Abstract
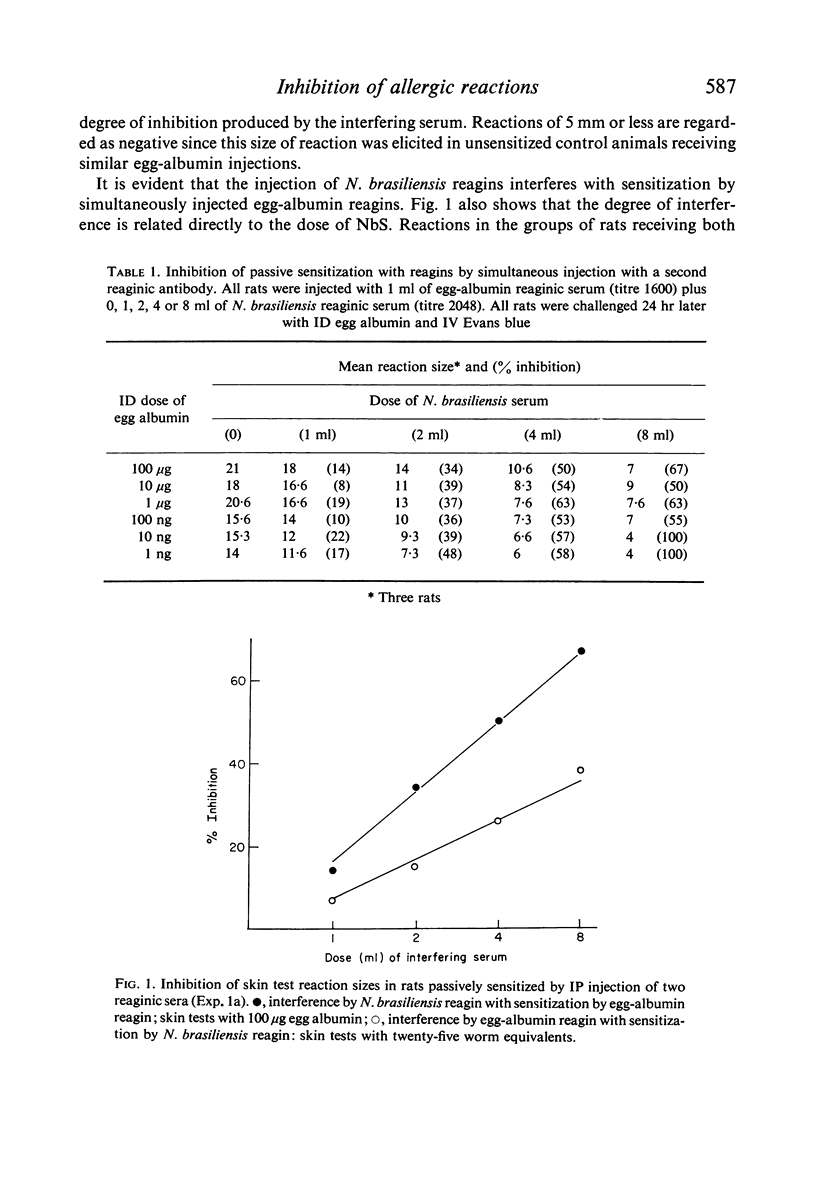
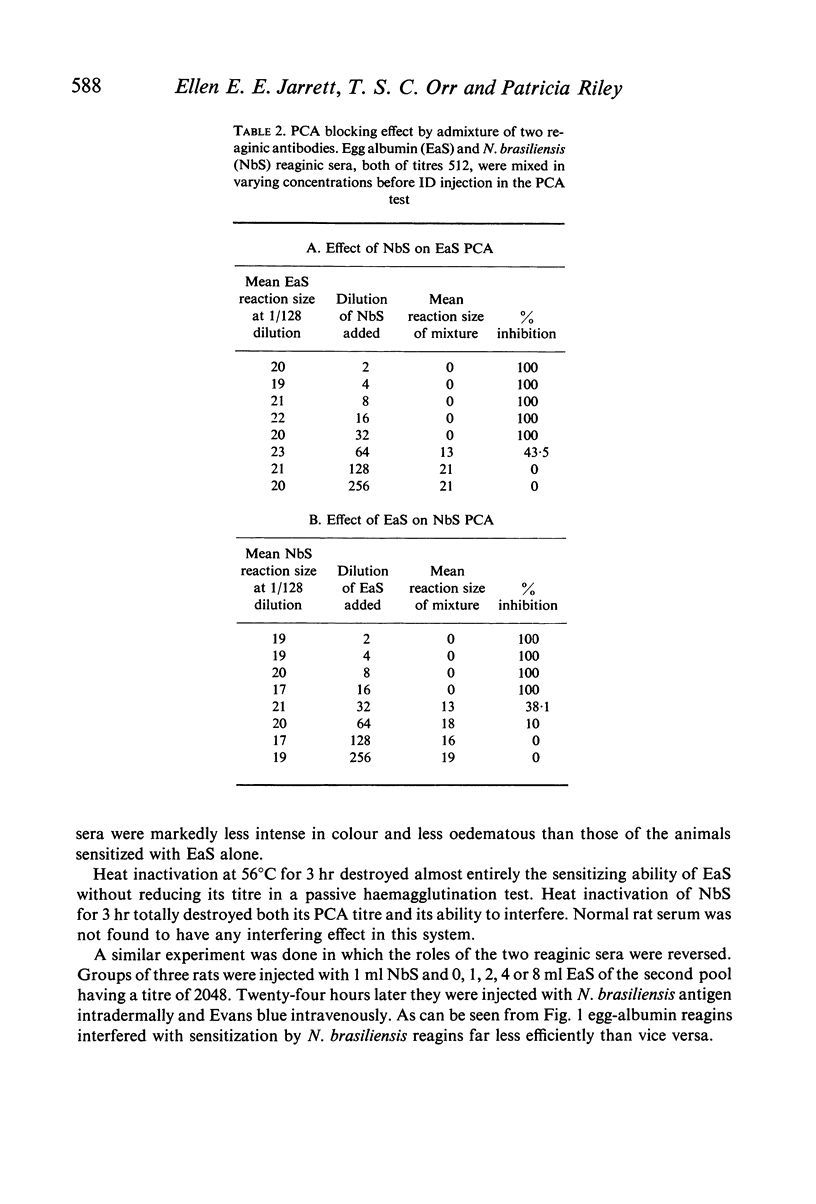
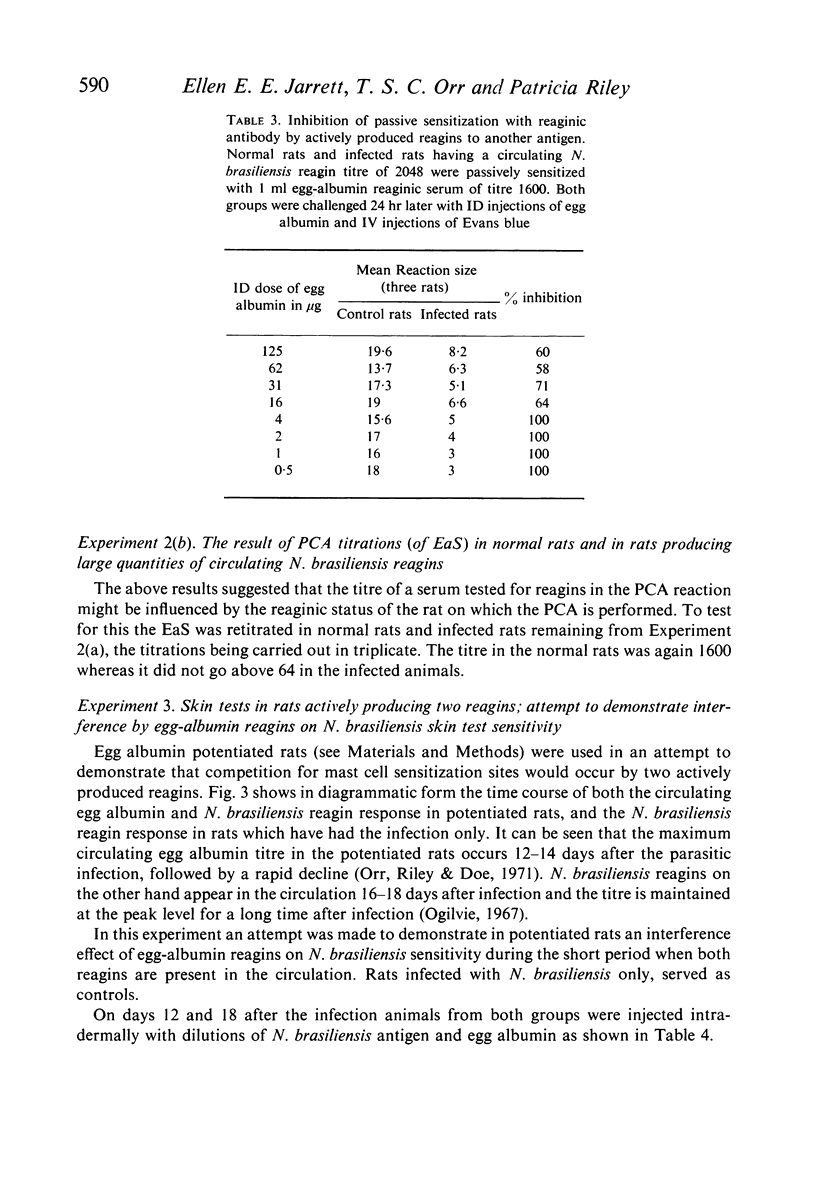
The ability of unrelated or incidental reagin to interfere competitively with mast cell sensitization by specific reagin has been examined using an experimental system whereby rats are induced to produce high levels of reaginic (IgE) antibody to two antigens. It is shown that passive sensitization by a reaginic antibody is inhibited (a) by simultaneous injection with a second reagin directed against another antigen, the degree of inhibition being related directly to the dose of the second serum or (b) if the test animal is actively producing unrelated reagin.
The skin test sensitivity of rats actively producing high levels of two reagins as opposed to only one is also discussed. The results are presented with particular reference to the interpretation of PCA and other skin tests and to the possible importance of interference effects in multiple allergies.
Full text
PDF



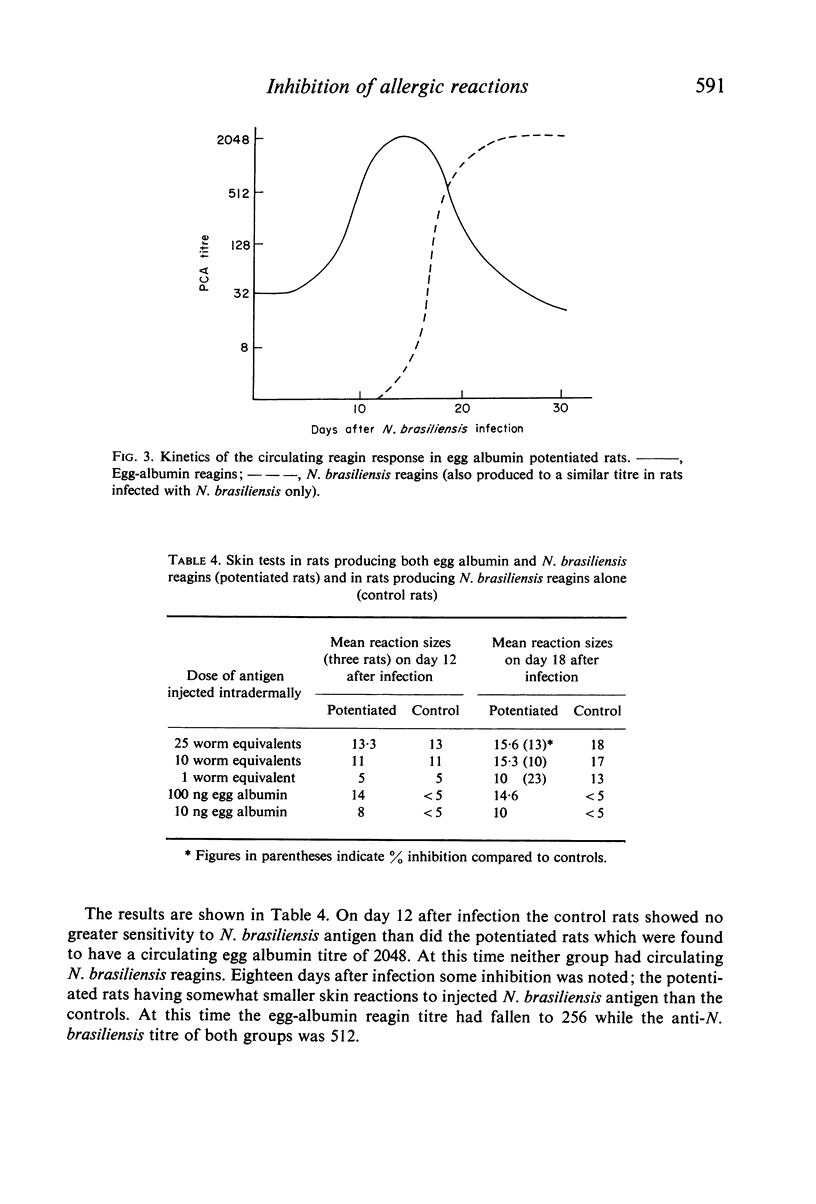



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Hornbrook M. M. Physicochemical properties of reaginic antibody. V. Correlation of reaginic activity wth gamma-E-globulin antibody. J Immunol. 1966 Dec;97(6):840–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka K., Ishizaka T., Lee E. H. Biologic function of the Fc fragments of E myeloma protein. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):687–702. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett E. E., Jarrett W. F., Urquhart G. M. Quantitative studies on the kinetics of establishment and expulsion of intestinal nematode populations in susceptible and immune hosts. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the rat. Parasitology. 1968 Aug;58(3):625–639. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000028924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson S. G., Mellbin T., Vahlquist B. Immunoglobulin levels in Ethiopian preschool children with special reference to high concentrations of immunoglobulin E (IgND). Lancet. 1968 May 25;1(7552):1118–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)90187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTA I. THE MECHANISM OF ANAPHYLAXIS. I. PRODUCTION AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF 'MAST CELL SENSITIZING' ANTIBODY. Immunology. 1964 Nov;7:681–699. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Lovett C. A., Taichman N. S. Demonstration of antigen on the surface of sensitized rat mast cells. Nature. 1966 Nov 19;212(5064):851–853. doi: 10.1038/212851b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie B. M. Reagin-like antibodies in rats infected with the nematode parasite Nippostrongylus brasiliensis. Immunology. 1967 Feb;12(2):113–131. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr T. S., Blair A. M. Potentiated reagin response to egg albumin and conalbumin in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infected rats. Life Sci. 1969 Oct 15;8(20):1073–1077. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr T. S., Riley P., Doe J. E. Potentiated reagin response to egg albumin in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infected rats. II. Time course of the reagin response. Immunology. 1971 Feb;20(2):185–189. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Humphrey J. H., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Inhibition of Prausnitz-Küstner reaction by proteolytic-cleavage fragments of a human myeloma protein of immunoglobulin class E. Lancet. 1968 Jul 6;2(7558):17–18. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanworth D. R., Humphrey J. H., Bennich H., Johansson S. G. Specific inhibition of the Prausnitz-Küstner reaction by an atypical human myeloma protein. Lancet. 1967 Aug 12;2(7511):330–332. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uvnäs B., Wold J. K. Isolation of a mast cell degranulating polypeptide from Ascaris suis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1967 Jul-Aug;70(3):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1967.tb03625.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]