Abstract
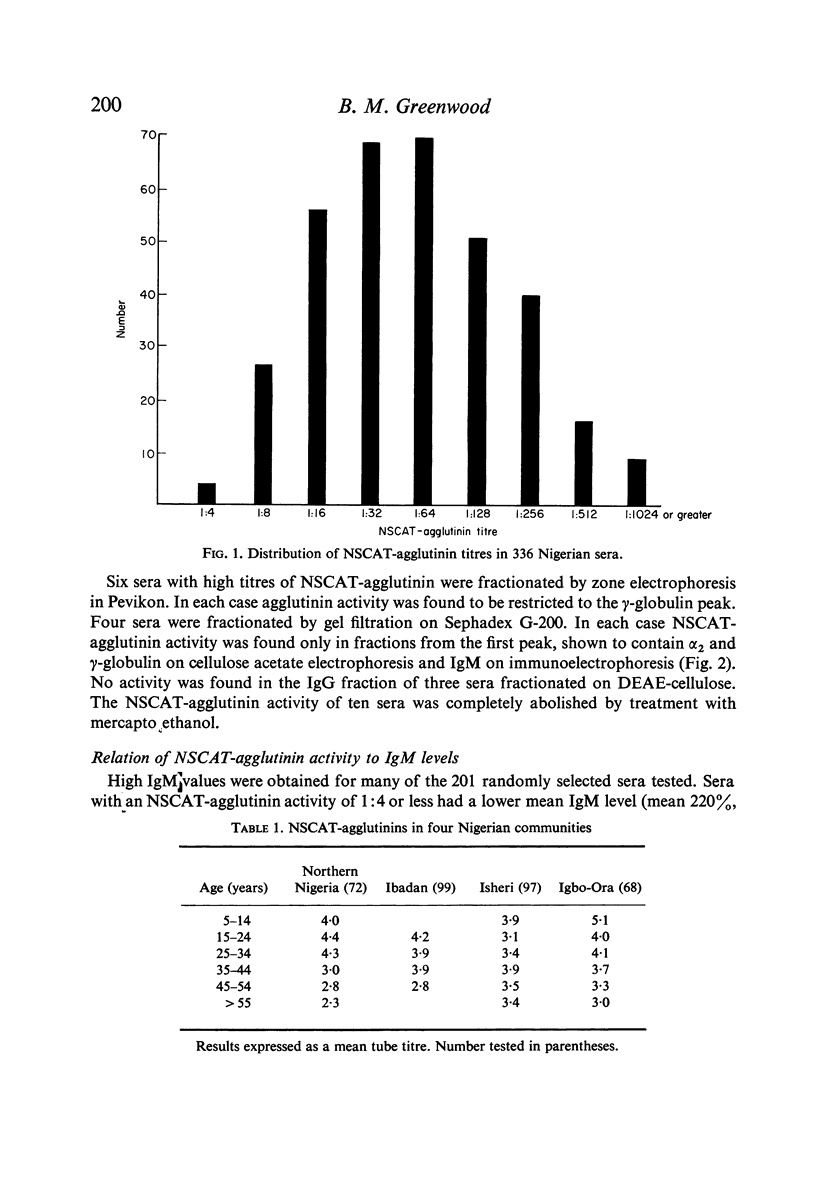
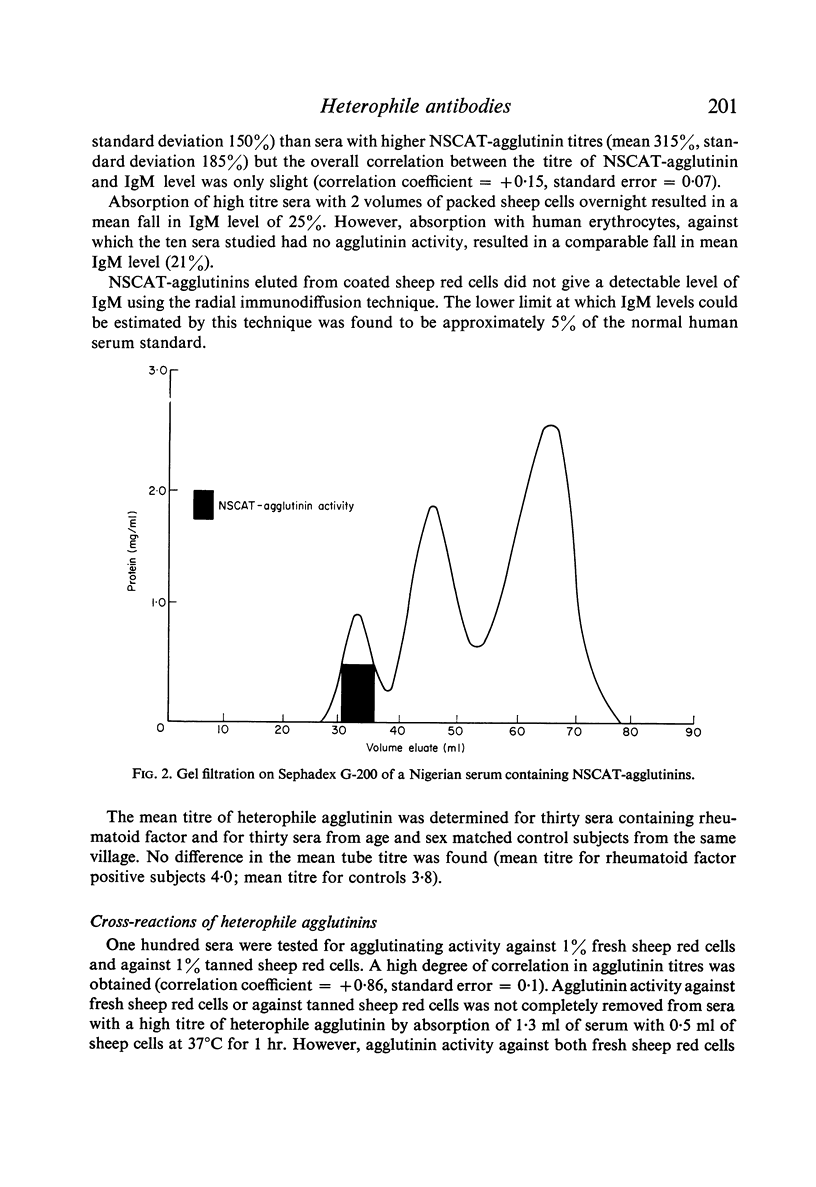
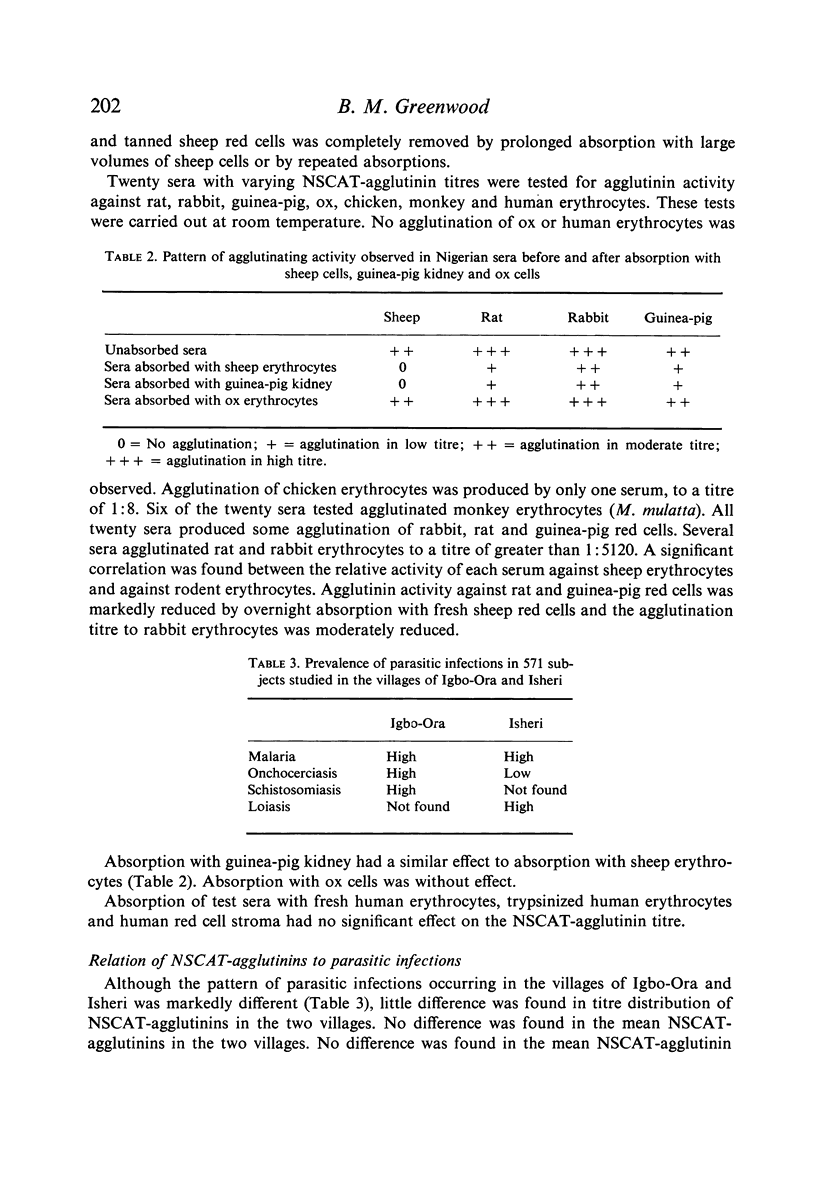
A heterophile agglutinin was found at a titre of 1:4 or greater in 332 of 336 Nigerian sera investigated. The antibody was demonstrated to be an IgM macroglobulin. Although many of the sera tested had high IgM levels, only a slight correlation was found between titres of heterophile agglutinin and IgM levels. Absorption studies differentiated the Nigerian heterophile agglutinin from the antibodies seen in glandular fever and serum sickness. No correlation was found between the occurrence of high titres of heterophile agglutinin and infection with malaria, onchocerciasis, loaisis or schistosomiasis. None of the subjects investigated was known to have trypanosomiasis, a parasitic infection in which heterophile antibodies are known to occur.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeniyi-Jones C. Agglutination of tanned sheep erythrocytes by serum from Nigerian adults and children. Lancet. 1967 Jan 28;1(7483):188–190. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91826-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUBB R., SWAHN B. Destruction of some agglutinins but not of others by two sulfhydryl compounds. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;43(3):305–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb04899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V., Allison A. C. M-antiglobulins (rheumatoid-factor-like globulins) and other gamma-globulins in relation to tropical parasitic infections. Lancet. 1966 Apr 16;1(7442):848–852. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90186-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houba V., Brown K. N., Allison A. C. Heterophile antibodies, M-antiglobulins and immunoglobulins in experimental trypanosomiasis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Jan;4(1):113–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano K., McGregor I. A., Milgrom F. Hemagglutinins in sera of Africans of Gambia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Dec;129(3):849–853. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaux J. L. Les immunoglobulines des Bantous à l'état normal et pathologique. Ann Soc Belges Med Trop Parasitol Mycol. 1966;46(5):483–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osler A. G., Mulligan J. J., Jr, Rodriguez E. Weight estimates of rabbit anti-human serum albumin based on antigen-binding and precipitin analyses: specific hemagglutinating activities of 7 S and 19 S components. J Immunol. 1966 Feb;96(2):334–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN H. Antibody elution from red blood cells. J Clin Pathol. 1963 Jan;16:70–73. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. S., McGregor I. A., Smith S. J., Hall P., Williams K. Plasma immunoglobulin concentrations in a West African (Gambian) community and in a group of healthy British adults. Clin Exp Immunol. 1968 Jan;3(1):63–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Voller A. Studies on immunoglobulins of Nigerians. I. The immunoglobulin levels of a Nigerian population. J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 May;69(5):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLLER A. FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY METHODS AND THEIR USE IN MALARIA RESEARCH. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:343–354. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


