Abstract
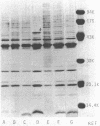
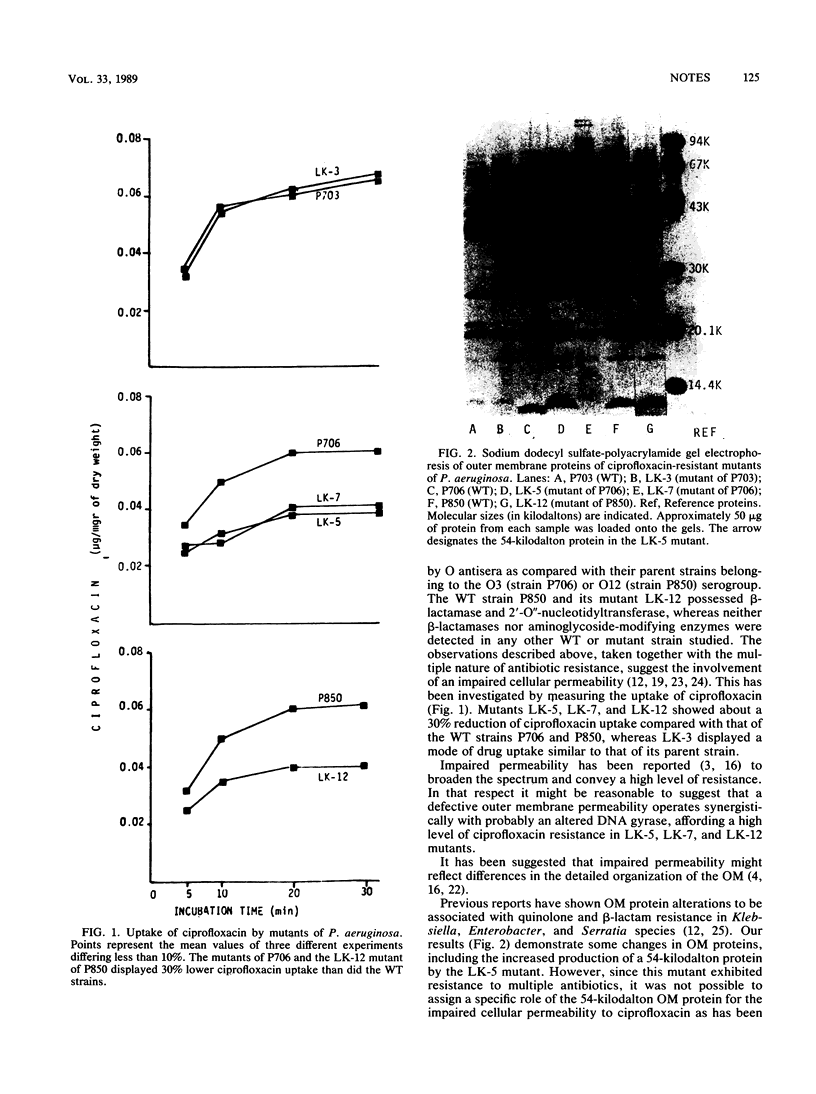
Spontaneous mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa selected by ciprofloxacin were studied for outer membrane alterations. Acquisition of ciprofloxacin resistance was at least partially related to defects in lipopolysaccharide synthesis. When ciprofloxacin resistance was combined with resistance to beta-lactams and aminoglycosides, several alterations in outer membrane proteins were noted.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama H., Sato K., Kato T., Hirai K., Mitsuhashi S. Norfloxacin resistance in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1640–1641. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan L. E., O'Hara K., Wong S. Lipopolysaccharide changes in impermeability-type aminoglycoside resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):250–255. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büscher K. H., Cullmann W., Dick W., Opferkuch W. Imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa resulting from diminished expression of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 May;31(5):703–708. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin N. X., Neu H. C. Ciprofloxacin, a quinolone carboxylic acid compound active against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Mar;25(3):319–326. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Lolans V. T., Jackson G. G. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith L., Wilkinson S. G., Legakis N. J., Genimata V., Katsorchis T. A., Rietschel E. T. Structural alterations in the envelope of a gentamicin-resistant rough mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Sep-Oct;135B(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Hatlelid L., Bryan L. E. Correlation between lipopolysaccharide structure and permeability resistance in beta-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):181–186. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey A. J., Shahrabadi M. S., Bryan L. E. Distribution of porin and lipopolysaccharide antigens on a Pseudomonas aeruginosa permeability mutant. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):802–805. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Differences in susceptibility to quinolones of outer membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):535–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kropinski A. M., Chan L., Jarrell K., Milazzo F. H. The nature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO bacteriophage receptors. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):653–658. doi: 10.1139/m77-098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Aliferopoulou M., Papavassiliou J., Papapetropoulou M. Serotypes of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in clinical specimens in relation to antibiotic susceptibility. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Sep;16(3):458–463. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.458-463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Koukoubanis N., Malliara K., Michalitsianos D., Papavassiliou J. Importance of carbenicillin and gentamicin cross-resistant serotype 0:12 Pseudomonas aeruginosa in six Athens hospitals. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;6(3):300–303. doi: 10.1007/BF02017618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michéa-Hamzehpour M., Auckenthaler R., Regamey P., Pechère J. C. Resistance occurring after fluoroquinolone therapy of experimental Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1803–1808. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preheim L. C., Penn R. G., Sanders C. C., Goering R. V., Giger D. K. Emergence of resistance to beta-lactam and aminoglycoside antibiotics during moxalactam therapy of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Dec;22(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V., Werner V. Selection of multiple antibiotic resistance by quinolones, beta-lactams, and aminoglycosides with special reference to cross-resistance between unrelated drug classes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Dec;26(6):797–801. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer B. G., Legakis N. J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence for the involvement of lipopolysaccharide in determining outer membrane permeability to carbenicillin and gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1985 Aug;152(2):351–355. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.2.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Kumada T., Hsieh W. C., Chung H. Y., Chong Y., Hare R. S., Miller G. H., Sabatelli F. J., Howard J. Comparison of aminoglycoside resistance patterns in Japan, Formosa, and Korea, Chile, and the United States. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Aug;28(2):282–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. The fluoroquinolones: structures, mechanisms of action and resistance, and spectra of activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Oct;28(4):581–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]