Abstract
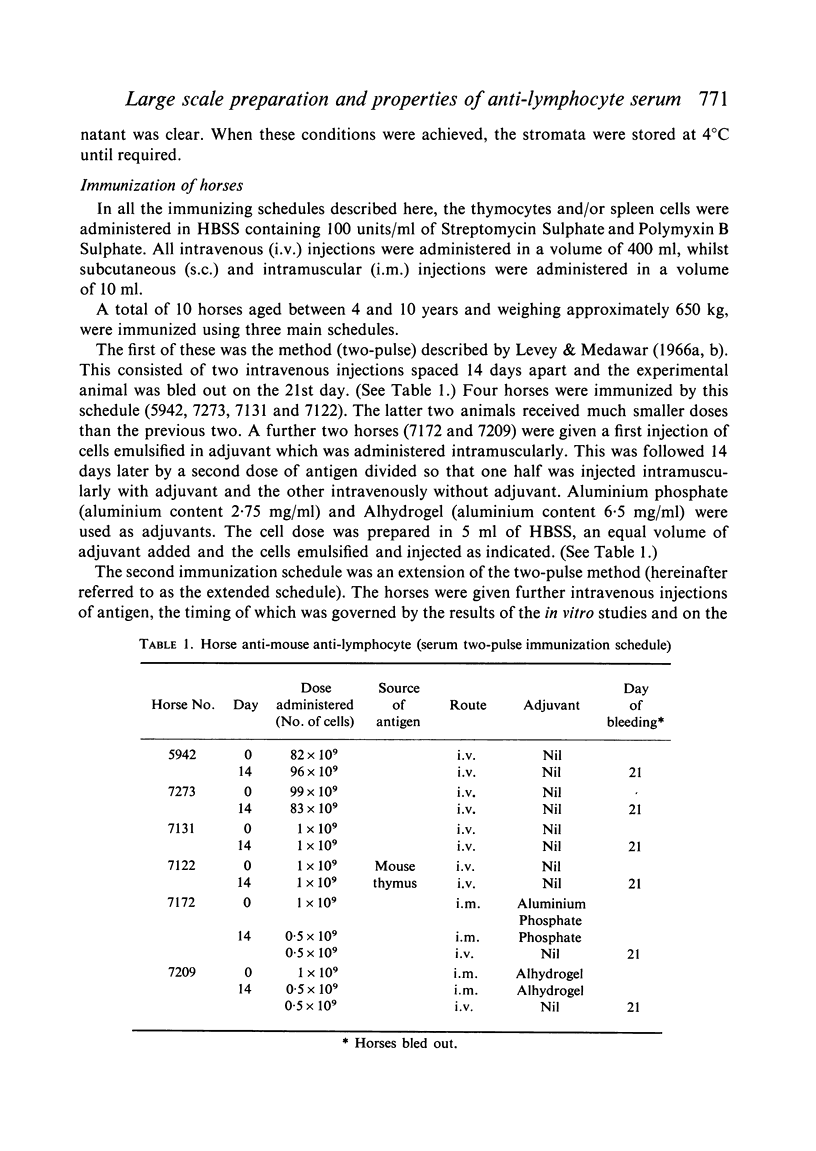
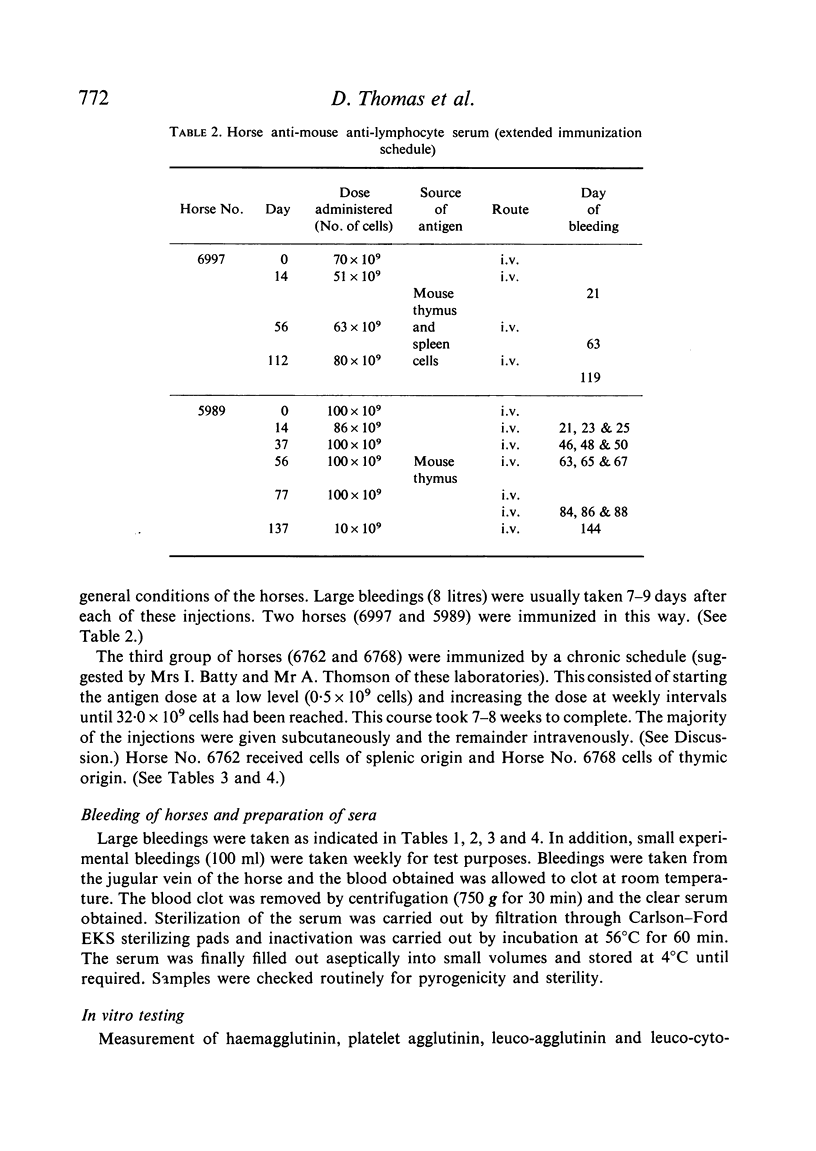
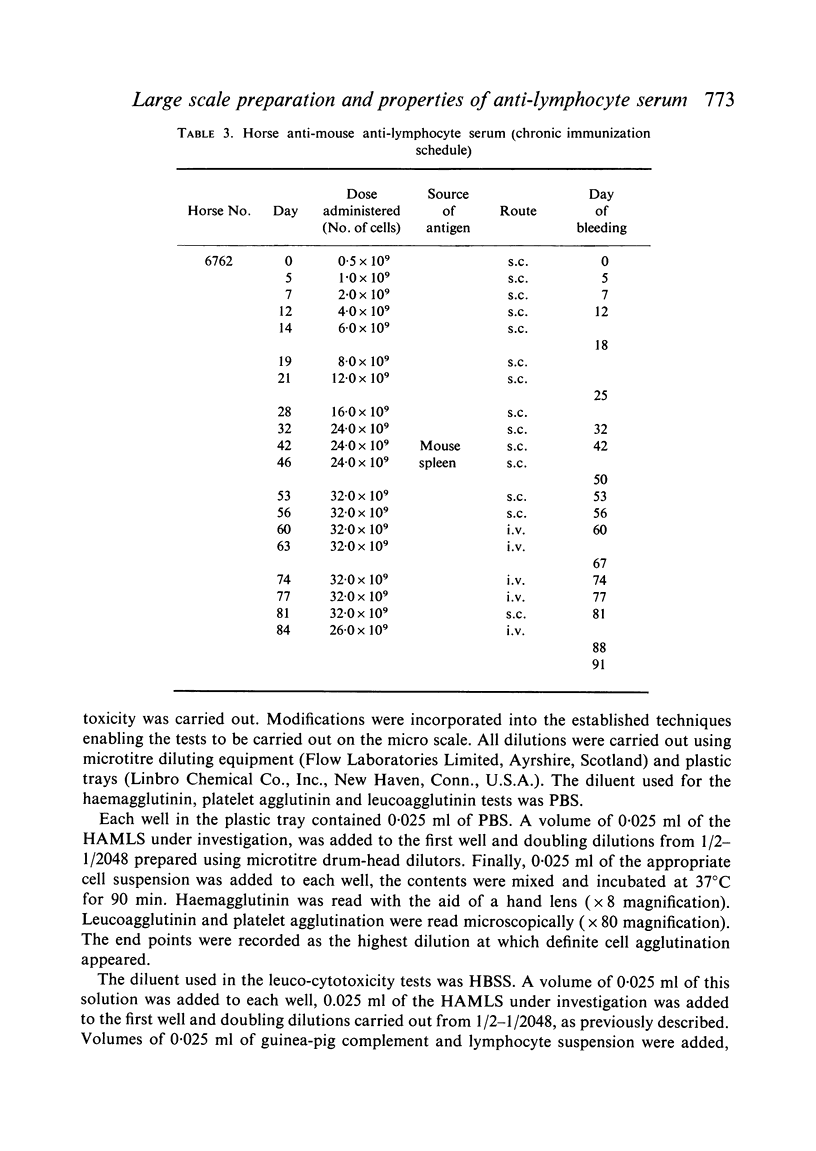
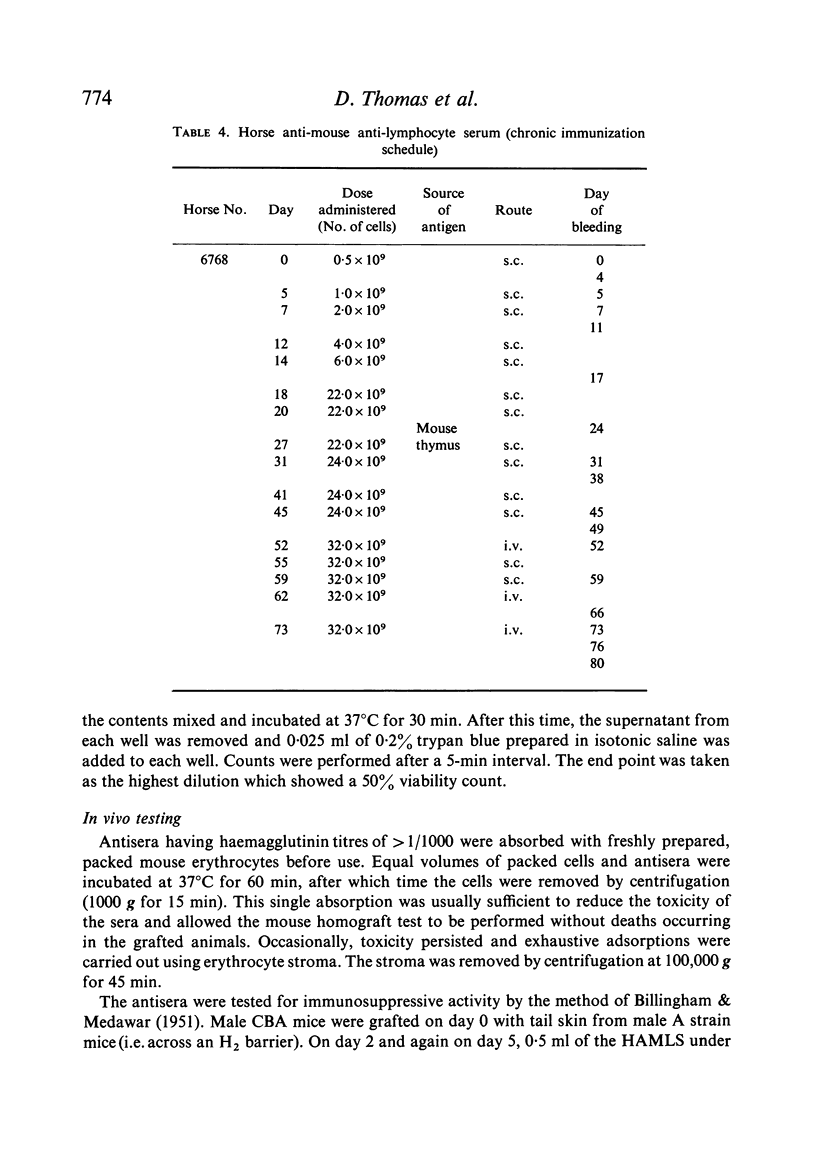
Mouse spleen and thymus cells have been used in the preparation of horse anti-mouse anti-lymphocyte serum (HAMLS). The cells were used either separately or in a mixture and three types of immunization schedules were used, viz. two-pulse, extended and chronic.
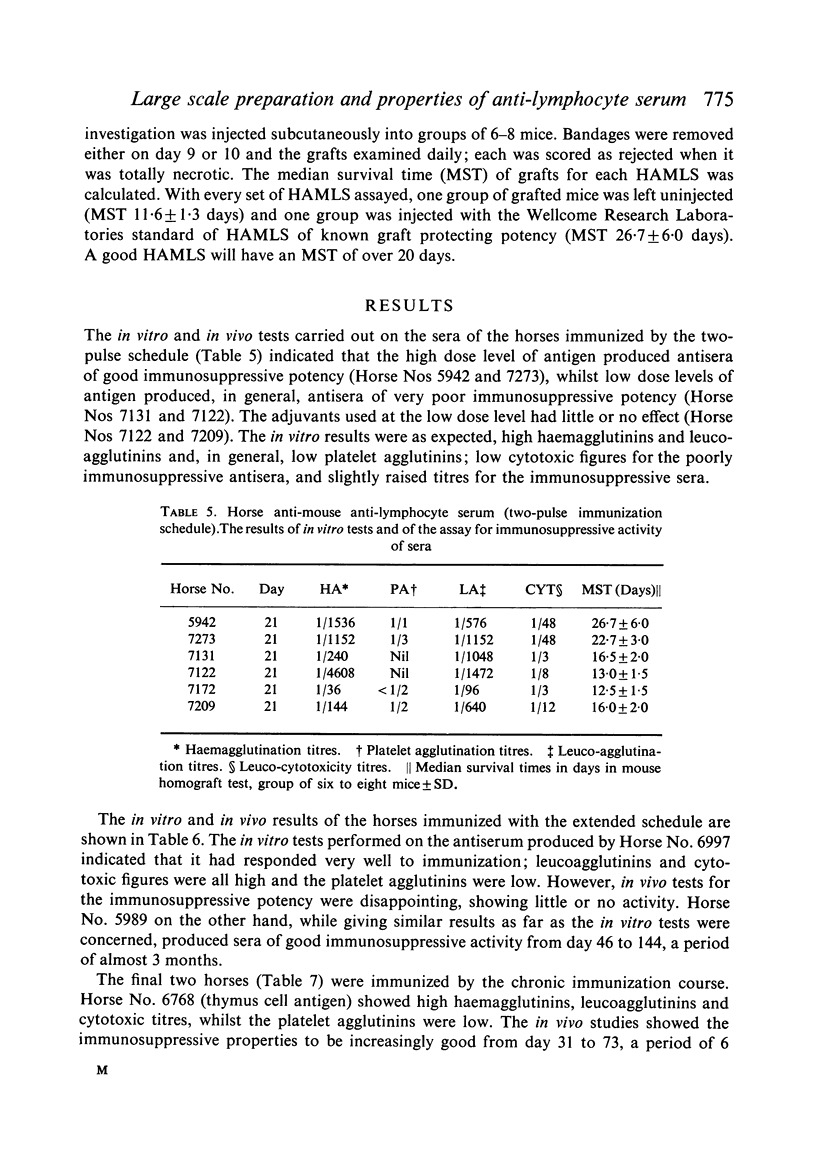
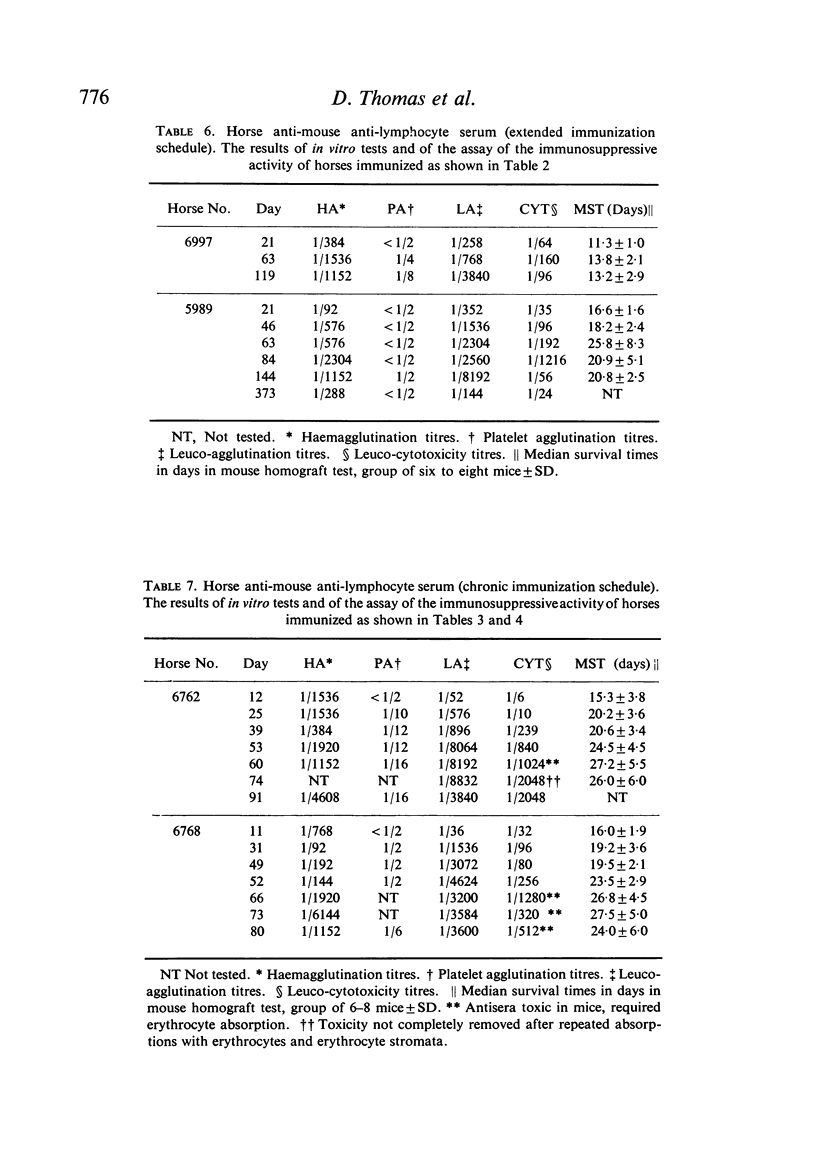
Antisera of marked immunosuppressive activity, as measured by the ability to prolong the life of skin homografts in mice, were obtained using all three schedules, the median survival time being, at best, 27·5 days for the chronic schedule, 26·7 days for the two-pulse schedule and 25·8 days for the extended schedule. The two-pulse and the extended schedules produced non-toxic antisera in a relatively short period of time but were uneconomic in terms of antigen and horses. The chronic schedule was preferred but after 10 weeks the development of unwanted antibodies precluded the further useful immunization of the horses.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GRAY J. G., MONACO A. P., RUSSELL P. S. HETEROLOGOUS MOUSE ANTI-LYMPHOCYTE SERUM TO PROLONG SKIN HOMOGRAFTS. Surg Forum. 1964;15:142–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jooste S. V., Lance E. M., Levey R. H., Medawar P. B., Ruszkiewicz M., Sharman R., Taub R. N. Notes on the preparation and assay of anti-lymphocytic serum for use in mice. Immunology. 1968 Nov;15(5):697–705. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lance E. M., Medawar P. B. Immunosuppressive effects of heterologous antilymphocyte serum in monkeys. Lancet. 1970 Jan 24;1(7639):167–170. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90407-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey R. H., Medawar P. B. Nature and mode of action of antilymphocytic antiserum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1130–1137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODRUFF M. F., ANDERSON N. A. EFFECT OF LYMPHOCYTE DEPLETION BY THORACIC DUCT FISTULA AND ADMINISTRATION OF ANTILYMPHOCYTIC SERUM ON THE SURVIVAL OF SKIN HOMOGRAFTS IN RATS. Nature. 1963 Nov 16;200:702–702. doi: 10.1038/200702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOODRUFF M. F., ANDERSON N. F. THE EFFECT OF LYMPHOCYTE DEPLETION BY THORACIC DUCT FISTULA AND ADMINISTRATION OF ANTILYMPHOCYTIC SERUM ON THE SURVIVAL OF SKIN HOMOGRAFTS IN RATS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Nov 30;120:119–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb34710.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woiwod A. J., Courtenay J. S., Edwards D. C., Epps H. B., Knight R. R., Mosedale B., Phillips A. W., Rahr L., Thomas D., Woodrooffe J. G. The preparation and properties of horse antihuman lymphocyte serum and globulin. Transplantation. 1970 Aug;10(2):173–186. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197008000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


