Abstract
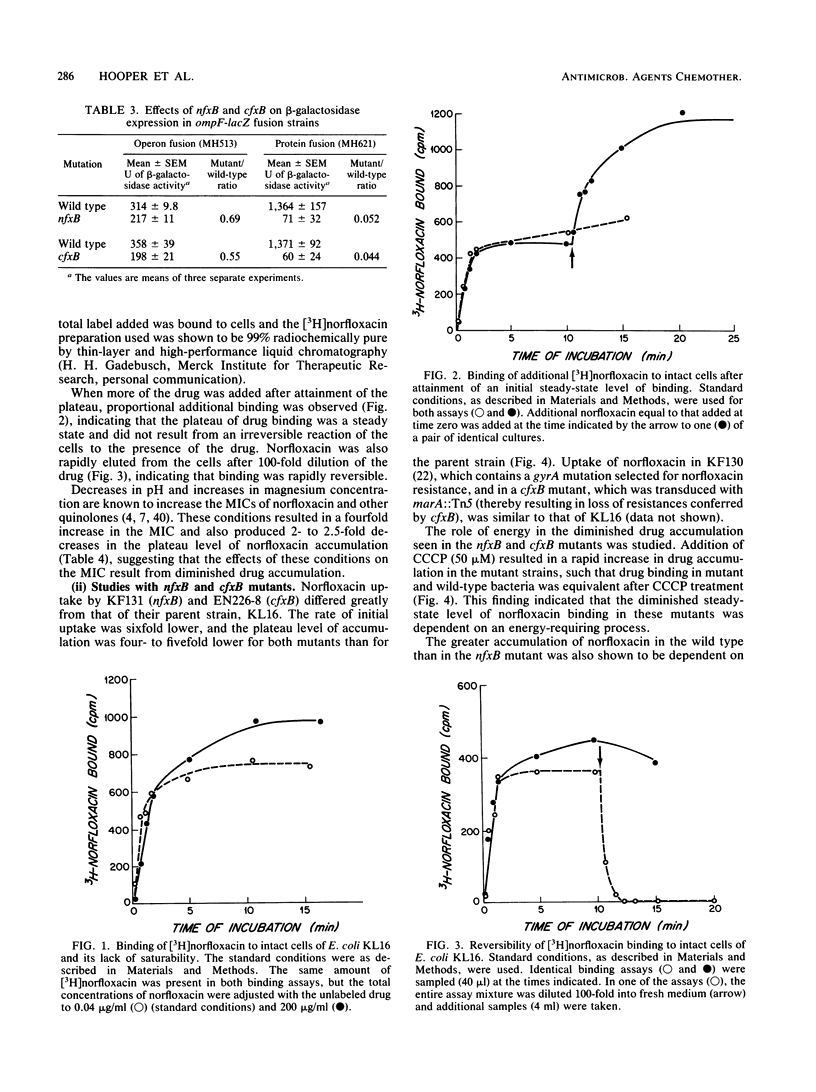
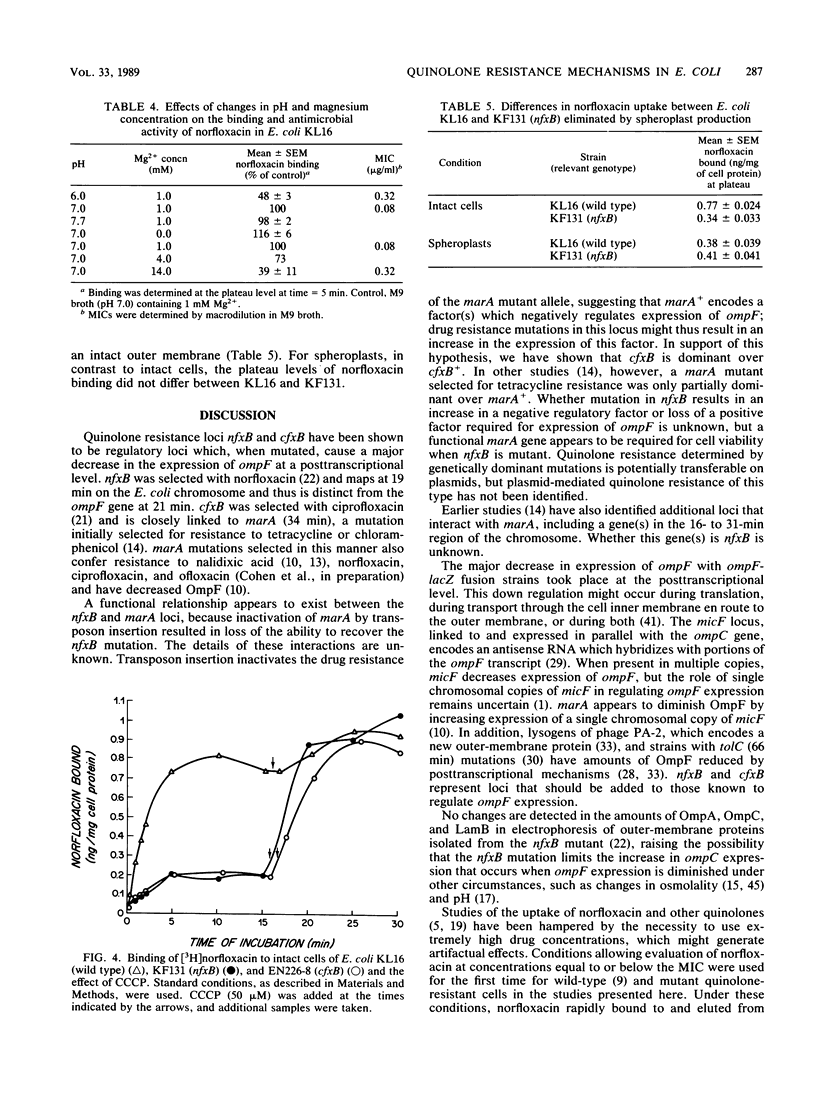
Two genetic loci selected for norfloxacin (nfxB) and ciprofloxacin (cfxB) resistance were characterized. Both mutations have previously been shown to confer pleiotropic resistance to quinolones, chloramphenicol, and tetracycline and to decrease expression of porin outer-membrane protein OmpF. nfxB was shown to map at about 19 min and thus to be genetically distinct from ompF (21 min), and cfxB was shown to be very closely linked to marA (34 min). cfxB was dominant over cfxB+ in merodiploids, in contrast to other quinolone resistance mutations. The two loci appear to interact functionally, because nfxB was not expressed in the presence of marA::Tn5. Both nfxB and cfxB decreased the expression of ompF up to 50-fold at the posttranscriptional level as determined in strains containing ompF-lacZ operon and protein fusions. Both mutations also decreased norfloxacin accumulation in intact cells. This decrease in accumulation was abolished by energy inhibitors and by removal of the outer membrane. These findings, in conjunction with those of Cohen et al. (S. P. Cohen, D. C. Hooper, J. S. Wolfson, K. S. Souza, L. M. McMurry, and S. B. Levy, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 32:1187-1191, 1988), suggest a model for quinolone resistance by decreased permeation in which decreased diffusion through porin channels in the outer membrane interacts with a saturable drug efflux system at the inner membrane.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Matsuyama S., Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Function of micF as an antisense RNA in osmoregulatory expression of the ompF gene in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3007–3012. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3007-3012.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alphen W. V., Lugtenberg B. Influence of osmolarity of the growth medium on the outer membrane protein pattern of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):623–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.623-630.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama H., Sato K., Fujii T., Fujimaki K., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification of Citrobacter freundii DNA gyrase and inhibition by quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jan;32(1):104–109. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama H., Sato K., Kato T., Hirai K., Mitsuhashi S. Norfloxacin resistance in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Oct;31(10):1640–1641. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.10.1640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A., Petermüller C. In vitro activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Apr;2(2):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02001575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard J., Wong S., Bryan L. E. Accumulation of enoxacin by Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1348–1354. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitner R. M., Kuempel P. L. P1 transduction map spanning the replication terminus of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(2):208–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00272906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser J., Dudley M. N., Gilbert D., Zinner S. H. Influence of medium and method on the in vitro susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria to ciprofloxacin and enoxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):927–929. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Georgopapadakou N. H. Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., McMurry L. M., Levy S. B. Endogenous active efflux of norfloxacin in susceptible Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., McMurry L. M., Levy S. B. marA locus causes decreased expression of OmpF porin in multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5416–5422. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5416-5422.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daikos G. L., Lolans V. T., Jackson G. G. Alterations in outer membrane proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with selective resistance to quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):785–787. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. M., Levy S. B. Amplifiable resistance to tetracycline, chloramphenicol, and other antibiotics in Escherichia coli: involvement of a non-plasmid-determined efflux of tetracycline. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):531–540. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.531-540.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. M., Levy S. B. Gene in the major cotransduction gap of the Escherichia coli K-12 linkage map required for the expression of chromosomal resistance to tetracycline and other antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):541–548. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.541-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. The ompB locus and the regulation of the major outer membrane porin proteins of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):23–43. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90364-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyde M., Portalier R. Regulation of major outer membrane porin proteins of Escherichia coli K 12 by pH. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):511–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00328148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Differences in susceptibility to quinolones of outer membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):535–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Ng E. Y., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of action of and resistance to ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Ohue T., Yamagishi J., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. Mode of incomplete cross-resistance among pipemidic, piromidic, and nalidixic acids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Aug;14(2):240–245. doi: 10.1128/aac.14.2.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Sato K., Fujii T., Hirai K., Inoue M., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Some properties of subunits of DNA gyrase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and its nalidixic acid-resistant mutant. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2322–2325. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2322-2325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L. M., Cullinane J. C., Levy S. B. Transport of the lipophilic analog minocycline differs from that of tetracycline in susceptible and resistant Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):791–799. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R., Reeves P. R. Role of micF in the tolC-mediated regulation of OmpF, a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4722–4730. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4722-4730.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A unique mechanism regulating gene expression: translational inhibition by a complementary RNA transcript (micRNA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1966–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morona R., Reeves P. The tolC locus of Escherichia coli affects the expression of three major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1016-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. VII. Evidence that bacteriophage-directed protein 2 functions as a pore. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1181-1189.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Haas D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO to nalidixic acid and low levels of beta-lactam antibiotics: mapping of chromosomal genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):242–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosner J. L. Formation, induction, and curing of bacteriophage P1 lysogens. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):679–689. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato K., Inoue Y., Fujii T., Aoyama H., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Purification and properties of DNA gyrase from a fluoroquinolone-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Nov;30(5):777–780. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.5.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T. Mutational resistance to 4-quinolone antibacterial agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;3(4):347–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01977492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T., Ratcliffe N. T. Einfluss von pH-Wert und Magnesium auf die antibakterielle Aktivität von Chinolonpräparaten. Infection. 1986;14 (Suppl 1):S31–S35. doi: 10.1007/BF01645195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodergren E. J., Davidson J., Taylor R. K., Silhavy T. J. Selection for mutants altered in the expression or export of outer membrane porin OmpF. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1047–1053. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1047-1053.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C., Ng E. Y., Souza K. S., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Antagonism of wild-type and resistant Escherichia coli and its DNA gyrase by the tricyclic 4-quinolone analogs ofloxacin and S-25930 stereoisomers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1861–1863. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagishi J., Furutani Y., Inoue S., Ohue T., Nakamura S., Shimizu M. New nalidixic acid resistance mutations related to deoxyribonucleic acid gyrase activity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):450–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.450-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F., Nikaido H. Diffusion of beta-lactam antibiotics through the porin channels of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Jan;27(1):84–92. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeiler H. J. Influence of pH and human urine on the antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin and ofloxacin. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(5):335–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


