Abstract
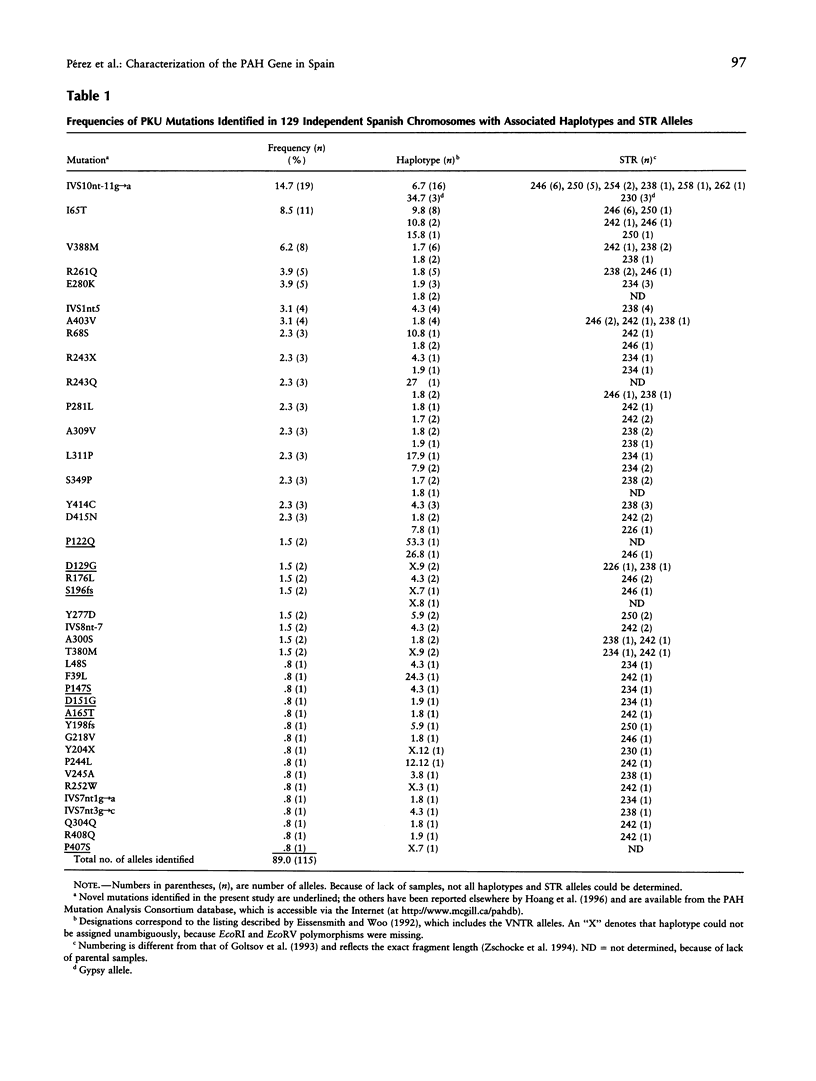
The aim of this study was to characterize the phenylketonuria (PKU) alleles in the Spanish population, by both identifying the causative mutations and analyzing the RFLP haplotypes and the VNTR and short-tandem-repeat alleles associated with the phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) gene. We have investigated 129 independent mutant chromosomes, using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) and direct sequencing. Ninety percent of the alleles were identified, and a total of 40 different mutations were detected. The mutational spectrum includes seven previously unreported mutations: P122Q, D129G, P147S, D151G, A165T, S196fs, and P407S. Seven mutations represent 43% of the Spanish PKU alleles, the most common being IVS10nt-11g-->a (14.7%), I65T (8.5%), and V388M (6.2%). The remaining 33 mutations are rare. The mutation profile and relative frequencies are markedly different from those in northern Europe, also showing unique features compared with those in other, southern European populations. The association analysis with polymorphic markers in the PAH gene provides valuable information for population-genetic studies and investigation of the origins of the mutations. This study may serve as reference in the analysis of the contemporary distributions and frequencies of the PKU mutations in related populations, with particular relevance in Latin American countries.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper D. N., Youssoufian H. The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00278187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darvasi A., Kerem B. Deletion and insertion mutations in short tandem repeats in the coding regions of human genes. Eur J Hum Genet. 1995;3(1):14–20. doi: 10.1159/000472269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desviat L. R., Pérez B., De Lucca M., Cornejo V., Schmidt B., Ugarte M. Evidence in Latin America of recurrence of V388M, a phenylketonuria mutation with high in vitro residual activity. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Aug;57(2):337–342. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desviat L. R., Pérez B., Ugarte M. Phenylketonuria in Spain: RFLP haplotypes and linked mutations. Hum Genet. 1993 Oct 1;92(3):254–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00244468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworniczak B., Aulehla-Scholz C., Kalaydjieva L., Bartholomé K., Grudda K., Horst J. Aberrant splicing of phenylalanine hydroxylase mRNA: the major cause for phenylketonuria in parts of southern Europe. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):242–246. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisensmith R. C., Woo S. L. Updated listing of haplotypes at the human phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;51(6):1445–1448. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goltsov A. A., Eisensmith R. C., Konecki D. S., Lichter-Konecki U., Woo S. L. Associations between mutations and a VNTR in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Sep;51(3):627–636. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goltsov A. A., Eisensmith R. C., Naughton E. R., Jin L., Chakraborty R., Woo S. L. A single polymorphic STR system in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene permits rapid prenatal diagnosis and carrier screening for phenylketonuria. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 May;2(5):577–581. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.5.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg P., Güttler F. 'Broad-range' DGGE for single-step mutation scanning of entire genes: application to human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 11;22(5):880–881. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.5.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg P., Henriksen K. F., Güttler F. Molecular analysis of phenylketonuria in Denmark: 99% of the mutations detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Genomics. 1993 Jul;17(1):141–146. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg P., Romano V., Ceratto N., Bosco P., Ciuna M., Indelicato A., Mollica F., Meli C., Giovannini M., Riva E. Mutational spectrum of phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency in Sicily: implications for diagnosis of hyperphenylalaninemia in southern Europe. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Oct;2(10):1703–1707. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.10.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güttler F., Guldberg P., Henriksen K. F., Mikkelsen I., Olsen B., Lou H. Molecular basis for the phenotypical diversity of phenylketonuria and related hyperphenylalaninaemias. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1993;16(3):602–604. doi: 10.1007/BF00711693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoang L., Byck S., Prevost L., Scriver C. R. PAH Mutation Analysis Consortium Database: a database for disease-producing and other allelic variation at the human PAH locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jan 1;24(1):127–131. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Royle N. J., Wilson V., Wong Z. Spontaneous mutation rates to new length alleles at tandem-repetitive hypervariable loci in human DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):278–281. doi: 10.1038/332278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S. W., Weitzner G., Rozen R., Scriver C. R. A rapid procedure for extracting genomic DNA from leukocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):408–408. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman S., Schwartz G., Woo S. L., Shiloh Y. A 22-bp deletion in the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene causing phenylketonuria in an Arab family. Hum Mutat. 1992;1(4):344–346. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Wang Y., Trefz F. K., Lichter-Konecki U., Woo S. L. Structural characterization of the 5' regions of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 8;31(35):8363–8368. doi: 10.1021/bi00150a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwok S. C., Ledley F. D., DiLella A. G., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Nucleotide sequence of a full-length complementary DNA clone and amino acid sequence of human phenylalanine hydroxylase. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):556–561. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leandro P., Rivera I., Ribeiro V., de Almeida I. T., da Silveira C., Lechner M. C. Mutation analysis of phenylketonuria in south and central Portugal: prevalence of V388M mutation. Hum Mutat. 1995;6(2):192–194. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380060217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichter-Konecki U., Schlotter M., Konecki D. S. DNA sequence polymorphisms in exonic and intronic regions of the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene aid in the identification of alleles. Hum Genet. 1994 Sep;94(3):307–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00208290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez B., Desviat L. R., De Lucca M., Schmidt B., Loghin-Grosso N., Giugliani R., Pires R. F., Ugarte M. Mutation analysis of phenylketonuria in south Brazil. Hum Mutat. 1996;8(3):262–264. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1004(1996)8:3<262::AID-HUMU10>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez B., Desviat L. R., De Lucca M., Ugarte M. Spectrum and origin of phenylketonuria mutations in Spain. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994 Dec;407:34–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13444.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez B., Desviat L. R., Díe M., Cornejo V., Chamoles N. A., Nicolini H., Ugarte M. Presence of the Mediterranean PKU mutation IVS10 in Latin America. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Aug;2(8):1289–1290. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.8.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramus S. J., Treacy E. P., Cotton R. G. Characterization of phenylalanine hydroxylase alleles in untreated phenylketonuria patients from Victoria, Australia: origin of alleles and haplotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 May;56(5):1034–1041. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos M., Kuzmin A. I., Eisensmith R. C., Goltsov A. A., Woo S. L., Barrantes R., de Céspedes C. Phenylketonuria in Costa Rica: preliminary spectrum of PAH mutations and their associations with highly polymorphic haplotypes. Hum Hered. 1996 May-Jun;46(3):128–131. doi: 10.1159/000154340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treacy E., Byck S., Clow C., Scriver C. R. 'Celtic' phenylketonuria chromosomes found? Evidence in two regions of Quebec Province. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(3):220–228. doi: 10.1159/000472415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugarte M., Maties M., Ugarte J. L. The offspring of a phenylketonuric couple. J Ment Defic Res. 1980 Jun;24(2):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.1980.tb00065.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschocke J., Graham C. A., Carson D. J., Nevin N. C. Phenylketonuria mutation analysis in Northern Ireland: a rapid stepwise approach. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Dec;57(6):1311–1317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zschocke J., Graham C. A., McKnight J. J., Nevin N. C. The STR system in the human phenylalanine hydroxylase gene: true fragment length obtained with fluorescent labelled PCR primers. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1994 Dec;407:41–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1994.tb13447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


