Abstract
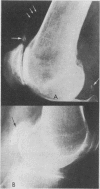
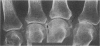
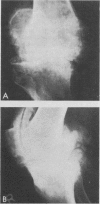
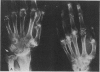
Pseudogout, defined as recurrent acute arthritis due to intrasynovial deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals, is a relatively common arthritic disorder of the elderly. The clinical and roentgenographic aspects of 50 cases of pseudogout in hospitalized patients are reviewed in this paper. Oligoarticular and polyarticular episodes were observed in half of these patients. Antecedent problems included infection, trauma, surgery and vascular events. Consistent with previous reports, most patients had roentgenographic evidence of chondrocalcinosis. A third had asymptomatic capsular or periarticular calcific deposits or both, and a third had pyrophosphate arthropathy, a progressive, destructive, accelerated form of osteoarthritis. An attack of pseudogout may offer a clue to the presence of an unsuspected metabolic disease, such as primary hyperparathyroidism or idiopathic hemochromatosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angevine C. D., Jacox R. F. Pseudogout in the elderly. Arch Intern Med. 1973 May;131(5):693–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins C. J., McIvor J., Smith P. M., Hamilton E., Williams R. Chondrocalcinosis and arthropathy: studies in haemochromatosis and in idiopathic chondrocalcinosis. Q J Med. 1970 Jan;39(153):71–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelle A., Sundén G. Pyrophosphate arthropathy: a clinical study of fifty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1974 May;56(2):246–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey H. L., Key J. J., Mason R. M., Swettenham K. V. Significance of radiological calcification of joint cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Jul;25(4):295–306. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.4.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currey H. L. Pyrophosphate arthropathy and calcific periarthris. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970;71:70–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dymock I. W., Hamilton E. B., Laws J. W., Williams R. Arthropathy of haemochromatosis. Clinical and radiological analysis of 63 patients with iron overload. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Sep;29(5):469–476. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman M. H., Krieger M. I., Brown N. Pseudogout mimicking synovial chondromatosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Sep;57(6):863–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman M. H., Levin B. Chondrocalcinosis in elderly persons. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jan-Feb;18(1):43–47. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fam A. G., Pritzker K. P., Stein J. L., Houpt J. B., Little A. H. Apatite-associated arthropathy: a clinical study of 14 cases and of 2 patients with calcific bursitis. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jul-Aug;6(4):461–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genant H. K. Roentgenographic aspects of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (pseudogout). Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):307–328. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<307::aid-art1780190705>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster J. C., Baud C. A., Lagier R., Boussina I., Fallet G. H. Tendon calcifications in chondrocalcinosis. A clinical, radiologic, histologic, and crystallographic study. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Mar;20(2):717–722. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster J. C., Vischer T. L., Fallet G. H. Destructive arthropathy in generalized osteoarthritis with articular chondrocalcinosis. J Rheumatol. 1975 Sep;2(3):265–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame R., Sutor D. J., Mitchener M. B. Crystal deposition in hyperparathyroidism. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Nov;30(6):597–604. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.6.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton E. B. Diseases associated with CPPD deposition disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):353–357. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<353::aid-art1780190708>3.0.co;2-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. S., Putman C. E. Current concepts with respect to chondrocalcinosis and the pseudogout syndrome. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1975 Mar;123(3):531–539. doi: 10.2214/ajr.123.3.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLGREN J. H., MOORE R. Generalized osteoarthritis and Heberden's nodes. Br Med J. 1952 Jan 26;1(4751):181–187. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4751.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagier R. Femoral cortical erosions and osteoarthrosis of the knee with chondrocalcinosis. An anatomo-radiological study of two cases. Fortschr Geb Rontgenstr Nuklearmed. 1974 Apr;120(4):460–467. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1229836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTY D. J., Jr, HASKIN M. E. THE ROENTGENOGRAPHIC ASPECTS OF PSEUDOGOUT (ARTICULAR CHONDROCALCINOSIS). AN ANALYSIS OF 20 CASES. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1963 Dec;90:1248–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCarty D. J., Jr, Silcox D. C. Gout and pseudogout. Geriatrics. 1973 Jun;28(6):110–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martel W., Champion C. K., Thompson G. R., Carter T. L. A roentgenologically distinctive arthropathy in some patients with the pseudogout syndrome. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1970 Jul;109(3):587–605. doi: 10.2214/ajr.109.3.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarty D. J. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease--1975. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):275–285. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<275::aid-art1780190702>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes C. J., Simon F., Chouraki M., Ecoffet M., Amor B., Delbarre F. Les arthropathies destructrices de la chondrocalcinose. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1973 Feb;40(2):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes C. J., Simon F., Delrieu F., Forest M., Delbarre F. Destructive arthropathy in chondrocalcinosis articularis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):329–348. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<329::aid-art1780190706>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor R. L. The arthroscope in the management of crystal-induced synovitis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973 Oct;55(7):1443–1449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps P., Steele A. D., McCarty D. J., Jr Compensated polarized light microscopy. Identification of crystals in synovial fluids from gout and pseudogout. JAMA. 1968 Feb 12;203(7):508–512. doi: 10.1001/jama.203.7.508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reginato A., Valenzuela F., Martinéz V., Passano G., Daza S. Polyarticular and familial chondrocalcinosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 May-Jun;13(3):197–213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Niwayama G., Goergen T. G., Utsinger P. D., Shapiro R. F., Haselwood D. H., Wiesner K. B. Clinical, radiographic and pathologic abnormalities in calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease (CPPD): pseudogout. Radiology. 1977 Jan;122(1):1–15. doi: 10.1148/122.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick D., Utsinger P. D. The wrist arthropathy of "pseudogout" occurring with and without chondrocalcinosis. Radiology. 1974 Dec;113(3):633–641. doi: 10.1148/113.3.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M., Cohen A. S. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Jun;123(6):636–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey G. O., Huskisson E. C. Unusual presentations of pyrophosphate arthropathy. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):21–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.21-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. A., Miller L. M., Weber A. L., Krane S. M. Pseudogout. A diagnostic clue to hyperparathyroidism. Am J Surg. 1969 Apr;117(4):558–565. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Corrigan A. B., Robinson R. G. Haemochromatosis and "pseudogout". Med J Aust. 1972 Jul 1;2(1):24–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb J., Deodhar S., Lee P. Chronic destructive polyarthritis due to pyrophosphate crystal arthritis ("pseudogout" syndrome). Med J Aust. 1974 Aug 10;2(6):206–209. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb70706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZITNAN D., SIT'AJ S. Chondrocalcinosis articularis Section L Clinical and radiological study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1963 May;22:142–152. doi: 10.1136/ard.22.3.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitnan D., Sitaj S. Natural course of articular chondrocalcinosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):363–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Korst J. K., Geerards J., Driessens F. C. A hereditary type of idiopathic articular chondrocalcinosis. Survey of a pedigree. Am J Med. 1974 Mar;56(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(74)90612-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]