Abstract
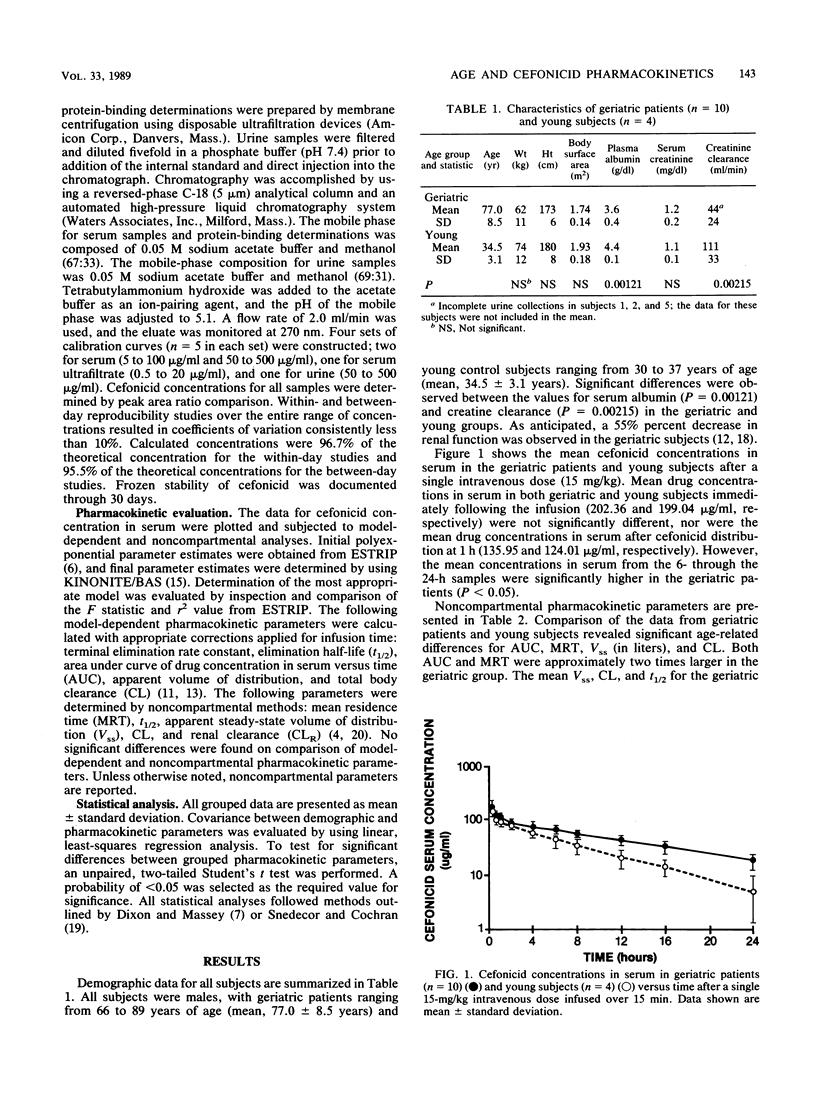
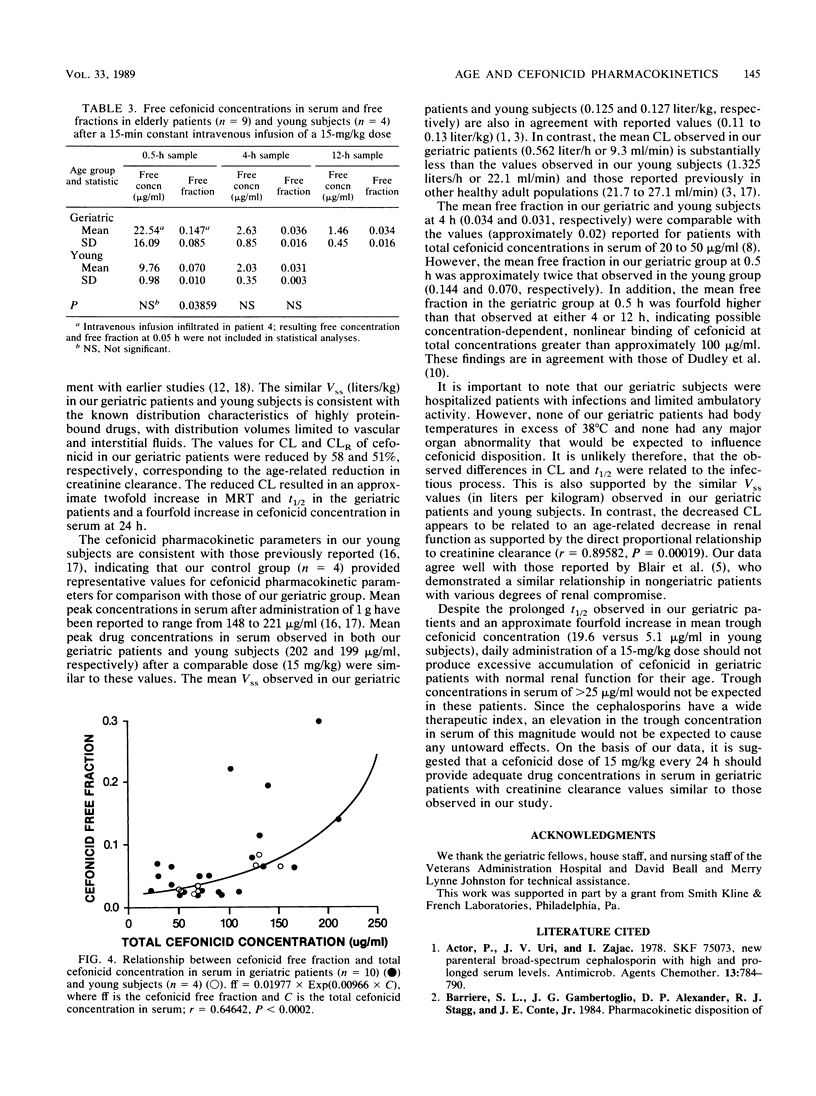
Cefonicid (15 mg/kg) was administered intravenously at a constant rate of infusion over 15 min to 10 geriatric patients (mean age, 77 years) and to 4 young subjects (mean age, 35 years). Model-dependent and noncompartmental pharmacokinetic parameters were calculated and found to be congruous; noncompartmental data are reported. Significant differences in the values for area under the curve, mean residence time, total body clearance, and renal clearance were observed between the geriatric and young groups. Mean elimination half-life values were 9.59 and 4.88 h for the geriatric and young groups, respectively. Total body and renal clearances were inversely correlated to age and directly correlated to creatinine clearance. Free fraction was not correlated to albumin concentration but was correlated exponentially to total cefonicid concentration. Despite the prolonged half-life values observed in our geriatric patients, the difference in mean trough concentrations was slight. Daily administration of a 15-mg/kg dose should provide adequate concentrations in serum and should not produce appreciable accumulation in geriatric patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Actor P., Uri J. V., Zajac I., Guarini J. R., Phillips L., Pitkin D. H., Berges D. A., Dunn G. L., Hoover J. R., Weisbach J. A. SK&F 75073, new parenteral broad-spectrum cephalosporin with high and prolonged serum levels. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 May;13(5):784–790. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.5.784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barriere S. L., Hatheway G. J., Gambertoglio J. G., Lin E. T., Conte J. E., Jr Pharmacokinetics of cefonicid, a new broad-spectrum cephalosporin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jun;21(6):935–938. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.6.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benet L. Z., Galeazzi R. L. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution. J Pharm Sci. 1979 Aug;68(8):1071–1074. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600680845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair A. D., Maxwell B. M., Forland S. C., Jacob L., Cutler R. E. Cefonicid kinetics in subjects with normal and impaired renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1984 Jun;35(6):798–803. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1984.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Manno J. E. ESTRIP, a BASIC computer program for obtaining initial polyexponential parameter estimates. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Dec;67(12):1687–1691. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600671214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Quintiliani R., Nightingale C. H. Review of cefonicid, a long-acting cephalosporin. Clin Pharm. 1984 Jan-Feb;3(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M. N., Shyu W. C., Nightingale C. H., Quintiliani R. Effect of saturable serum protein binding on the pharmacokinetics of unbound cefonicid in humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Oct;30(4):565–569. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley M., Barriere S., Mills J. Cost comparisons among antimicrobial agents. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):689–689. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Sellers E. M., Shader R. I. Drug therapy: drug disposition in old age. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 6;306(18):1081–1088. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205063061804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo J. C., Riegelman S. Assessment of pharmacokinetic constants from postinfusion blood curves obtained after I.V. infusion. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jan;59(1):53–55. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan W. J., Martin P., Mason B. J. Protein intake and serum albumin levels in the elderly. Gerontology. 1977;23(5):360–367. doi: 10.1159/000212209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen-Kudsk F. A microcomputer program in Basic for iterative, non-linear data-fitting to pharmacokinetic functions. Int J Biomed Comput. 1983 Mar;14(2):95–107. doi: 10.1016/0020-7101(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitkin D., Dubb J., Actor P., Alexander F., Ehrlich S., Familiar R., Stote R. Kinetics and renal handling of cefonicid. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Nov;30(5):587–593. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G. Biological determinants of altered pharmacokinetics in the elderly. Gerontology. 1982;28 (Suppl 1):8–17. doi: 10.1159/000212568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Dec;6(6):547–558. doi: 10.1007/BF01062109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


