Abstract
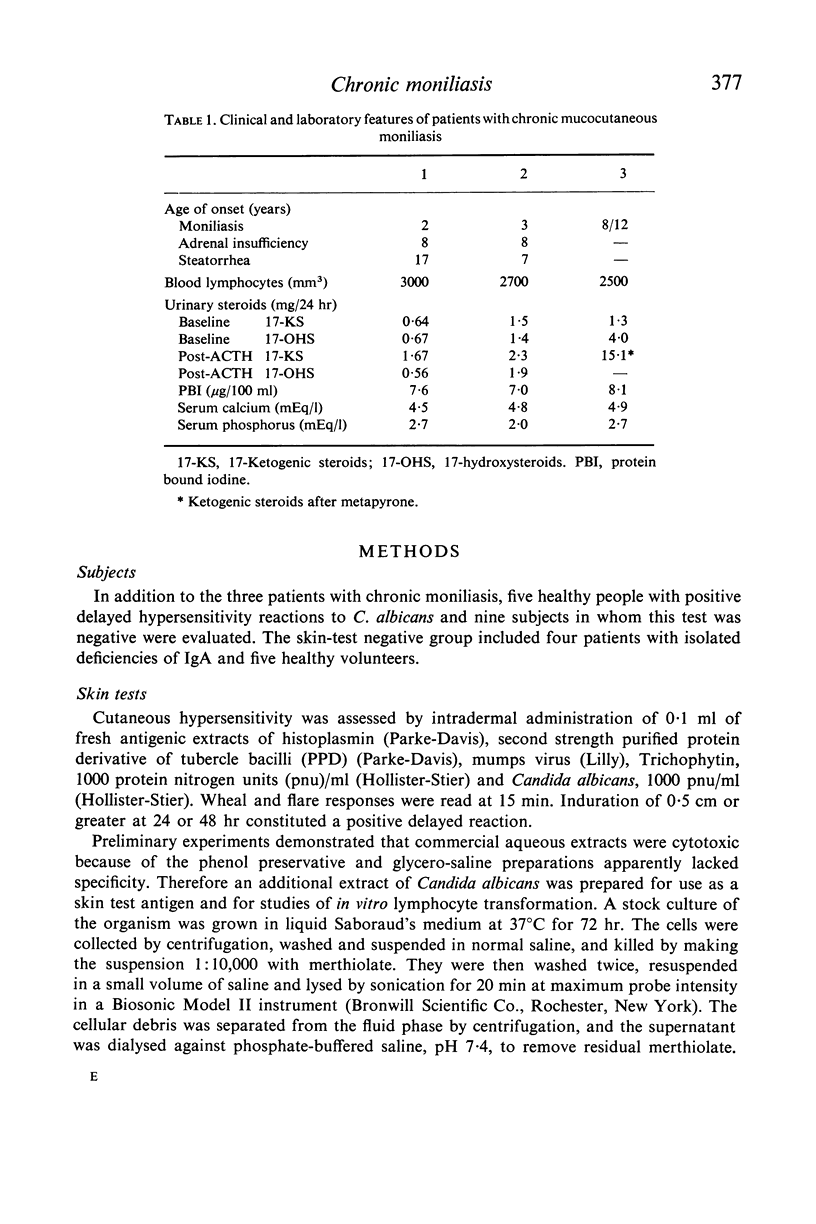
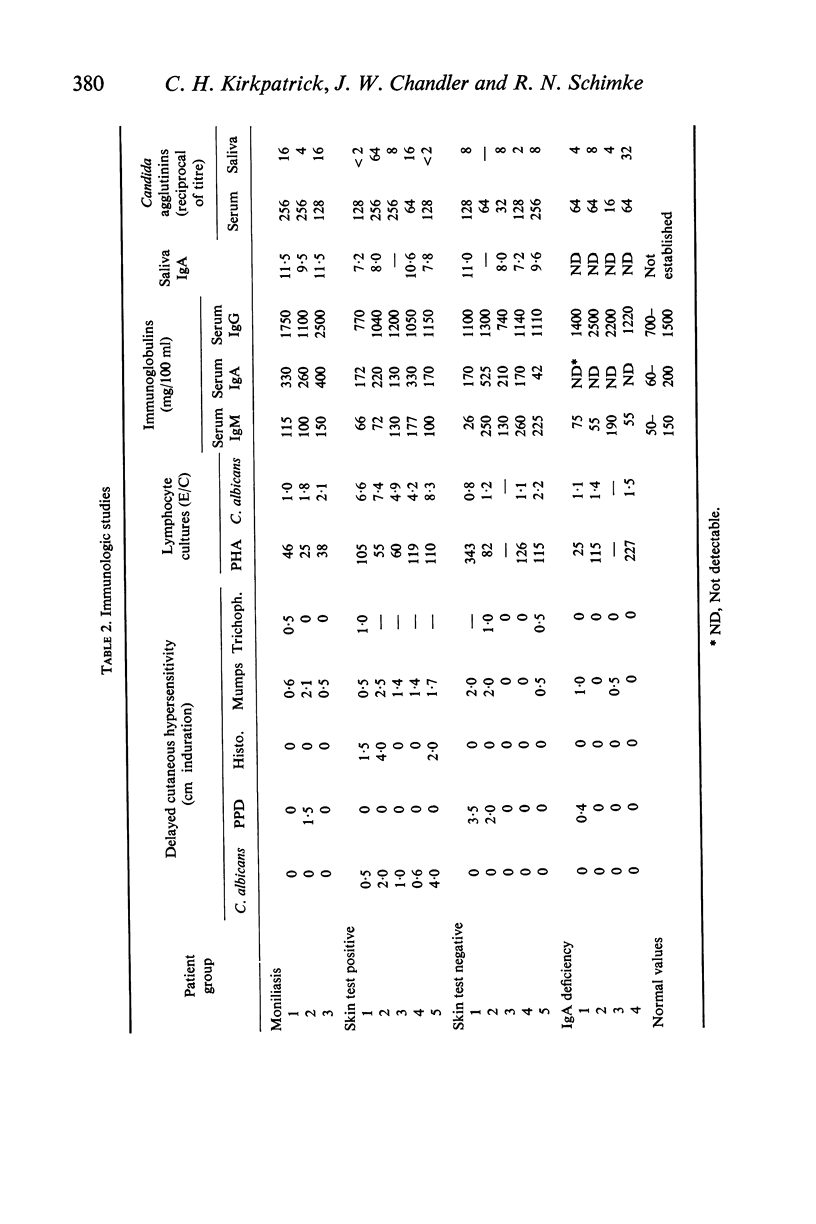
Three patients, including two brothers, with chronic mucocutaneous moniliasis and endocrinopathy were evaluated from an immunological viewpoint. Each patient had defective delayed hypersensitivity to Candida albicans as manifested by a negative skin test and absent lymphocyte response after in vitro exposure to the antigen. Cutaneous responses to other antigens were intact, and there were no demonstrable abnormalities in humoral immunity. In one case, the in vitro lymphocyte response was restored following an injection of a leucocyte extract from a skin test positive subject, although the cutaneous lesions remained unchanged.
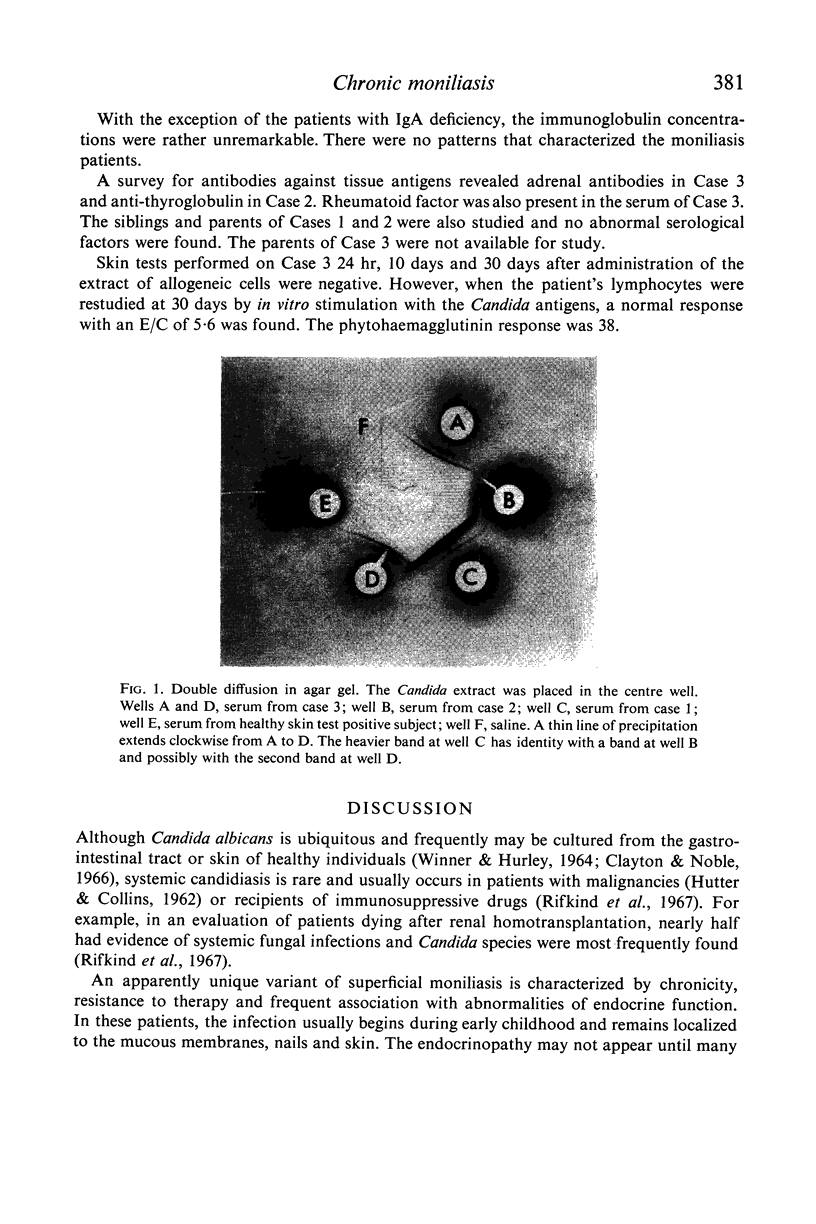
It is possible that cells of both the endocrine and lymphoid systems share a defect in synthesis and release of their respective humoral products. In the case of lymphoid cells, the defect would be limited to populations of cells participating in delayed hypersensitivity, and impair production of mediators such as macrophage migration inhibiting factor, lymphotoxin, etc., while sparing the processes of antibody synthesis. Alternatively, the selective failure in delayed hypersensitivity may result from defective lymphocyte differentiation or from loss of immune responsiveness through densensitization by chronic exposure to the fungal antigens.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blizzard R. M., Gibbs J. H. Candidiasis: studies pertaining to its association with endocrinopathies and pernicious anemia. Pediatrics. 1968 Aug;42(2):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Lucas Z. J., Hattler B. G., Jr, Zmijewski C. M., Amos D. B. Defective cellular immunity associated with chronic mucocutaneous moniliasis and recurrent staphylococcal botryomycosis: immunological reconstitution by allogeneic bone marrow. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Feb;3(2):153–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilgren R. A., Hong R., Quie P. G. Human serum interactions with Candida albicans. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):128–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilgren R. A., Quie P. G., Meuwissen H. J., Hong R. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, deficiency of delayed hypersensitivity, and selective local antibody defect. Lancet. 1967 Sep 30;2(7518):688–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90974-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton Y. M., Noble W. C. Observations on the epidemiology of Candida albicans. J Clin Pathol. 1966 Jan;19(1):76–78. doi: 10.1136/jcp.19.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland W. W., Fogel B. J., Brown W. T., Kay H. E. Foetal thymic transplant in a case of Digeorge's syndrome. Lancet. 1968 Dec 7;2(7580):1211–1214. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91694-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOBIAS B. SPECIFIC AND NONSPECIFIC IMMUNITY IN CANDIDA INFECTIONS. EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF CANDIDA CELL CONSTITUENTS AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE. Acta Med Scand. 1964;176:SUPPL 421–421:1+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Macrophage migration. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNG W., MIGEON C. J., PARROTT R. H. A POSSIBLE AUTOIMMUNE BASIS FOR ADDISON'S DISEASE IN THREE SIBLINGS, ONE WITH IDIOPATHIC HYPOPARATHYROIDISM, PERNICIOUS ANEMIA AND SUPERFICIAL MONILIASIS. N Engl J Med. 1963 Sep 26;269:658–663. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196309262691303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTER R. V., COLLINS H. S. The occurrence of opportunistic fungus infections in a cancer hospital. Lab Invest. 1962 Nov;11:1035–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENNY F. M., HOLLIDAY M. A. HYPOPARATHYROIDISM, MONILIASIS, ADDISON'S AND HASHIMOTO'S DISEASES. HYPERCALCEMIA TREATED WITH INTRAVENOUSLY ADMINISTERED SODIUM SULFATE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Oct 1;271:708–713. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196410012711404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIGMAN A. M. Hyposensitization against Rhus dermatitis. AMA Arch Derm. 1958 Jul;78(1):47–72. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1958.01560070051008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: characterization of human lymphotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1250–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer R., Say B., Brown D., Rosen F. S. Congenital aplasia of the thymus gland (DiGeorge's syndrome). N Engl J Med. 1968 Dec 12;279(24):1295–1301. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196812122792401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOURIA D. B., BRAYTON R. G. A SUBSTANCE IN BLOOD LETHAL FOR CANDIDA ALBICANS. Nature. 1964 Jan 18;201:309–309. doi: 10.1038/201309a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louria D. B., Shannon D., Johnson G., Caroline L., Okas A., Taschdjian C. The susceptibility to moniliasis in children with endocrine hypofunction. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1967;80:236–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmor M. F., Barnett E. V. Cutaneous anergy without systemic disease. A syndrome associated with mucocutaneous fungal infection. Am J Med. 1968 Jun;44(6):979–989. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill D., Hartley T. F., Claman H. N. Electroimmunodiffusion (EID): a simple, rapid method for quantitation of immunoglobulins in dilute biological fluids. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):151–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry W. M., Jr, Chandler J. W., Jr, Chin T. D., Kirkpatrick C. H. Immunology of the mycoses. I. Depressed lymphocyte transformation in chronic histoplasmosis. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):436–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind D., Marchioro T. L., Schneck S. A., Hill R. B., Jr Systemic fungal infections complicating renal transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy. Clinical, microbiologic, neurologic and pathologic features. Am J Med. 1967 Jul;43(1):28–38. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Dobkin G. B., Caroline L., Kozinn P. J. Immune studies relating to candidiasis. II. Experimental and preliminary clinical studies on antibody formation in systemic candidiasis. Sabouraudia. 1964 Feb;3(2):129–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschdjian C. L., Kozinn P. J., Okas A., Caroline L., Halle M. A. Serodiagnosis of systemic candidiasis. J Infect Dis. 1967 Apr;117(2):180–187. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.2.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr Human immunoglobulin A. N Engl J Med. 1968 Dec 12;279(24):1327–1330. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196812122792408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINNER H. I. A study of Candida albicans agglutinins in human sera. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Dec;53(4):509–512. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400001005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Remold H. G., David J. R. Leukotactic factor produced by sensitized lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Mar 7;163(3871):1079–1081. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3871.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Fudenberg H. H. Moniliasis, 'autoimmune' polyendocrinopathy, and immunologic family study. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jan;2(1):71–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuepper K. D., Wegienka L. C., Fudenberg H. H. Immunologic aspects of adrenocortical insufficiency. Am J Med. 1969 Feb;46(2):206–216. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]