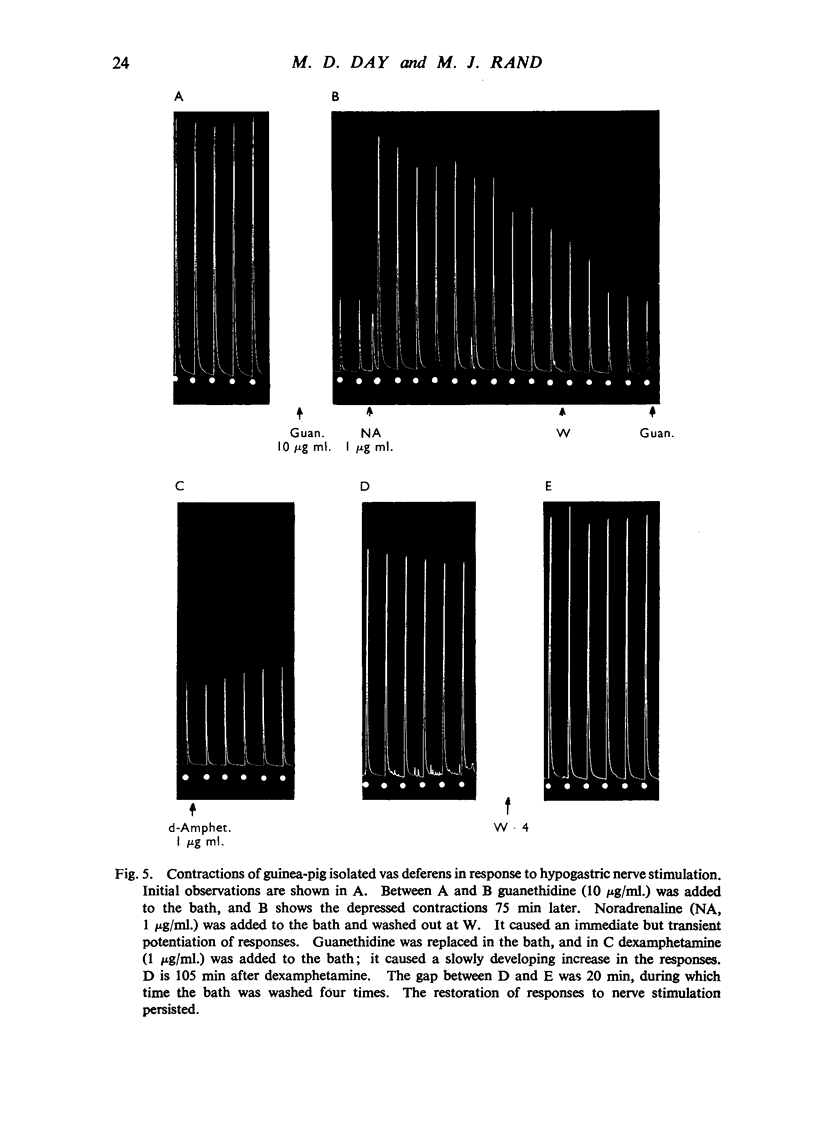
After guanethidine had blocked the response of the cat nictitating membrane to sympathetic nerve stimulation, dexamphetamine restored the responses to all frequencies of stimulation. Dexamphetamine antagonized the sympathetic nerve block by guanethidine in the isolated sympathetically innervated rabbit ileum; the evidence suggests that the antagonism was competitive. Dexamphetamine antagonized the sympathetic nerve block by guanethidine in the isolated hypogastric nerve-vas deferens preparation of the guinea-pig. Doses of dexamphetamine, larger than those required to antagonize the blocking action of guanethidine, abolished the responses of the nictitating membrane, ileum and vas deferens to nerve stimulation. Dexamphetamine did not influence the depletion of noradrenaline by guanethidine in the heart and spleen of rabbits. The hypothesis is advanced that both dexamphetamine and guanethidine act on the store of noradrenaline at sympathetic nerve endings.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD J., WHITBY L. G., HERTTING G. Effect of psychotropic drugs on the uptake of H3-norepinephrine by tissues. Science. 1961 Feb 10;133(3450):383–384. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3450.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The action of sympathomimetic amines in animals treated with reserpine. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):314–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASS R., KUNTZMAN R., BRODIE B. B. Norepinephrine depletion as a possible mechanism of action of guanethidine (SU 5864), a new hypotensive agent. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:871–872. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASS R., SPRIGGS T. L. Tissue amine levels and sympathetic blockade after guanethidine and bretylium. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Dec;17:442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAY M. D. Effect of sympathomimetic amines on the blocking action of guanethidine, bretylium and xylocholine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Apr;18:421–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAY M. D., RAND M. J. Antagonism of guanethidine by dexamphetamine and other related sympathomimetic amines. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1962 Sep;14:541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1962.tb11137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAY M. D., RAND M. J. Effect of guanethidine in revealing cholinergic sympathetic fibres. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Oct;17:245–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENGLER H. J., SPIEGEL H. E., TITUS E. O. Effects of drugs on uptake of isotopic norepinephrine by cat tissues. Nature. 1961 Aug 19;191:816–817. doi: 10.1038/191816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIS C. N., NASH C. W. The initial pressor actions of bretylium tosylate and guanethidine sulfate and their relation to release of catecholamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Oct;134:1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTTING G., AXELROD J., PATRICK R. W. Actions of bretylium and guanethidine on the uptake and release of [3H]-noradrenaline. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Feb;18:161–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL R. A., MULL R. P., PLUMMER A. J. [2-Octahydro-1-azocinyl)-ethyl]-guanidine sulfate (CIBA 5864-SU), a new synthetic antithypertensive agents]. Experientia. 1959 Jul 15;15:267–267. doi: 10.1007/BF02158076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAXWELL R. A., PLUMMER A. J., SCHNEIDER F., POVALSKI H., DANIEL A. I. Pharmacology of [2-(octahydro-1-azocinyl)-ethyl]-guanidine sulfate (Su-5864). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Jan;128:22–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCEWEN L. M. The effect on the isolated rabbit heart of vagal stimulation and its modification by cocaine, hexamethonium and ouabain. J Physiol. 1956 Mar 28;131(3):678–689. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE I. H., DUSTAN H. P. A new, potent antihypertensive drug: preliminary study of [2-(octahydro-1-azocinyl)-ethyl]-guanidine sulfate (guanethidine). J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Jul 11;170(11):1265–1271. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.03010110013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANAN S., VOGT M. Effect of drugs on the noradrenaline content of brain and peripheral tissues and its significance. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Feb;18:109–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUEMANN H. J., PHILIPPU A. Release of catechol amines from isolated medullary granules by sympathomimetic amines. Nature. 1962 Mar 3;193:890–891. doi: 10.1038/193890a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJOSTRAND N. O. Effect of some smooth muscle stimulants on the motor response of the isolated guinea pig vas deferens to hypogastric nerve stimulation. Nature. 1961 Dec 23;192:1190–1191. doi: 10.1038/1921190a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEPHENSON R. P. A modification of receptor theory. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Dec;11(4):379–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb00006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYLIE D. W. Augmentation of the pressor response to guanethedine by inhibition of catechol O-methyltransferase. Nature. 1961 Feb 11;189:490–491. doi: 10.1038/189490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


