Abstract
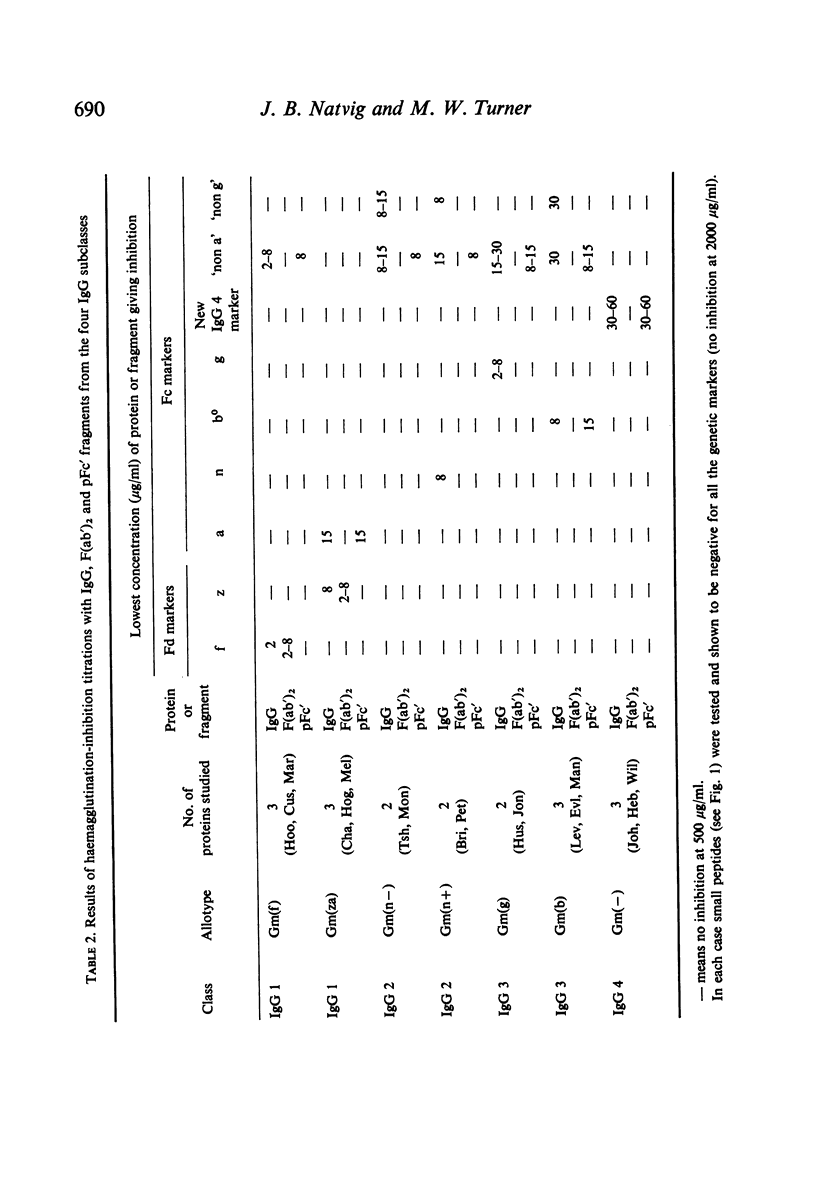
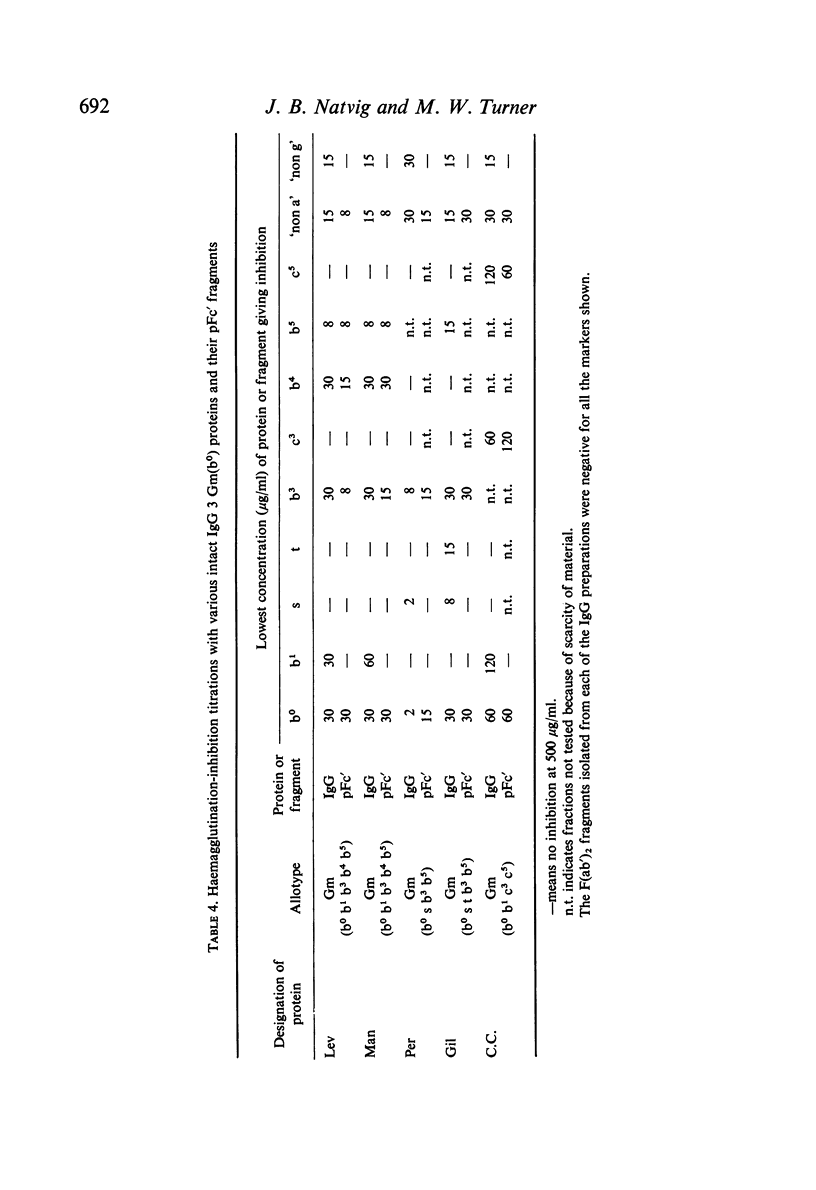
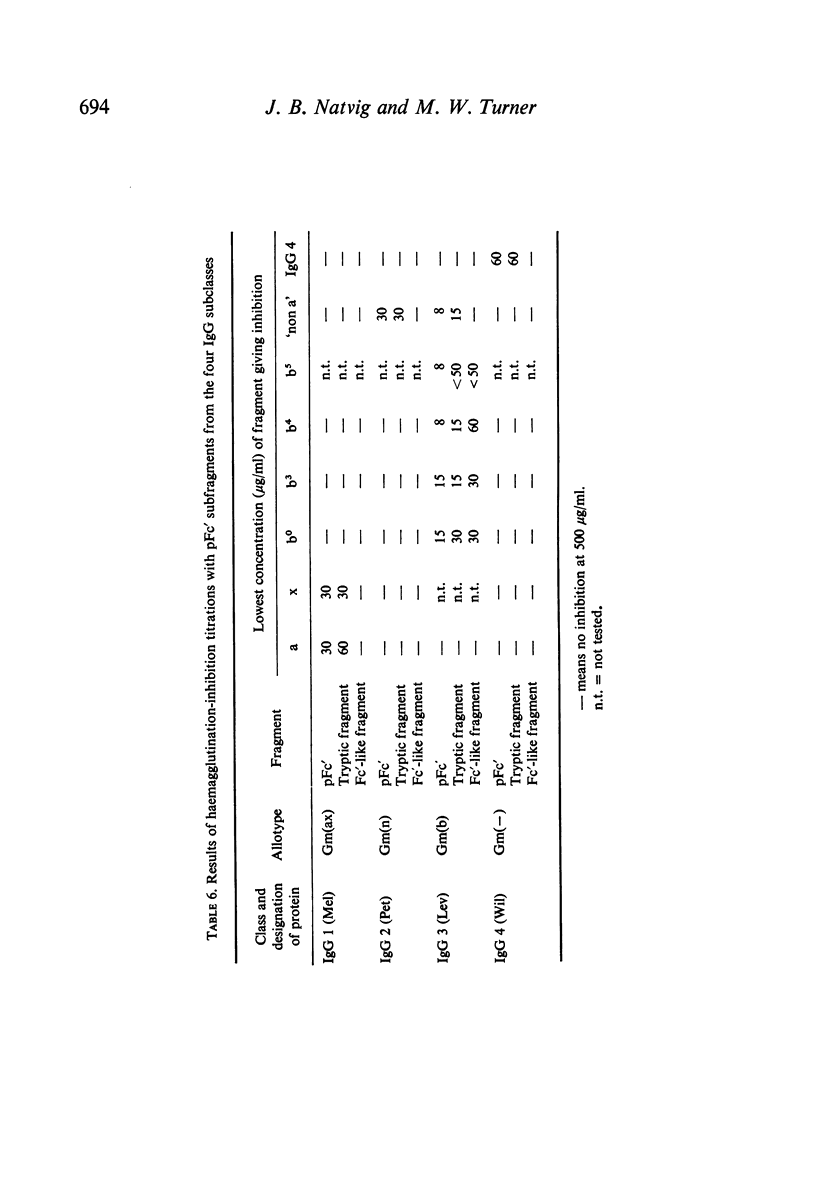
pFc' fragments (corresponding to homology region Cγ3) and smaller subfragments produced by trypsin and papain have been studied by haemagglutination inhibition techniques for the presence of a range of Fcγ allotypic markers. The markers which were identified in the pFc' fragment included Gm(a), (x), (b0), (b3), (b4), (b5), (c3), (c5) and `non a'. In addition, an IgG 4 marker which possibly occupies the same molecular region as the Gm(a) and `non a' antigens was detected in pFc' fragments from IgG 4 proteins.
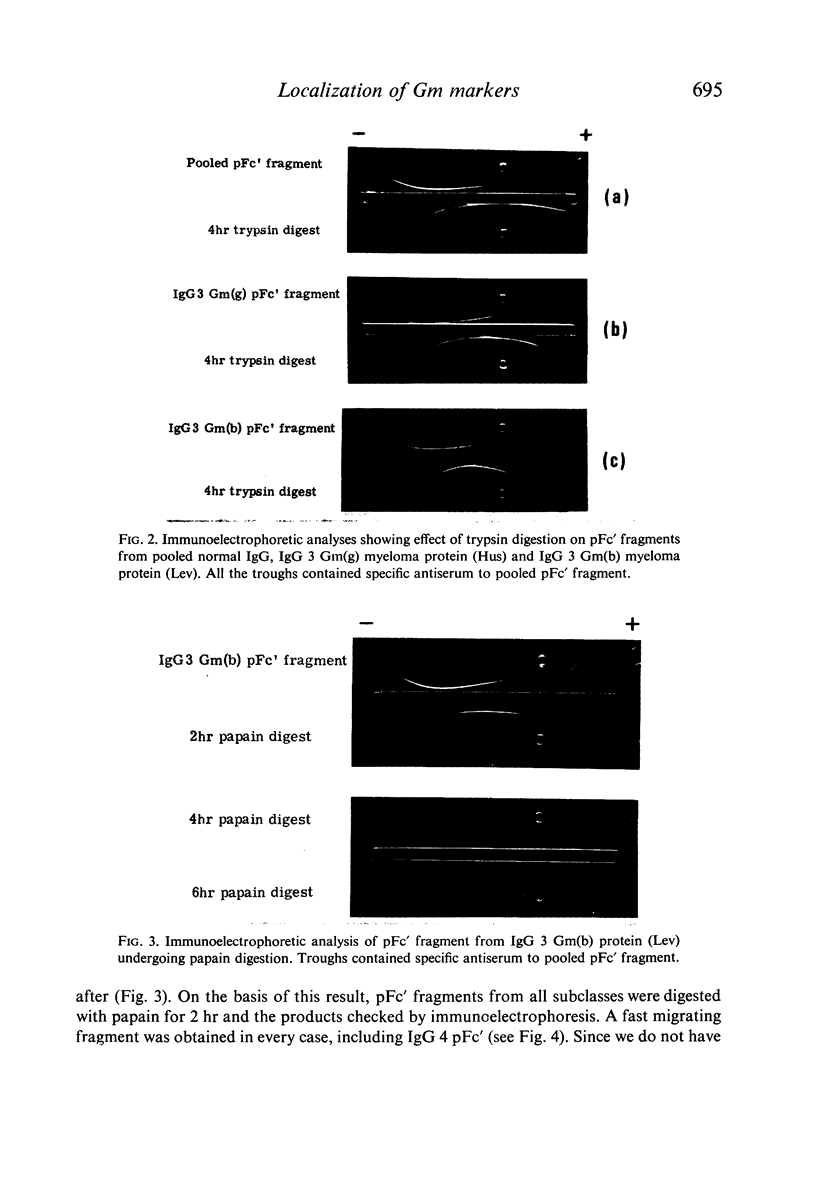
Limited tryptic cleavage of pFc' fragment resulting in the loss of approximately seven N-terminal residues had no effect on the antigenic expression of the genetic markers. More extensive degradation of pFc' fragments with papain yielded Fc'-like fragments which are presumed to lack a C-terminal tridecapeptide as well as eight or nine N-terminal residues. In these fragments antigenic expression of Gm(a), (x) and `non a' was lost, but Gm(b0), (b3), (b4) and (b5) antigens were still detectable.
The other allotypic markers of the Fc region (Gm(n), (b1), (g) and `non g') were not detected in any of the fragments investigated and it is probable that they are in homology region Cγ2.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A., Gall W. E., Gottlieb P. D., Rutishauser U., Waxdal M. J. The covalent structure of an entire gammaG immunoglobulin molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):78–85. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCLAUGHLIN C. PREPARATION OF ANTISERA SPECIFIC FOR 6.6 S GAMMA-GLOBULINS, BETA 2A-GLOBULINS, GAMMA-1.-MACROGLOBULINS, AND FOR TYPE I AND II COMMON GAMMA-GLOBULIN DETERMINANTS. J Immunol. 1963 Oct;91:484–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C., Franklin E. C. Intrachain disulphide bridges in immunoglobulin G heavy chains. The Fc fragment. Biochem J. 1968 Jan;106(1):15–21. doi: 10.1042/bj1060015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangione B., Milstein C., Pink J. R. Structural studies of immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1969 Jan 11;221(5176):145–148. doi: 10.1038/221145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaarder P. I., Natvig J. B. Hidden rheumatoid factors reacting with "non a" and other antigens of native autologous IgG. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):928–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Abel C. A. Structural characteristics of the Fc' fragment of human gamma-G-globulin. Immunochemistry. 1967 Sep;4(5):315–317. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90114-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington J. T., Hood L., Terry W. D. C-terminal peptides from human gamma-chains of differing subclass and allotype. Immunochemistry. 1970 Apr;7(4):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimer R., Schnoll S. H. FC-like fragments in peptic digests of human immunoglobulin G. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):231–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irimajiri S., Franklin E. C., Woods K. R. C-terminal sequence of the F'c fragment of human gamma G globulin. Nature. 1968 Nov 9;220(5167):612–614. doi: 10.1038/220612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Joslin F. G., Penn G. M., Natvig J. B. Genetic variants of G4 globulin. A unique relationship to other classes of G globulin. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):508–520. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårtensson L., van Loghem E., Matsumoto H., Nielsen J. Gm(s) and Gm(t): genetic determinants of human gamma-globulin. Vox Sang. 1966 Jul-Aug;11(4):393–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1966.tb04237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Turner M. W. Rheumatoid anti Gm gactors with specificity for the pFc' subfragment of human immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1970 Feb 28;225(5235):855–857. doi: 10.1038/225855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pink J. R., Buttery S. H., De Vries G. M., Milstein C. Human immunoglobulin subclasses. Partial amino acid sequence of the constant region of a gamma 4 chain. Biochem J. 1970 Mar;117(1):33–47. doi: 10.1042/bj1170033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prahl J. W. The C-terminal sequences of the heavy chains of human immunoglobulin G myeloma proteins of differing isotopes and allotypes. Biochem J. 1967 Dec;105(3):1019–1028. doi: 10.1042/bj1051019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
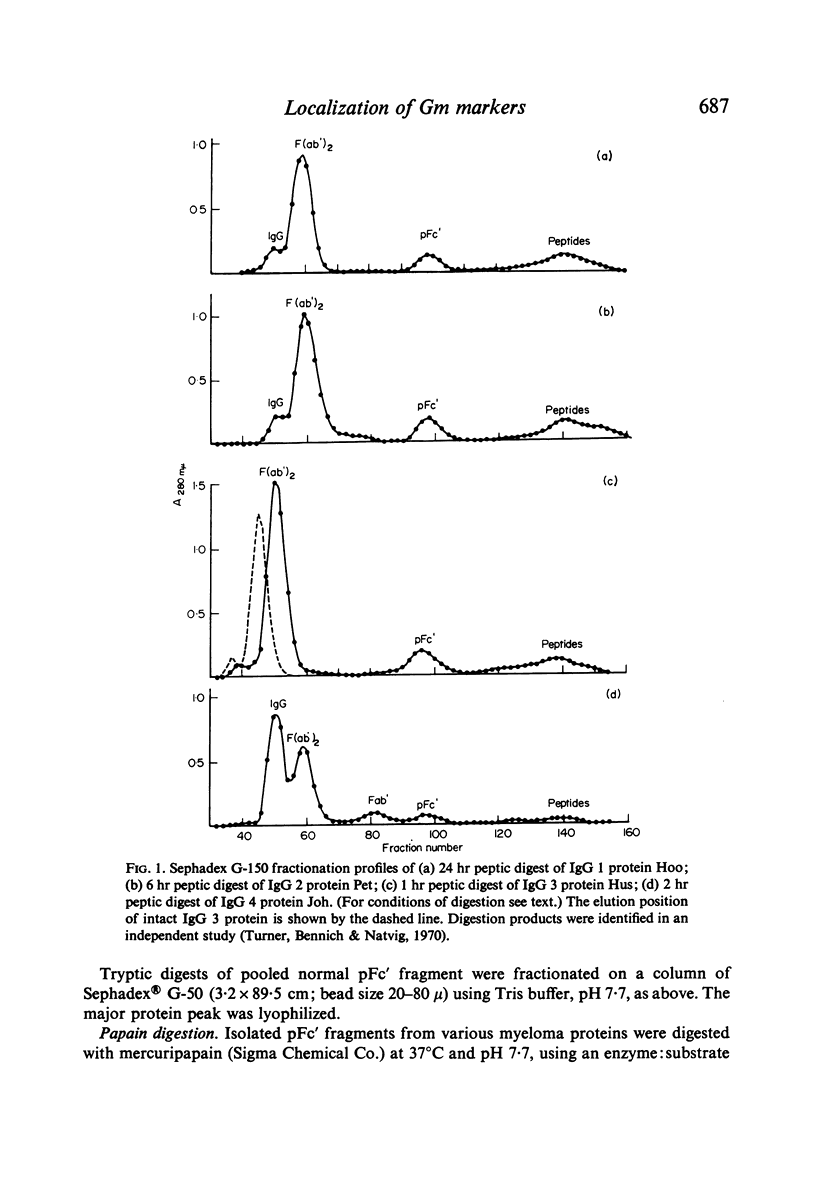
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. H., Natvig J. B. Pepsin digestion of human G-myeloma proteins of different subclasses. I. The characteristic features of pepsin cleavage as a function of time. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Nov;7(5):603–625. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Bennich H. Subfragments from the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G. Isolation and physicochemical charaterization. Biochem J. 1968 Mar;107(2):171–178. doi: 10.1042/bj1070171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. W., Mårtensson L., Natvig J. B., Bennich H. Genetic (Gm) antigens associated with subfragments from the Fc fragment of human immunoglobulin G. Nature. 1969 Mar 22;221(5186):1166–1169. doi: 10.1038/2211166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsumi S. Stepwise cleavage of rabbit immunoglobulin G by papain and isolation of four types of biologically active Fc fragments. Biochem J. 1969 Apr;112(3):343–355. doi: 10.1042/bj1120343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Fudenberg H. H., Pretty H. M., Gold E. R. A new rapid method for genetic typing of human immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1968 Feb;100(2):274–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loghem E., Mårtensson L. Genetic (Gm) determinants of the gamma-2c (Vi) subclass of human IgG immunoglobulins. A study with special reference to Gm(c3) and Gm(c5), and their relationship with the Gm(b) determinants. Vox Sang. 1967 Nov;13(5):369–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1967.tb03782.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loghem E., de Lange G. Human sera as source of IgG subclass-specific reagents. Vox Sang. 1970 Jan;18(1):81–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1970.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]