Abstract
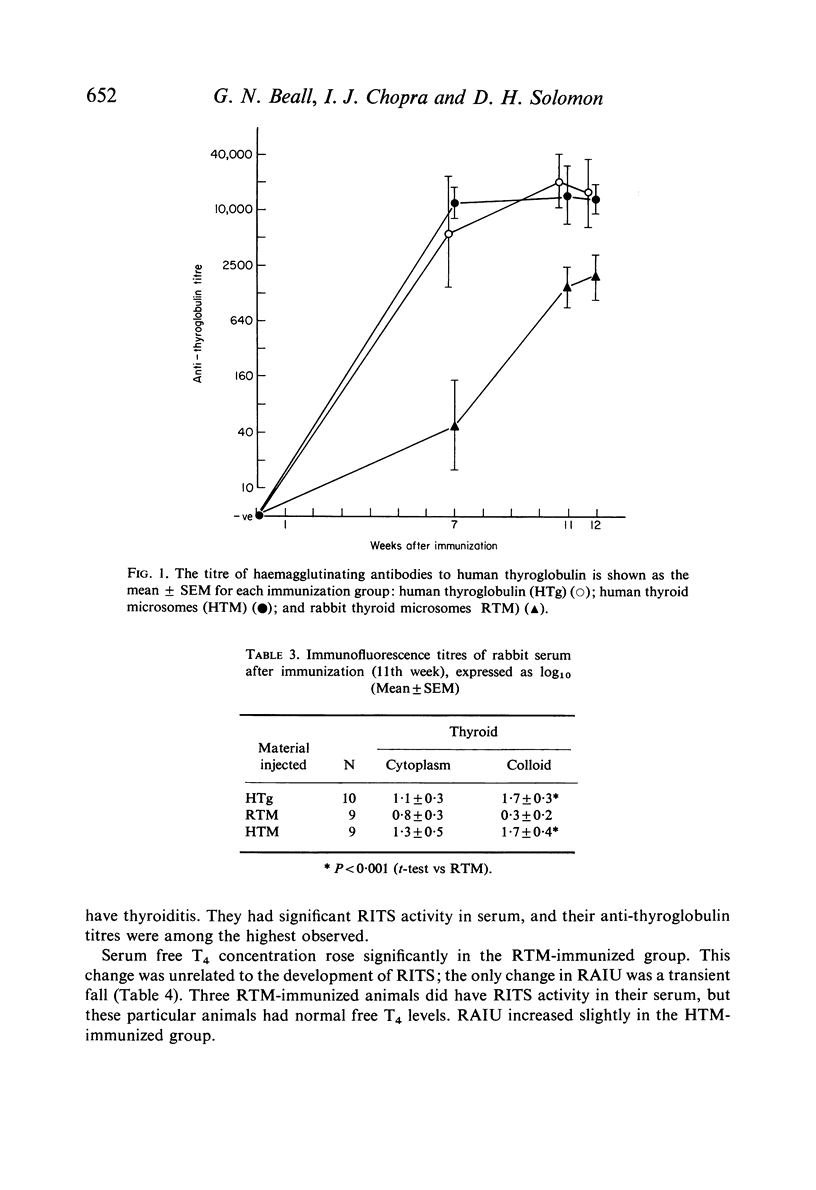
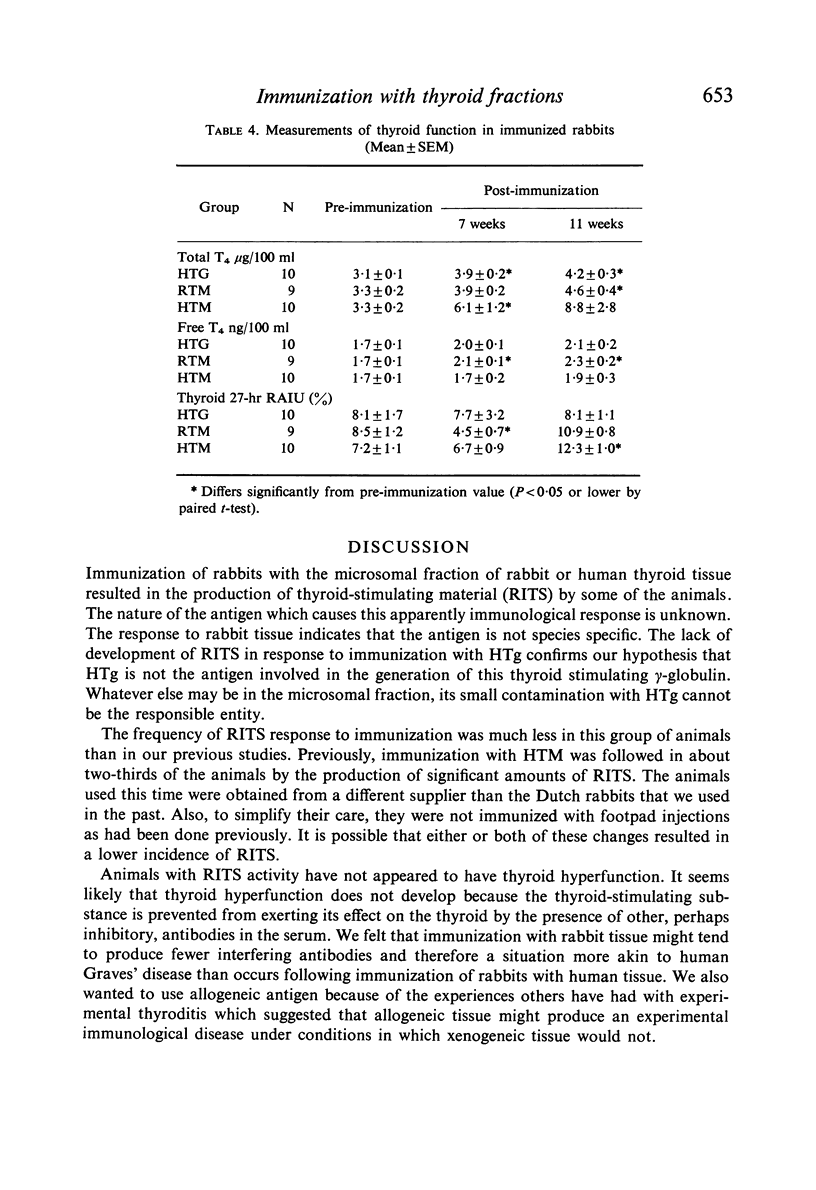
Dutch rabbits were immunized with human thyroglobulin and human and rabbit thyroid microsomal fractions. The animals were bled at intervals and their serum was assayed for thyroid-stimulating activity, thyroglobulin haemagglutinins, and total and free thyroxine (T4). Their thyroidal radio-iodine uptake and thyroid histology was also studied. Five out of ten animals immunized with human thyroglobulin developed histological evidence of thyroiditis but none had thyroid-stimulating activity in the serum. Only one out of twenty-six animals immunized with rabbit or human thyroid microsomal fractions had any histological abnormality in the thyroid, but eight had significant amounts of thyroid-stimulating activity in their serum. Although the frequency of the latter response was no greater after immunization with rabbit as compared to human thyroid microsomal fraction, there was a significant increase in serum free T4 in the group immunized with rabbit tissue.
Thyroiditis and rabbit immunologic thyroid stimulator (RITS) formation appear to be completely separable phenomena, and RITS is not a by-product of thyroiditis. The absence of thyroid-stimulating activity in the serum of rabbits immunized with thyroglobulin is further evidence that thyroglobulin is not the important antigen leading to the production of this thyroid-stimulating globulin.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beall G. N., Daniel P. M., Pratt O. E., Solomon D. H. Effects of immunization of baboons with human thyroid tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Nov;29(11):1460–1469. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-11-1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall G. N., Solomon D. H. Inhibition of long-acting thyroid stimulator by thyroid particulate fractions. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):552–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI105369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall G. N., Solomon D. H. Thyroid-stimulating activity in the serum of rabbits immunized with thyroid microsomes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Apr;28(4):503–510. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-4-503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beall G., Doniach D., Roitt I., el Kabir D. Inhibition of the long-acting thyroid stimulator (LATS) by soluble thyroid fractions. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jun;73(6):988–999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FULTHORPE A. J., ROITT I. M., DONIACH D., COUCHMAN K. A stable sheep cell preparation for detecing thyroglobulin auto-antibodies and its clinical applications. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Nov;14:654–660. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.6.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY B. E., PATTEE C. J. DETERMINATION OF THYROXINE UTILIZING THE PROPERTY OF PROTEIN-BINDING. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:187–196. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M. Experimental production of a thyroid-stimulating antithyroid antibody. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 May;28(5):596–602. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-5-596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinchera A., Liberti P., Badalamenti G. Long-acting thyroid stimulator and thyroid antibodies. Lancet. 1966 Feb 12;1(7433):374–375. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91379-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose N. R., Kite J. H., Jr, Doebbler T. K., Spier R., Skelton F. R., Witebsky E. Studies on experimental thyroiditis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jun 30;124(1):201–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb18957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schussler G. C., Plager J. E. Effect of preliminary purification of 131-I-thyroxine on the determination of free thyroxine in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):242–250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Effect of thyroxine on the thyroid-stimulating activity in the serum of rabbits immunized with thyroid tissue. Endocrinology. 1970 Feb;86(2):191–195. doi: 10.1210/endo-86-2-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon D. H., Beall G. N. Thyroid-stimulating activity in the serum of immunized rabbits. II. Nature of the thyroid-stimulating material. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Oct;28(10):1496–1502. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-10-1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERPLAN K. L., WITEBSKY E., ROSE N. R., PAINE J. R., EGAN R. W. Experimental thyroiditis in rabbits, guinea pigs and dogs, following immunization with thyroid extracts of their own and of heterologous species. Am J Pathol. 1960 Feb;36:213–239. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIGLE W. O. THE INDUCTION OF AUTOIMMUNITY IN RABBITS FOLLOWING INJECTION OF HETEROLOGOUS OR ALTERED HOMOLOGOUS THYROGLOBULIN. J Exp Med. 1965 Feb 1;121:289–308. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O., High G. J., Nakamura R. M. The role of mycobacteria and the effect of proteolytic degradation of thyroglobulin on the production of autoimmune thyroiditis. J Exp Med. 1969 Aug 1;130(2):243–262. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigle W. O., Nakamura R. M. The development of autoimmune thyroiditis in rabbits following injection of aqueous preparations of heterologous thyroglobulins. J Immunol. 1967 Jul;99(1):223–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


