Abstract
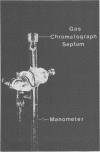
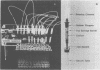
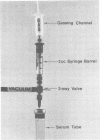
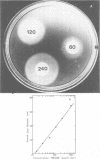
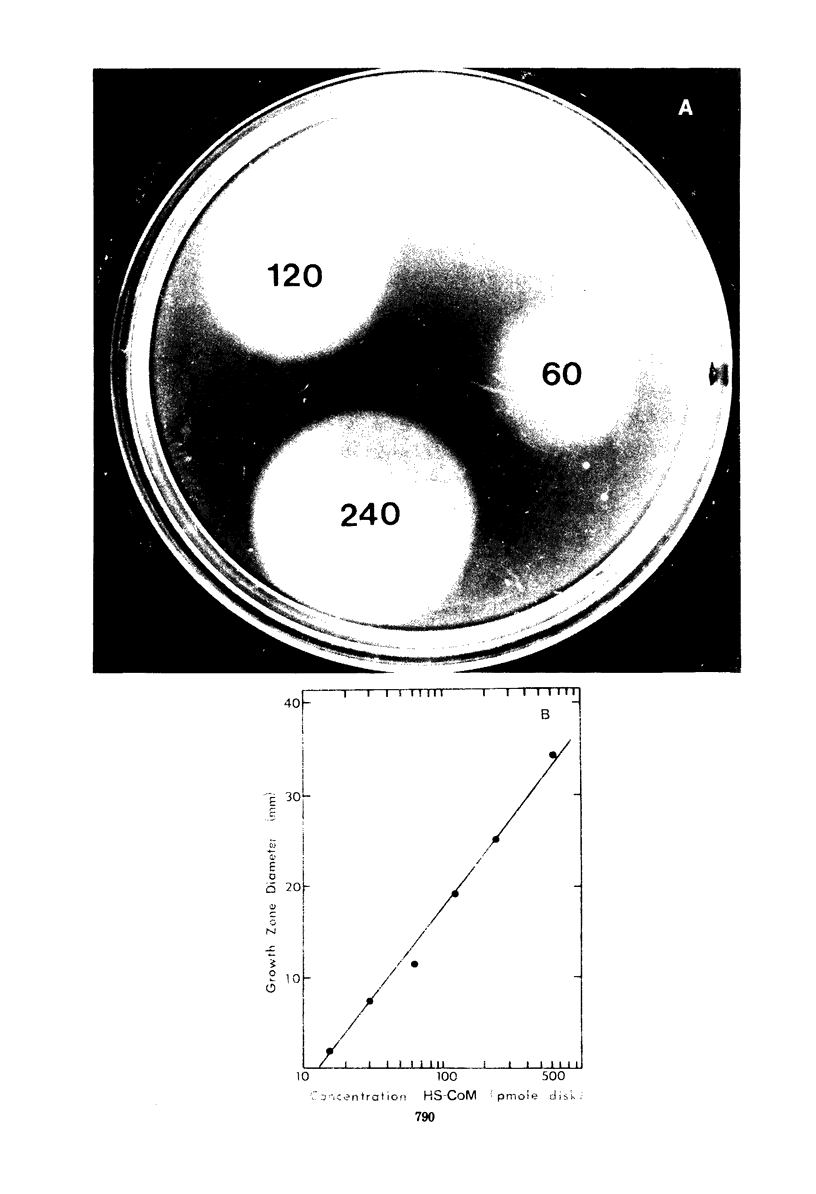
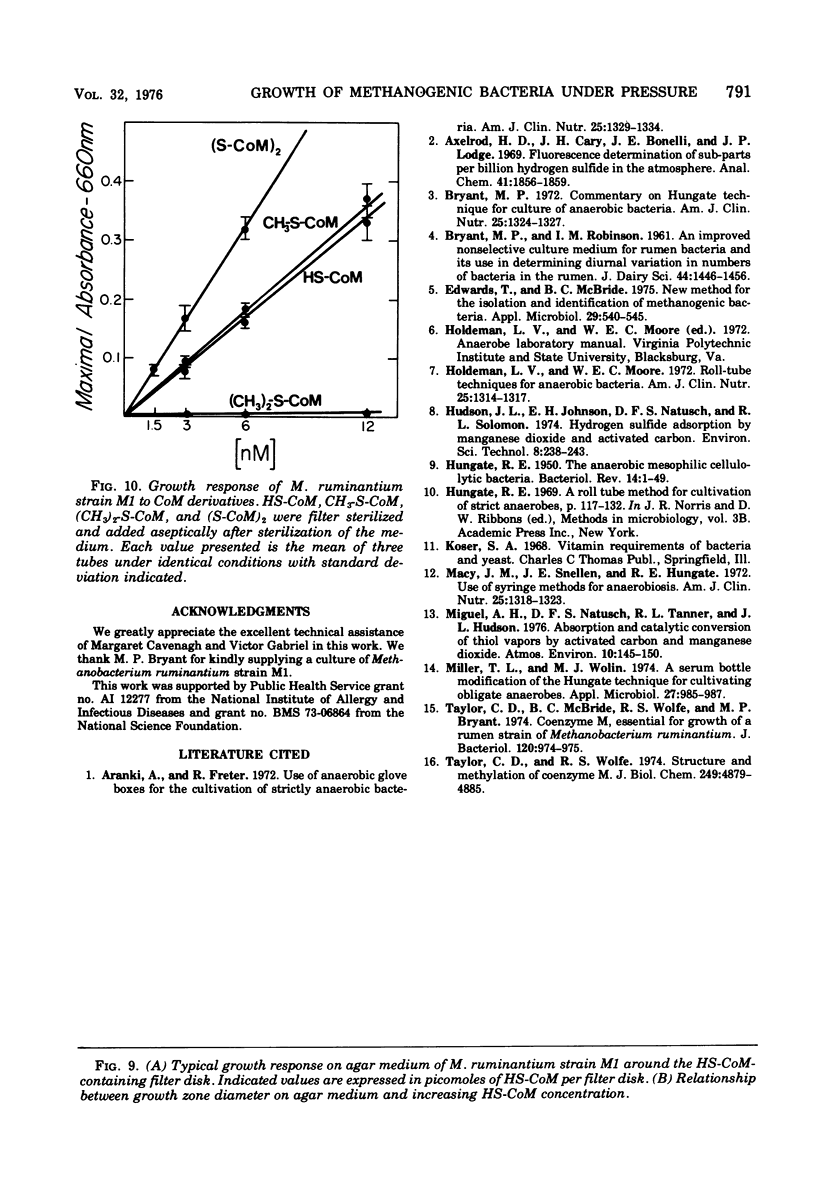
The sensitivity of the requirement of Methanobacterium ruminantium strain M1 to a new coenzyme, 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM) was examined by use of new techniques that were developed for rapid and efficient handling of large numbers of cultures of methanogenic bacteria. The system uses sealed tubes that contain a gas mixture of 80% hydrogen and 20% carbon dioxide under a pressure of 2 to 3 atm. This modification of the Hungate technique reduces variability among replicate cultures and simplifies the dispensing, sterilization, and storage of liquid media as well as the transfer and maintenance of methanogenic bacteria. Results indicate a limit of sensitivity of the assay at 5 nM HS-CoM, with half-maximal growth at 25 nM HS-CoM. Coenzyme activity could be replaced by 2,2'-dithiodiethanesulfonic acid at a half-molar equivalent of the HS-CoM concentration, or by 2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonic acid on an equimolar basis. These data reveal a very sensitive and precise requirement for HS-CoM in the nutrition of this fastidious anaerobe.
Full text
PDF

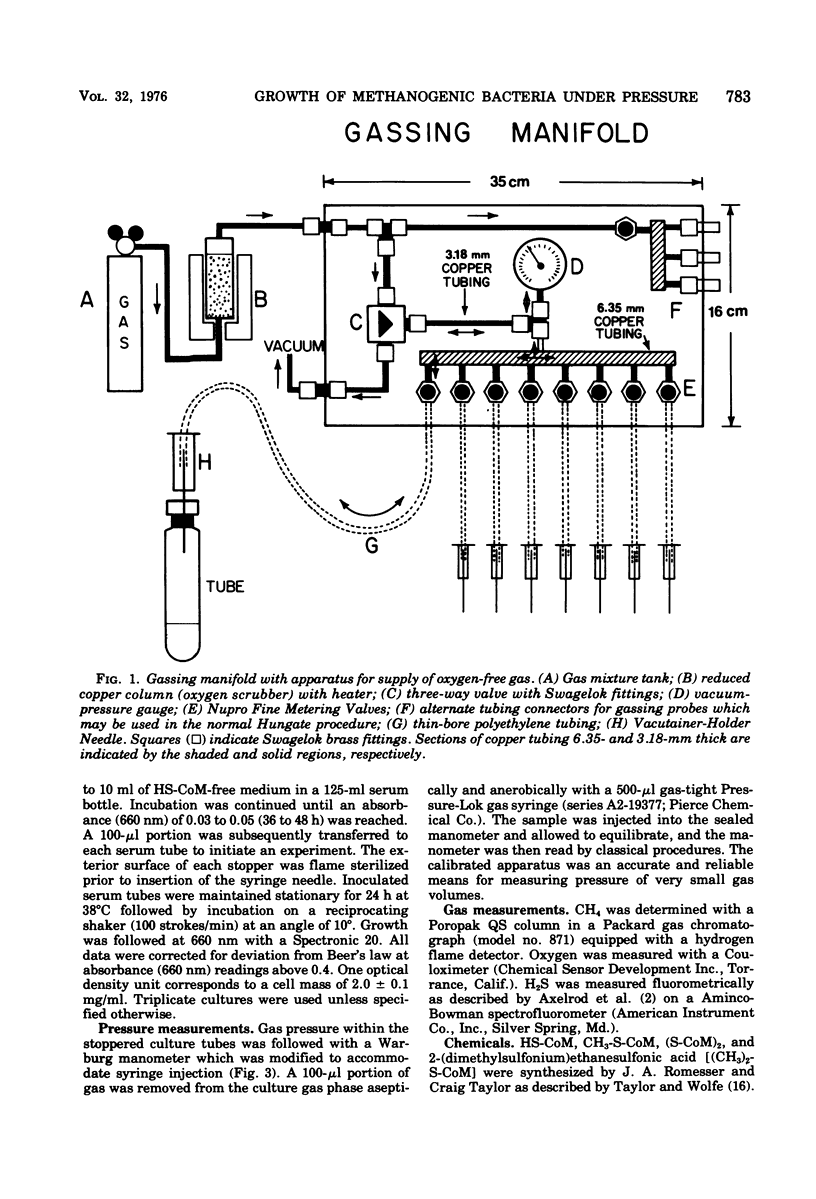


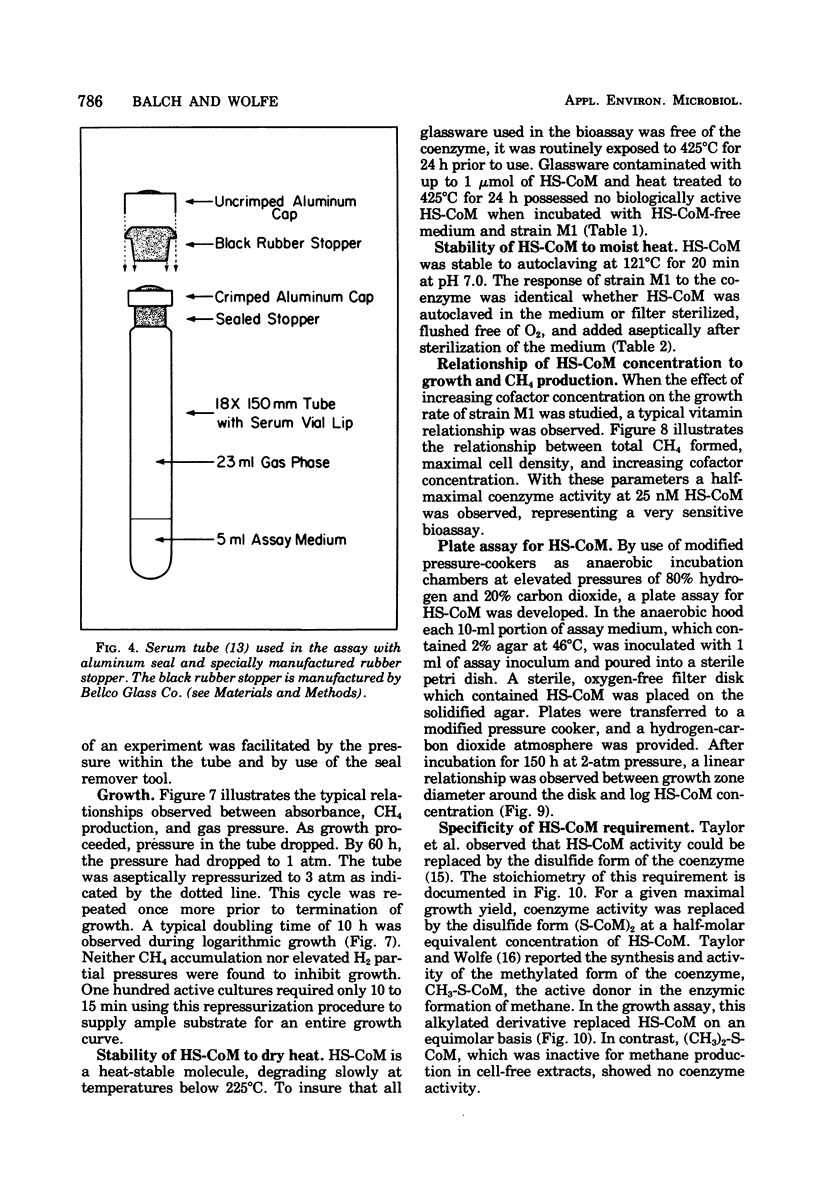

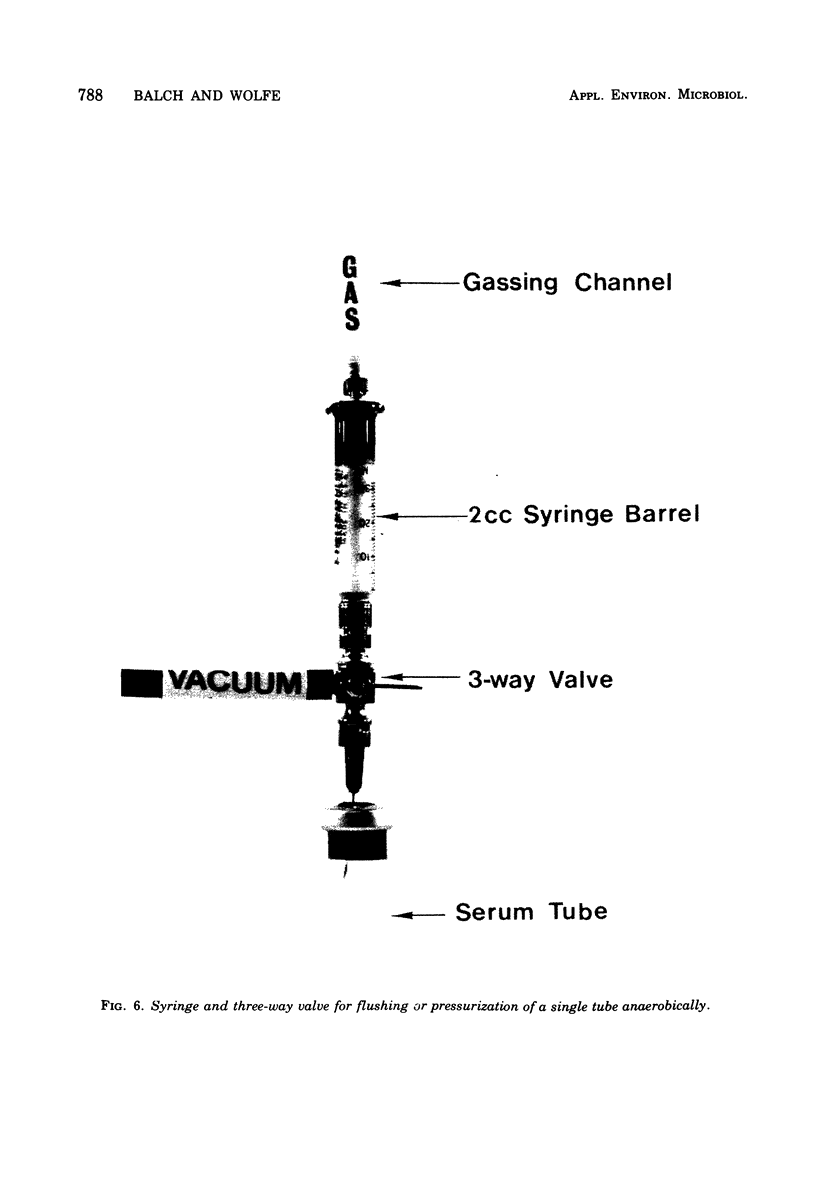
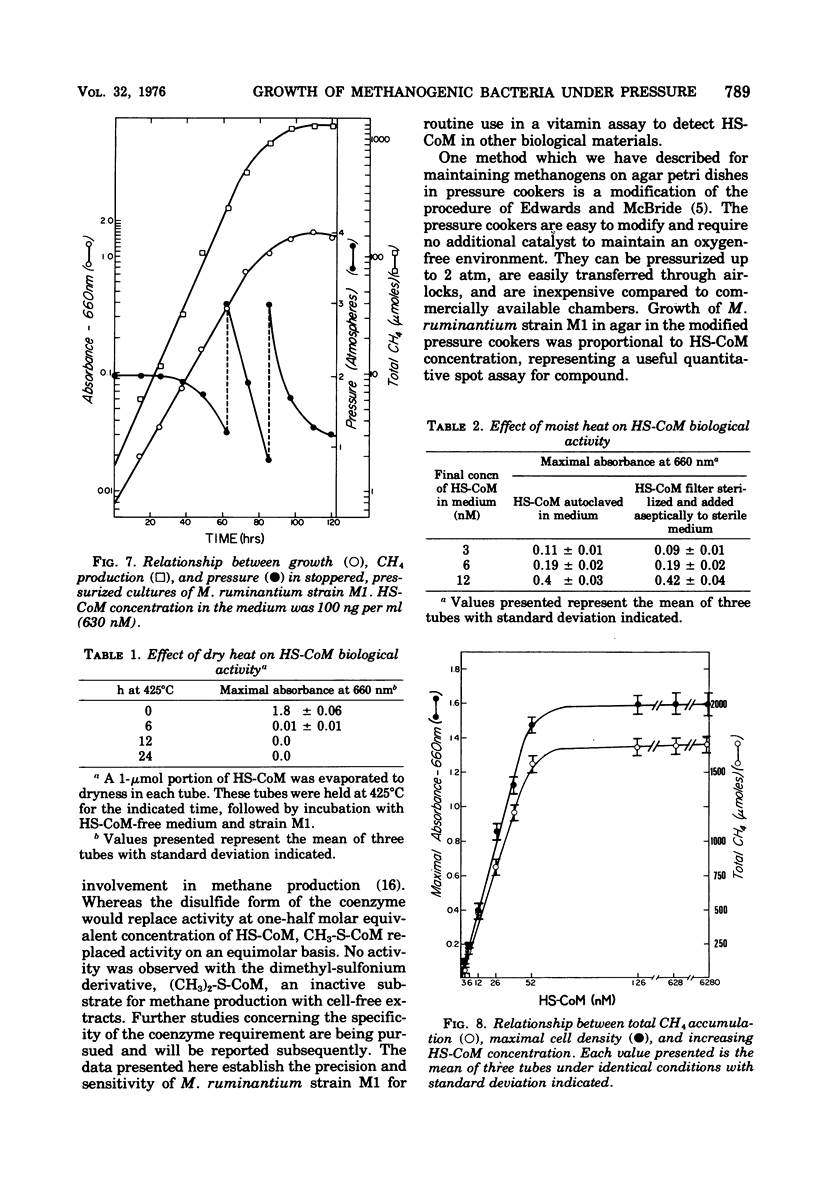
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod H. D., Cary J. H., Bonelli J. E., Lodge J. P., Jr Fluorescence determinatioof sub-parts per billion hydrogen sulfide in the atmosphere. Anal Chem. 1969 Nov;41(13):1856–1858. doi: 10.1021/ac60282a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards T., McBride B. C. New method for the isolation and identification of methanogenic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):540–545. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.540-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Roll-tube techniques for anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1314–1317. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J. M., Snellen J. E., Hungate R. E. Use of syringe methods for anaerobiosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1318–1323. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. L., Wolin M. J. A serum bottle modification of the Hungate technique for cultivating obligate anaerobes. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):985–987. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.985-987.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S., Bryant M. P. Coenzyme M, essential for growth of a rumen strain of Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):974–975. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.974-975.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]