Abstract
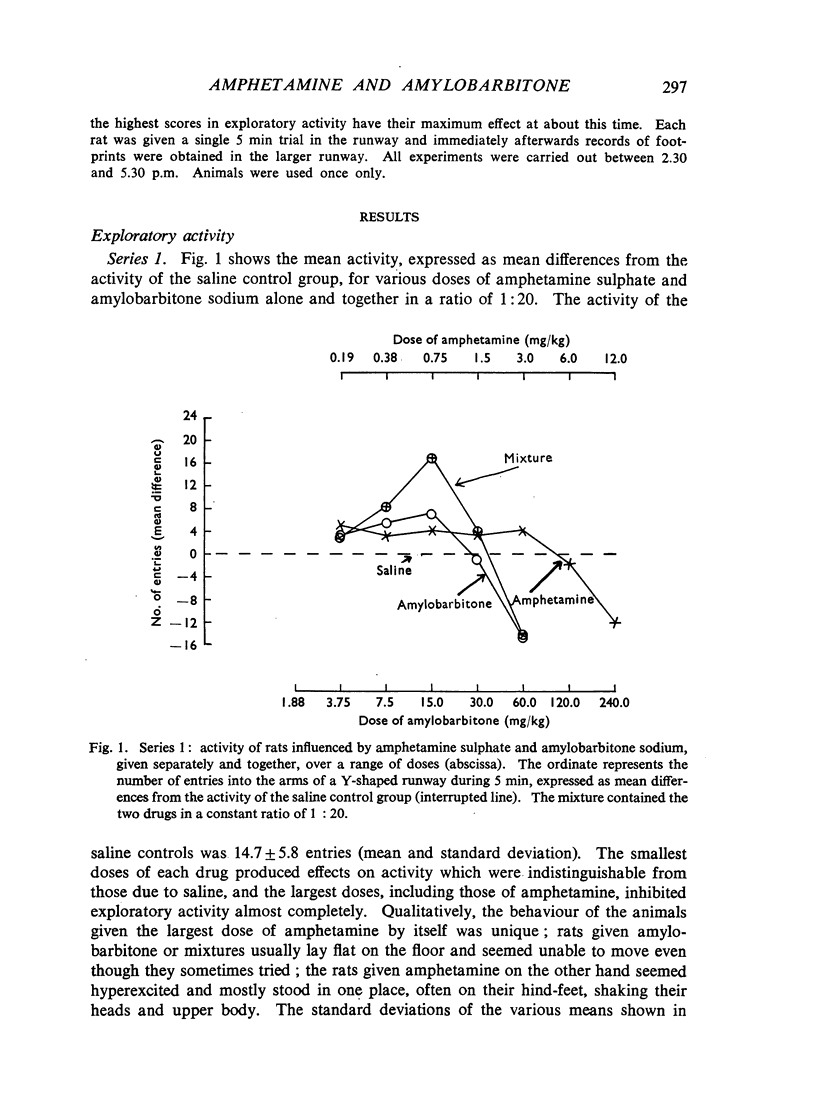
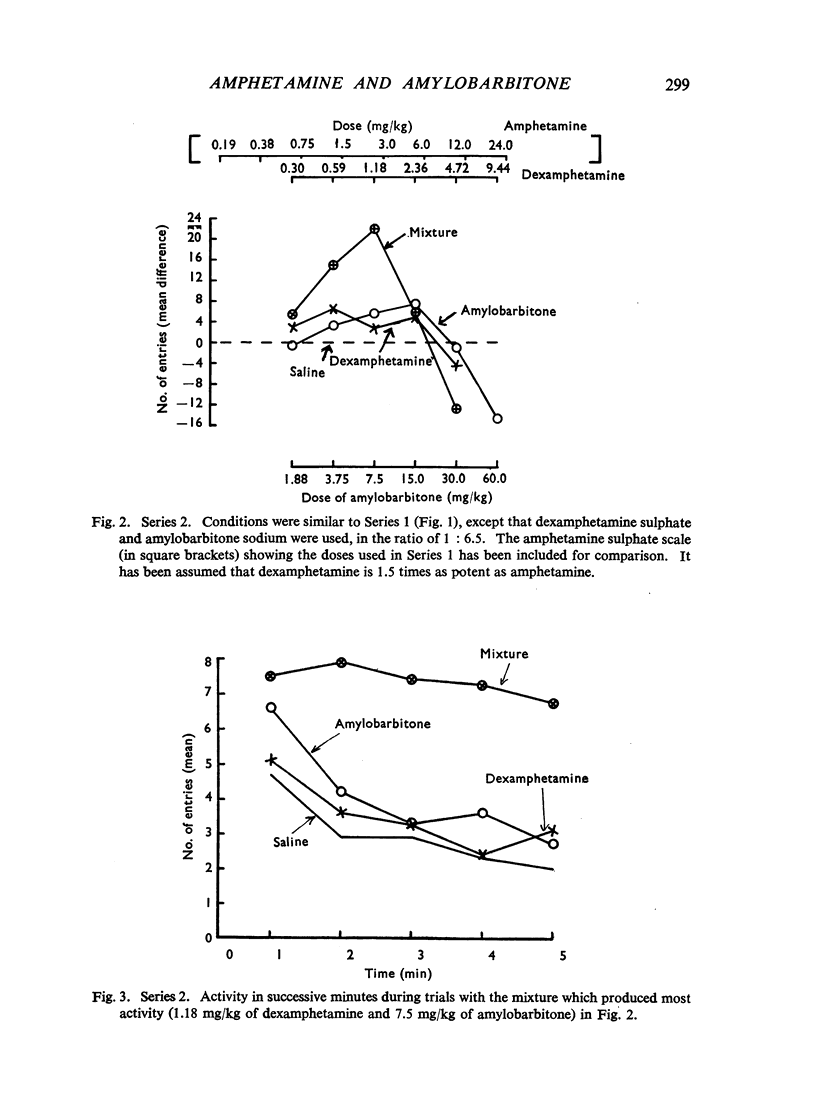
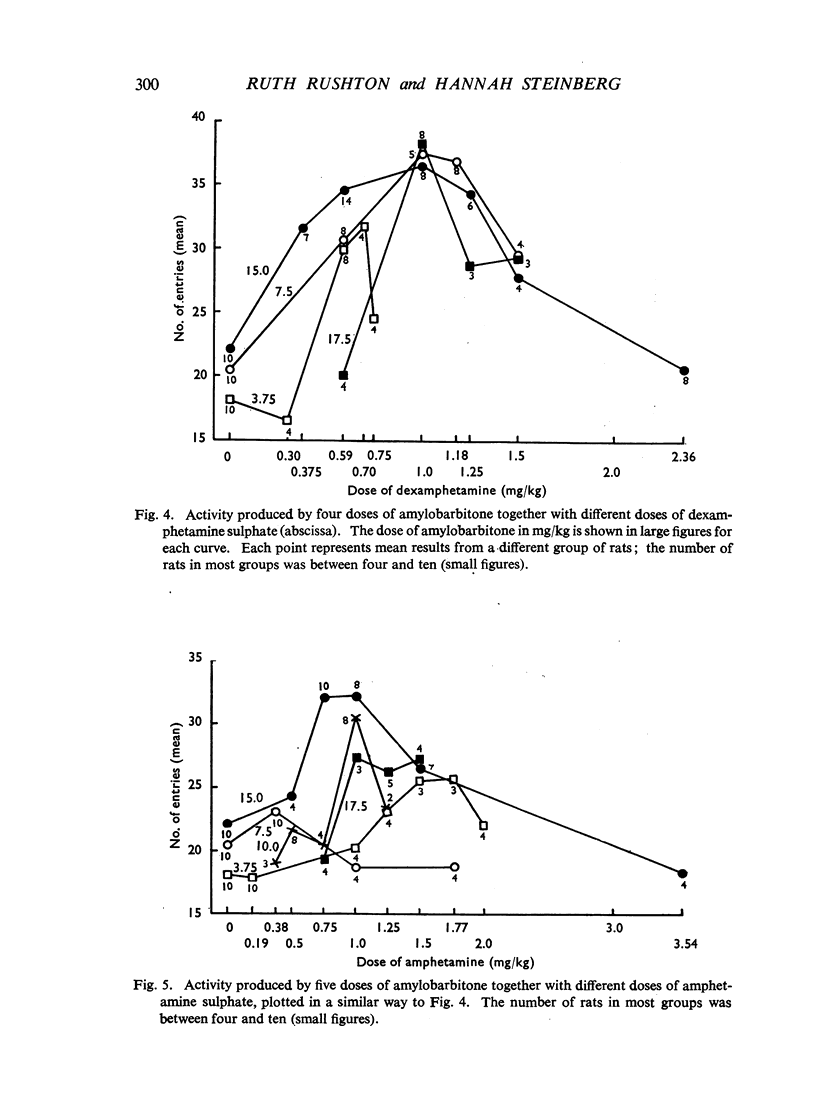
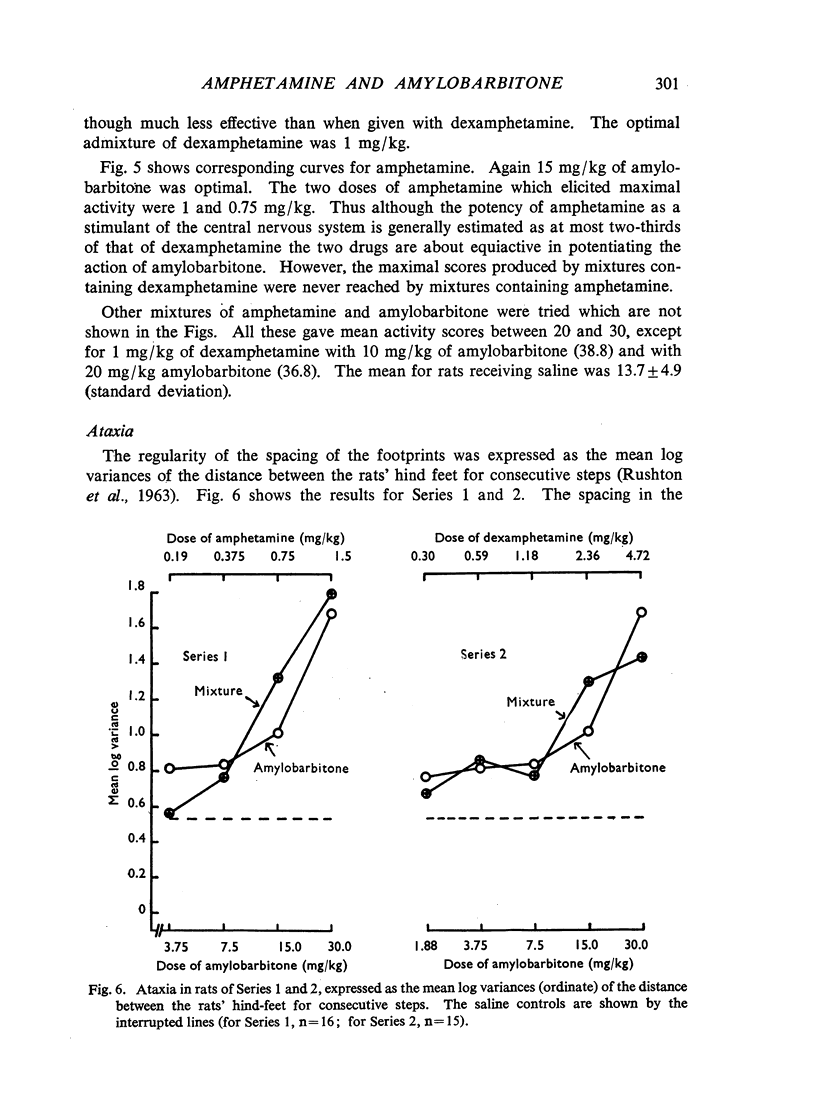
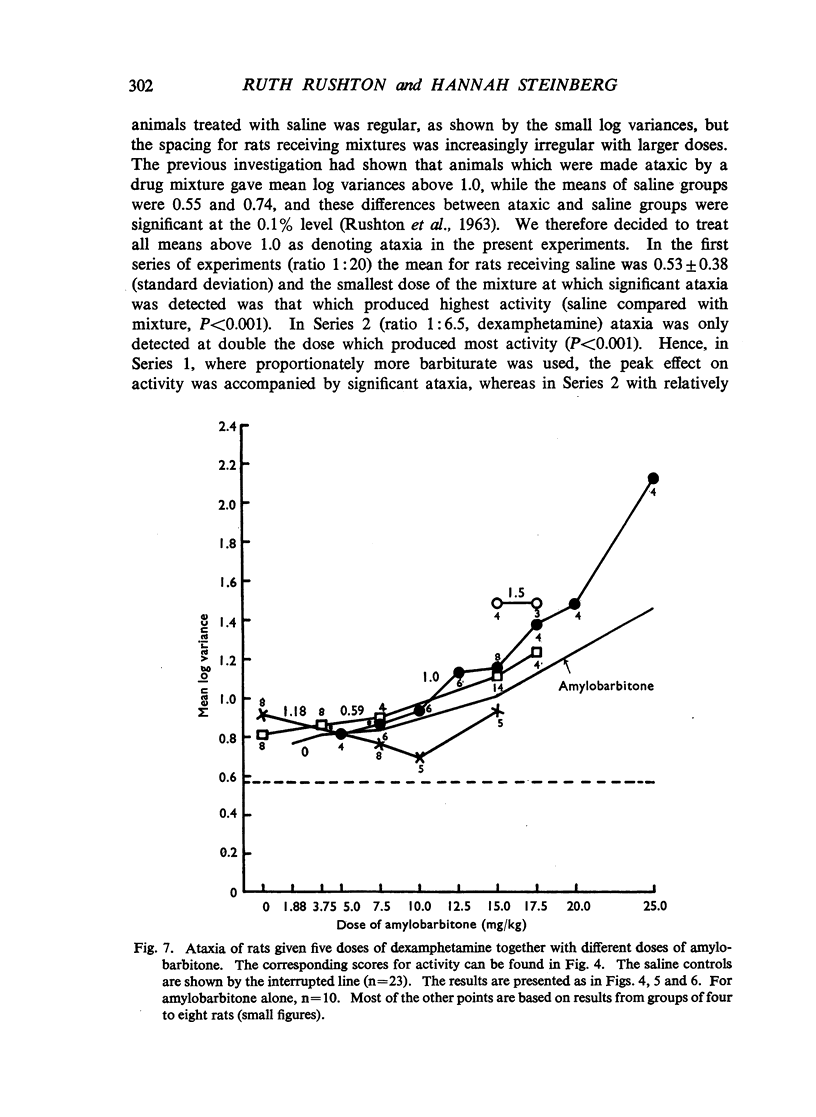
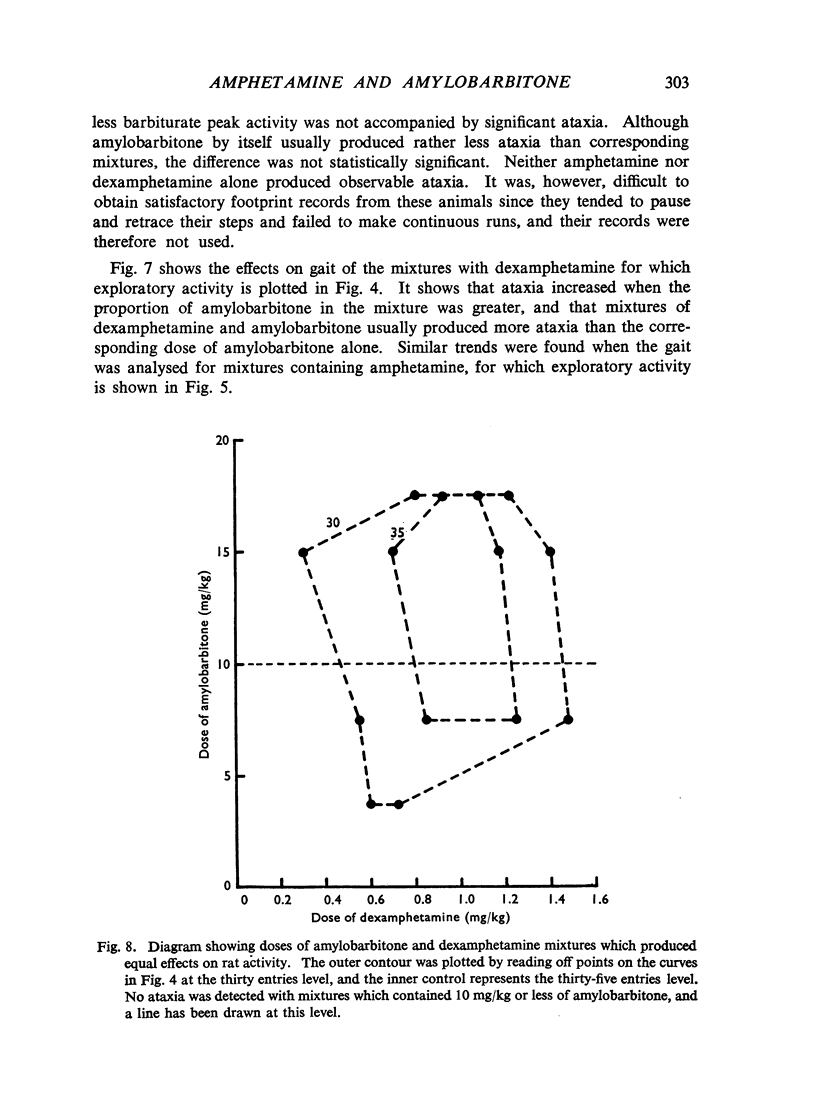
Dose/response relations have been analysed for the actions of amphetamine-barbiturate mixtures on exploratory activity and ataxia in rats. Amphetamine sulphate and amylobarbitone sodium were studied separately and together (in a constant ratio of 1:20) in doses which ranged from those producing no effect to those which incapacitated the animals. Dexamphetamine and amylobarbitone were similarly studied in a ratio of 1:6.5; this corresponds to the ratio of a commercial preparation, Drinamyl. The results showed that mixtures could stimulate exploratory activity and their maximal effects were much greater than the effects produced by any dose of the separate drugs. The maximal effect with the first dose-ratio included conspicuous ataxia, but the maximal effect with the second ratio did not. Further experiments in which the dose of one drug was held constant and that of the other was varied showed that maximal effects on activity could be obtained with mixtures of dexamphetamine and amylobarbitone. Equivalent effects could be obtained both with relatively small and with relatively large amounts of the two drugs, in varying ratios; some constituent doses of the individual drugs were found to be optimal; whether the mixture effect was accompanied by ataxia depended largely on the constituent amount of barbiturate. For practical purposes mixtures producing maximal effects on activity with the smallest amounts of both drugs and not accompanied by ataxia might be most desirable, and these can be approximately read off from an isobol plotted from the results. It was concluded that the marked stimulant effects of the amphetamine-barbiturate mixtures on activity of rats could be regarded as due to true potentiation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- LEGGE D., STEINBERG H. Actions of a mixture of amphetamine and a barbiturate in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Jun;18:490–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON R., STEINBERG H. Dose-response relations of amphetamine-barbiturate mixtures. Nature. 1963 Mar 9;197:1017–1018. doi: 10.1038/1971017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSHTON R., STEINBERG H., TINSON C. Effects of a single experience on subsequent reactions to drugs. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Feb;20:99–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINBERG H., RUSHTON R., TINSON C. Modification of the effects of an amphetamine-barbiturate mixture by the past experience of rats. Nature. 1961 Nov 11;192:533–535. doi: 10.1038/192533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


