Abstract
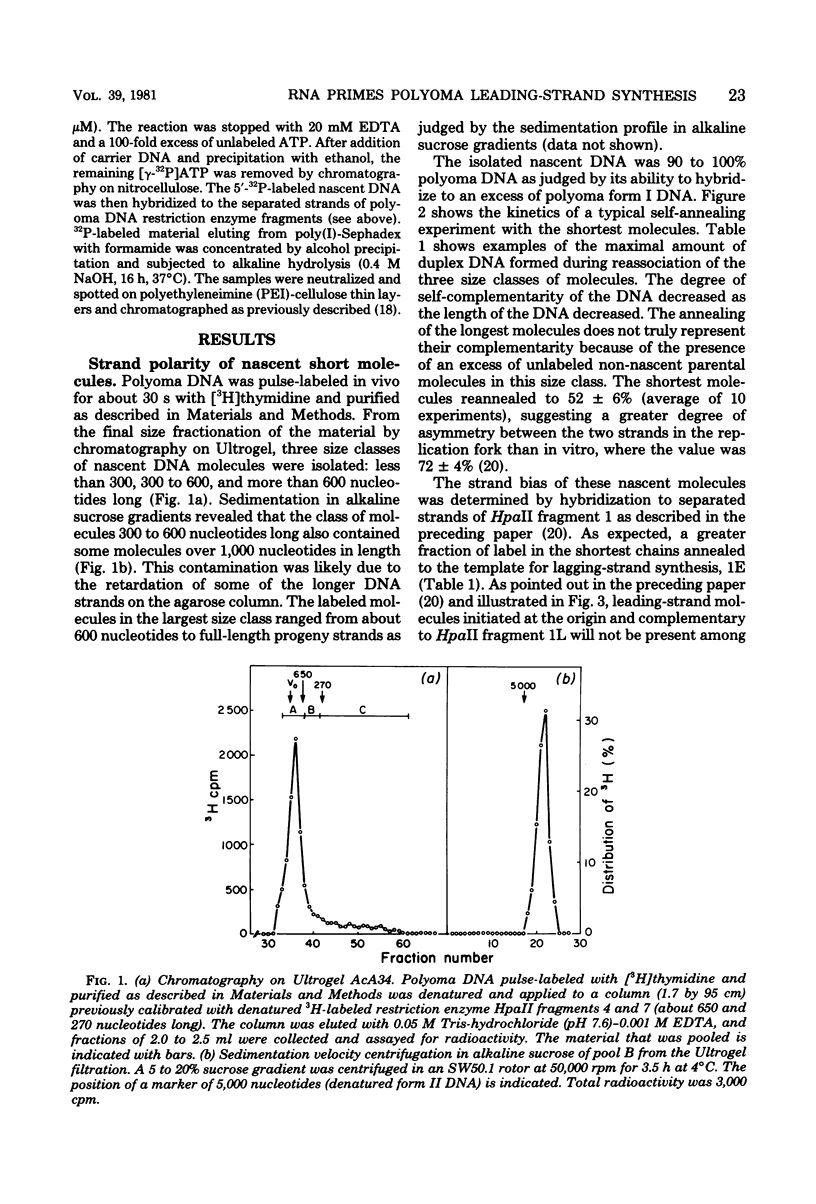
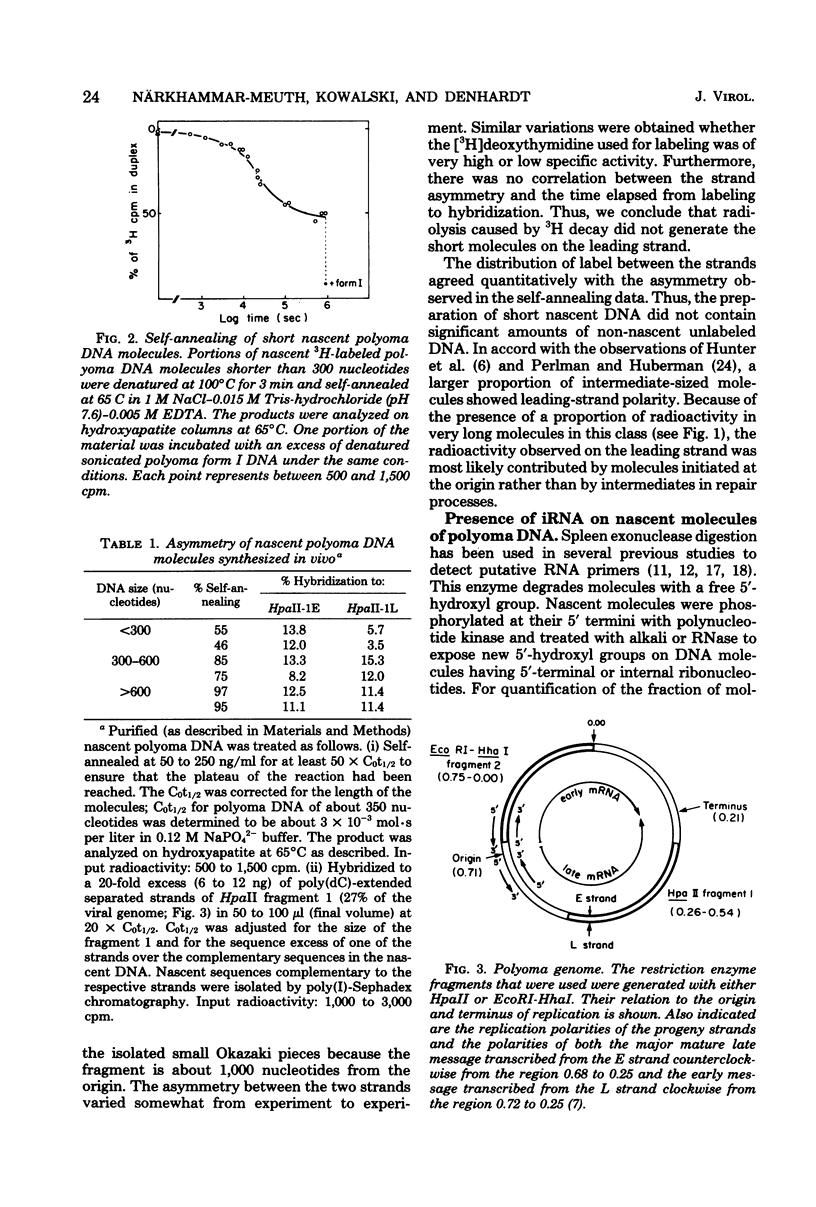
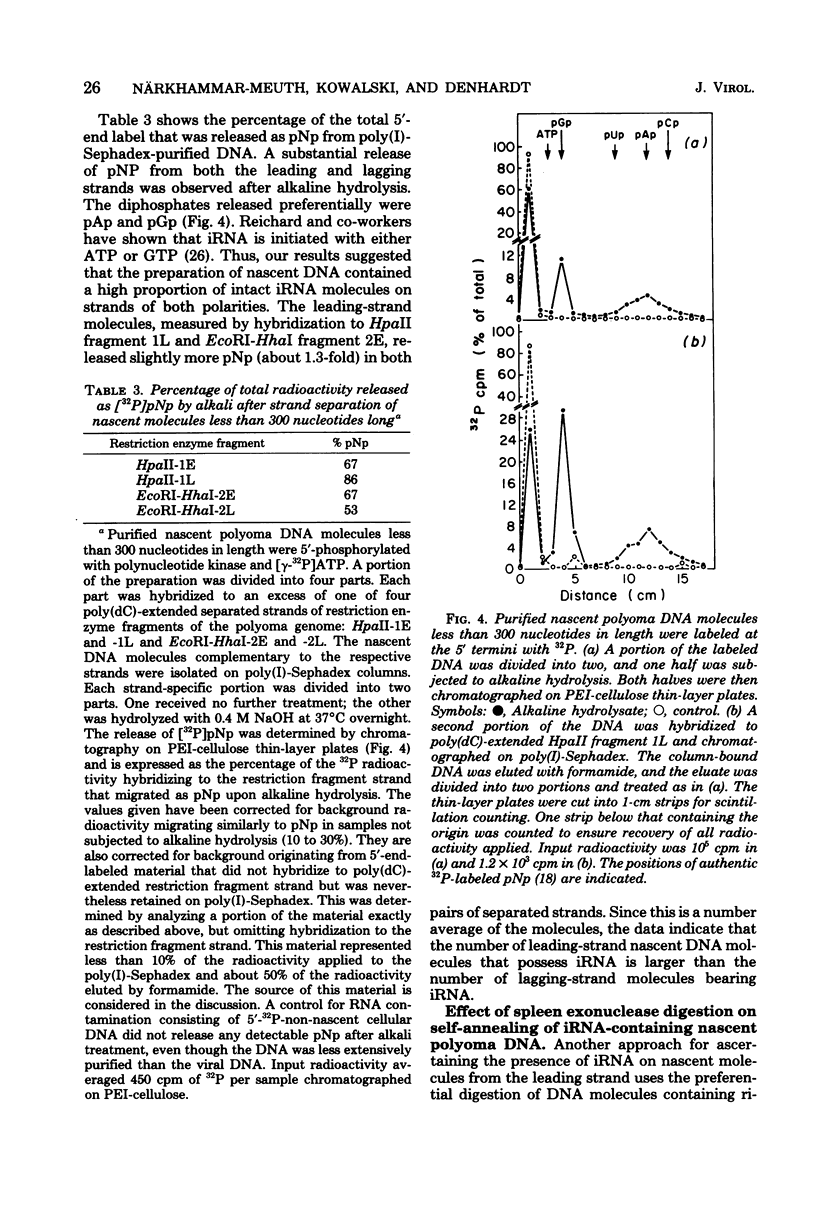
Nascent polyoma DNA molecules were isolated after pulse-labeling of infected murine 3T6 cells with [3H]thymidine. The extent of digestion of these DNA molecules by spleen exonuclease was increased by exposure to alkali or RNase, suggesting that ribonucleotides were present at or near the 5' terminal of the newly synthesized pieces of DNA. Intermediates shorter than 300 nucleotides were hybridized to the separated strands of restriction enzyme fragments of the polyoma genome: 2.5 to 3-fold more radioactivity was found in the strand whose synthesis is necessarily discontinuous (the lagging strand) than in the strand whose synthesis is potentially continuous (the leading strand) than in the strand whose synthesis is potentially continuous (the leading strand). Separation of the strands of [5'-32P]DNA molecules showed that the excess [3H]thymidine in lagging-strand molecules was not simply the result of an increased number of molecules. Therefore, assuming equivalent efficiencies of labeling, lagging-strand pieces must be slightly longer than those with leading-strand polarity. The presence of ribonucleotides on the 5' termini of molecules with both leading- and lagging-strand polarity was demonstrated by (i) release of 32P-ribonucleoside diphosphates upon alkaline hydrolysis of [5'-32P]DNA separated according to replication polarity and (ii) the change in the degree of self-annealing of nascent molecules upon preferential degradation of DNA molecules possessing initiator RNA moieties by spleen exonuclease. We conclude that replication of polyoma DNA in vivo occurs discontinuously on both sides of the growing fork, using RNA as the major priming mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernardi A., Bernardi G. Studies on acid hydrolases. IV. Isolation and characterization of spleen exonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):360–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliasson R., Reichard P. Replication of polyoma DNA in isolated nuclei. Synthesis and distribution of initiator RNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7469–7475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flory P. J., Jr Strandedness of newly synthesized short pieces of polyoma DNA from isolated nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1449–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi J. R., Clarkson J. M. Discontinuous DNA replication in mouse P-815 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jan 2;50(2):403–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb09816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Chappell J. B. A simple method for the preparation of 32-P-labelled adenosine triphosphate of high specific activity. Biochem J. 1964 Jan;90(1):147–149. doi: 10.1042/bj0900147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Francke B., Bacheler L. In vitro polyoma DNA synthesis: asymmetry of short DNA chains. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1021–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90166-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Sedat J., Ziff E. Orientation of the complementary strands of polyoma virus DNA with respect to the DNA physical map. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):212–218. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.212-218.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann G., Bar-Shavit R., DePamphilis M. L. Okazaki pieces grow opposite to the replication fork direction during simian virus 40 DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jul;5(7):2535–2545. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.7.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kit S., Dubbs D. R., Frearson P. M. Enzymes of nucleic acid metabolism in cells infected with polyoma virus. Cancer Res. 1966 Apr;26(4):638–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski J., Denhardt D. T. Ribonucleotides in DNA newly synthesised in 3T6 cells in vivo. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):704–706. doi: 10.1038/281704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Ogawa T., Hirose S., Okazaki T., Okazaki R. Mechanism of DNA chain growth. XV. RNA-linked nascent DNA pieces in Escherichia coli strains assayed with spleen exonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1975 Aug 25;96(4):653–664. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurosawa Y., Okazaki R. Mechanism of DNA chain growth. XIII. Evidence for discontinuous replication of both strands of P2 phage DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 15;94(2):229–241. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev Z., Kamen R., Manor H. Topography of polyoma virus-specific giant nuclear RNA molecules containing poly(A) sequences. Virology. 1979 Mar;93(2):445–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90248-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida Y., Okazaki T., Okazaki R. Discontinuous replication of replicative form DNA from bacteriophage phiX174. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2776–2779. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Nilsson M. G. Replication of polyoma DNA in isolated nuclei: analysis of replication fork movement. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):386–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.386-393.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson G., Winnacker E. L., Eliasson R., Reichard P. Replication of polyoma DNA in isolated nuclei. II. Evidence for semi-conservative replication. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):539–552. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes M., Denhardt D. T. The mechanism of replication of phi x174 DNA. XVI. Evidence that the phi x174 viral strand is synthesized discontinuously. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jan 5;136(1):45–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90365-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Denhardt D. T. Evidence for the presence of ribonucleotides at the 5' termini of some DNA molecules isolated from Escherichia coli polAex2. J Mol Biol. 1977 Nov;116(4):681–707. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson S., Reichard P., Skoog L. Deoxyuridine triphosphate pools after polyoma virus infection. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9552–9555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Närkhammar-Meuth M., Eliasson R., Magnusson G. Discontinuous synthesis of both strands at the growing fork during polyoma DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.11-20.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Närkhammar M., Magnusson G. DNA polymerase activities induced by polyoma virus infection of 3T3 mouse fibroblasts. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.1-6.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Kurosawa Y., Ogawa T., Seki T., Shinozaki K., Hirose S., Fujiyama A., Kohara Y., Machida Y., Tamanoid F. Structure and metabolism of the RNA primer in the discontinuous replication of prokaryotic DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):203–219. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman D., Huberman J. A. Asymmetric Okazaki piece synthesis during replication of simian virus 40 DNA in vivo. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1029–1043. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90167-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZZELL W. E., KHORANA H. G. Studies on polynucleotides. X. Enzymic degradation. Some properties and mode of action of spleen phosphodiesterase. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1144–1149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P., Eliasson R., Söderman G. Initiator RNA in discontinuous polyoma DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4901–4905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng B. Y., Goulian M. DNA synthesis in human lymphocyts: intermediates in DNA synthesis, in vitro and in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 5;99(2):317–337. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80149-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Live T. R., Richardson C. C. Enzymatic breakage and joining of deoxyribonucleic acid. V. End group labeling and analysis of deoxyribonucleic acid containing single straned breaks. J Biol Chem. 1968 Sep 10;243(17):4530–4542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winnacker E. L., Magnusson G., Reichard P. Replication of polyoma DNA in isolated nuclei. I. Characterization of the system from mouse fibroblast 3T6 cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):523–537. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90172-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


