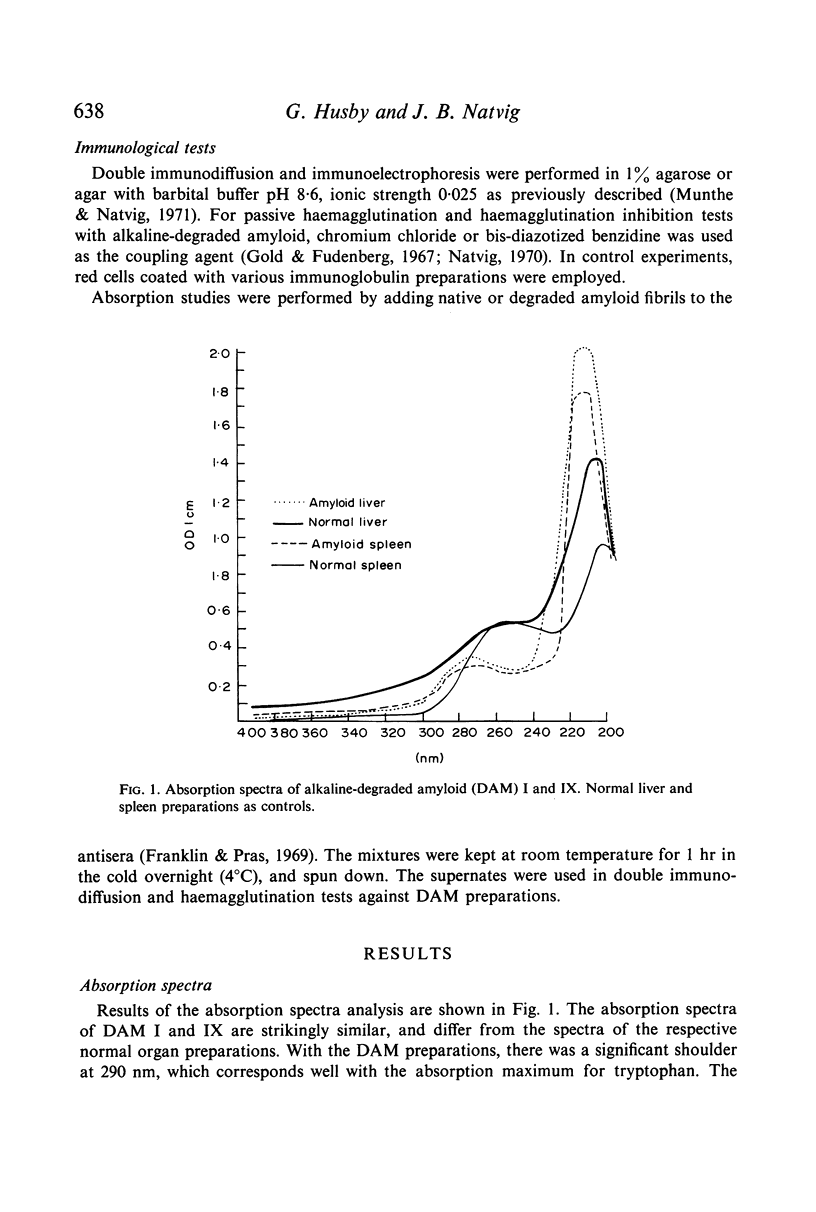
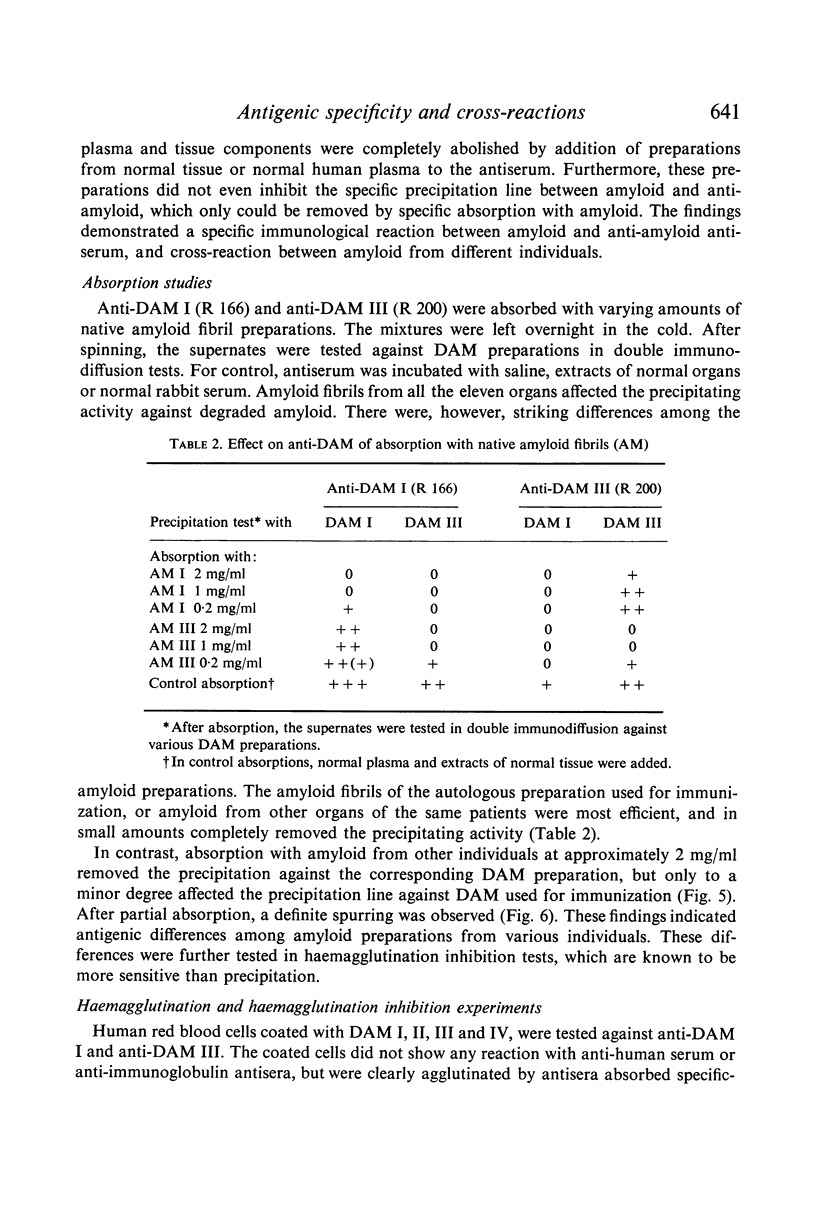
Abstract
Amyloid fibrils were isolated from eleven amyloid-laden organs of six patients. By alkaline degradation, soluble units were obtained which gave antibody formation in rabbits. Gel precipitation and haemagglutination inhibition were used to characterize antigens of the amyloid. Evidence was obtained that amyloids from different organs of the same individual were identical in the antigenicity. In contrast, amyloids from different individuals each showed unique individual specificity. Besides this, antigenic cross-reactions were noted between the amyloid preparations. Finally, evidence for antigenic cross-reactivity between certain amyloid preparations and immunoglobulin light chains was obtained.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bladen H. A., Nylen M. U., Glenner G. G. The ultrastructure of human amyloid as revealed by the negative staining technique. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Mar;14(5):449–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. Electron microscopic observations on a fibrous component in amyloid of diverse origins. Nature. 1959 Apr 25;183(4669):1202–1203. doi: 10.1038/1831202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin E. C., Pras M. Immunologic studies of water-soluble human amyloid fibrils. Comparative studies of eight amyloid preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):797–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREY H. M., MANNIK M., KUNKEL H. G. INDIVIDUAL ANTIGENIC SPECIFICITY OF MYELOMA PROTEINS. CHARACTERISTICS AND LOCALIZATION TO SUBUNITS. J Exp Med. 1965 Apr 1;121:561–575. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.4.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Cuatrecasas P., Isersky C., Bladen H. A., Eanes E. D. Physical and chemical properties of amyloid fibers. II. Isolation of a unique protein constituting the major component from human splenic amyloid fibril concentrates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Dec;17(12):769–780. doi: 10.1177/17.12.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Keiser H. R., Bladen H. A., Cuatrecasas P., Eanes E. D., Ram J. S., Kanfer J. N., DeLellis R. A. Amyloid. VI. A comparison of two morphologic components of human amyloid deposits. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Oct;16(10):633–644. doi: 10.1177/16.10.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Terry W., Harada M., Isersky C., Page D. Amyloid fibril proteins: proof of homology with immunoglobulin light chains by sequence analyses. Science. 1971 Jun 11;172(3988):1150–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3988.1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold E. R., Fudenberg H. H. Chromic chloride: a coupling reagent for passive hemagglutination reactions. J Immunol. 1967 Nov;99(5):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Mannik M., Williams R. C. Individual Antigenic Specificity of Isolated Antibodies. Science. 1963 Jun 14;140(3572):1218–1219. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3572.1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MISSMAHL H. P., HARTWIG M. Polarisationsoptische Untersuchungen an der Amyloidsubstanz. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1953;324(4):489–508. doi: 10.1007/BF00954791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munthe E., Natvig J. B. Characterization of IgG complexes in eluates from rheumatoid tissue. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Feb;8(2):249–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B. Human anti-gamma-globulin antibodies specific for gamma G heavy chain subclasses. Immunology. 1970 Jul;19(1):125–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. Physical, chemical, and ultrastructural studies of water-soluble human amyloid fibrils. Comparative analyses of nine amyloid preparations. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):777–796. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sri Ram J., DeLellis R. A., Glenner G. G. Amyloid. IV. Is human amyloid immunogenic? Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(3):269–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAN M., EPSTEIN W. V. A DIRECT IMMUNOLOGIC ASSAY OF HUMAN SERA FOR BENCE JONES PROTEINS (L-CHAINS). J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Aug;66:344–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]