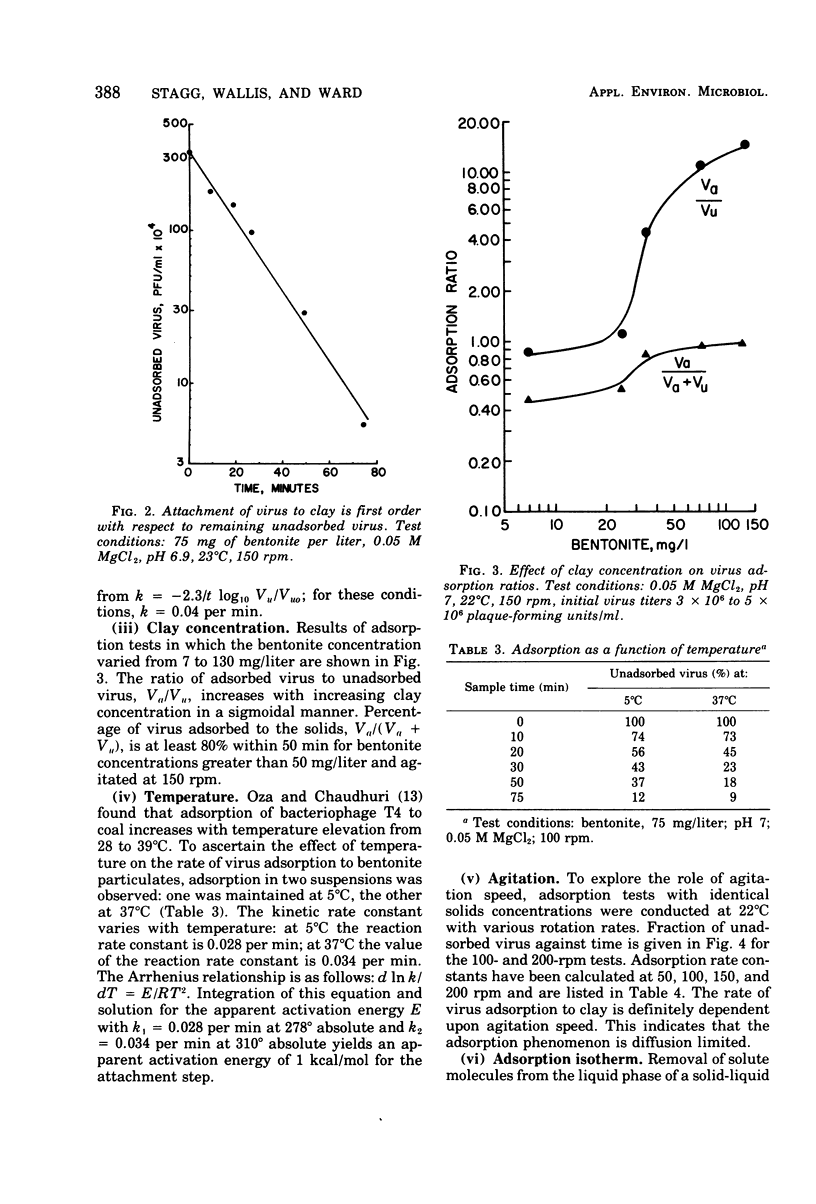
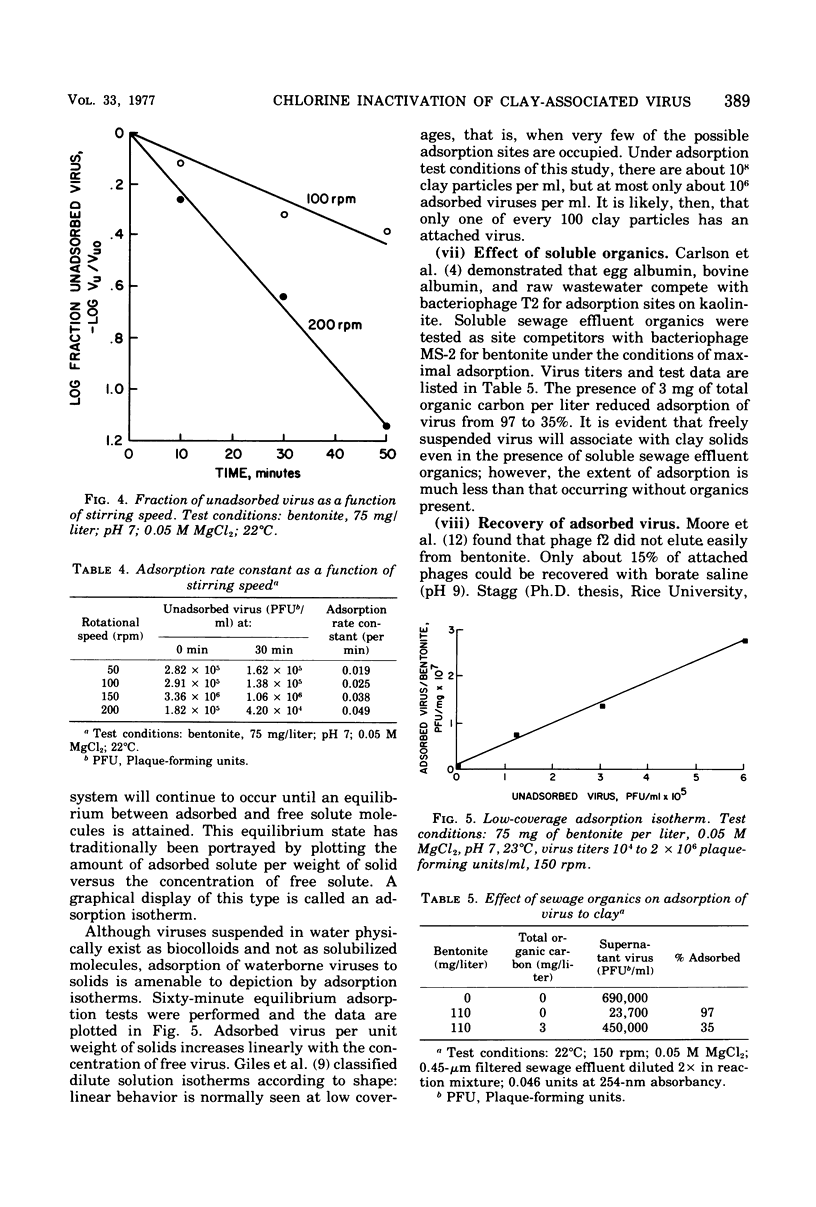
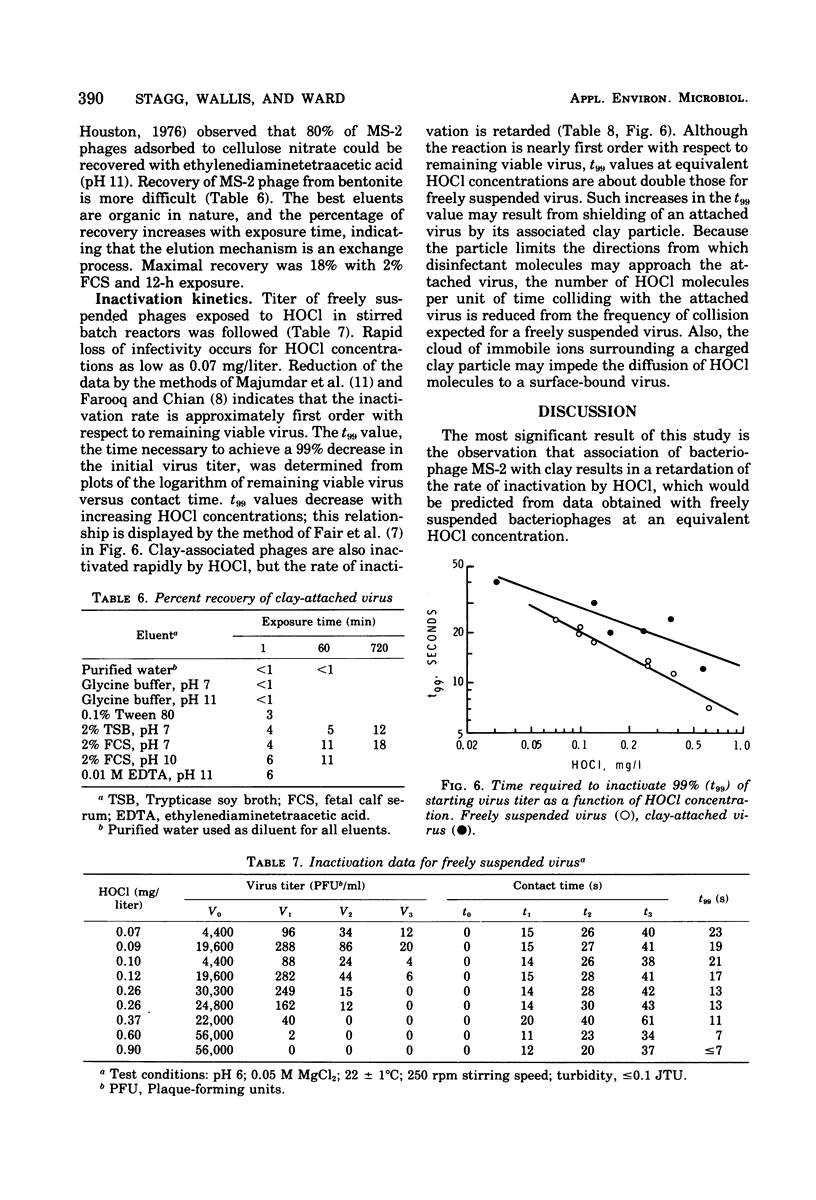
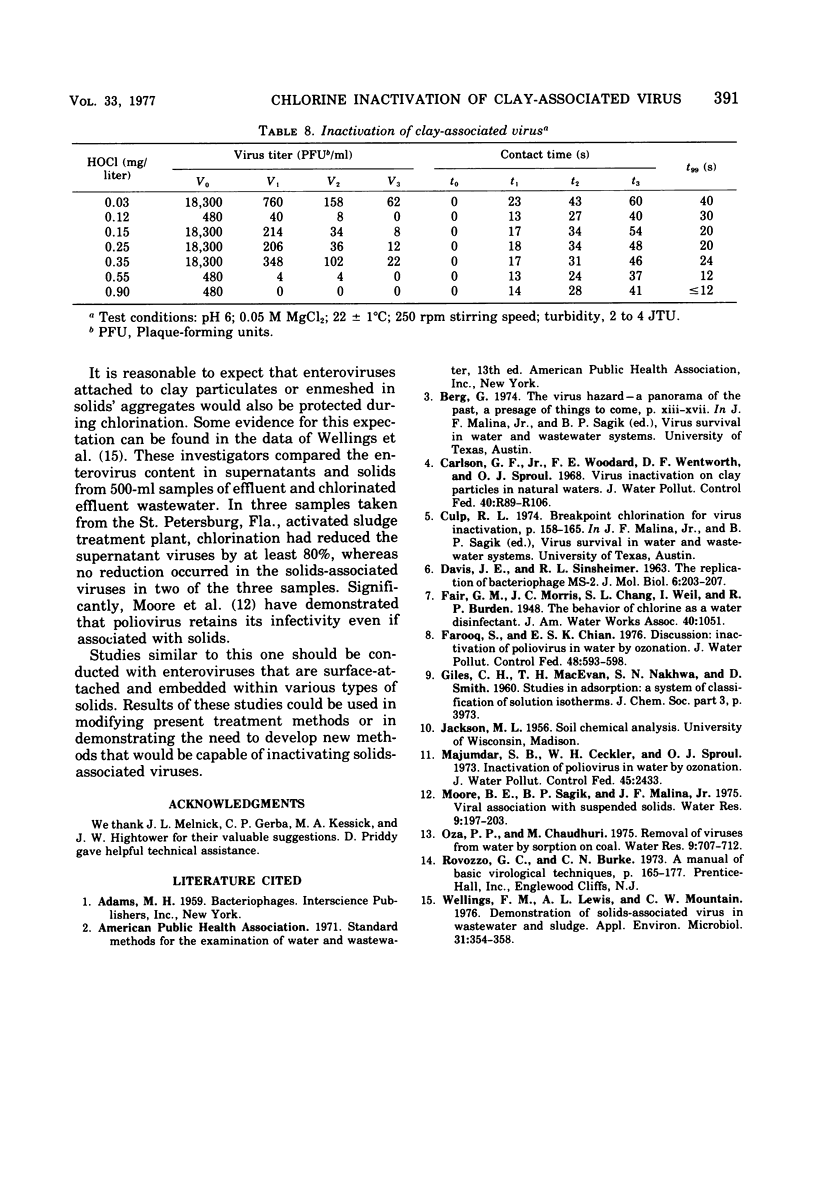
Abstract
The model system consisted of bacteriophage MS-2, bentonite clay, and hypochlorous acid (HOC1). Factors that influenced association of the bacterial virus with bentonite were the titer of unadsorbed viruses, clay concentration, cation concentration, temperature, stirring rate, and the presence of soluble organics. Variation of the kinetic adsorption rate constant with stirring speed indicates that phage attachment is a diffusion-limited process; the attachment reaction has an apparent activation energy of 1 kcal/mol. About 18% of clay-associated bacteriophages was recovered by mixing the suspension with an organic eluent. Inactivation data were obtained from batch reactors operated under those conditions in which loss of HOC1 was minimal during the reaction. Bacteriophages attached to clay were more resistant to HOC1 than were freely suspended phages; for equivalent HOC1 concentrations, clay-associated phages required about twice the time that freely suspended phages required for loss of 99% of the initial virus titer.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS J. E., SINSHEIMER R. L. The replication of bacteriophage MS2. 1. Transfer of parental nucleic acid to progeny phage. J Mol Biol. 1963 Mar;6:203–207. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(63)80069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farooq S., Chian E. S. Inactivation of poliovirus in water by ozonation. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1976 Mar;48(3 Pt 1):593–598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar S. B., Ceckler W. H., Sproul O. J. Inactivation of poliovirus in water by ozonation. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1973 Dec;45(12):2433–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W. Demonstration of solids-associated virus in wastewater and sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):354–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.354-358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


