Abstract
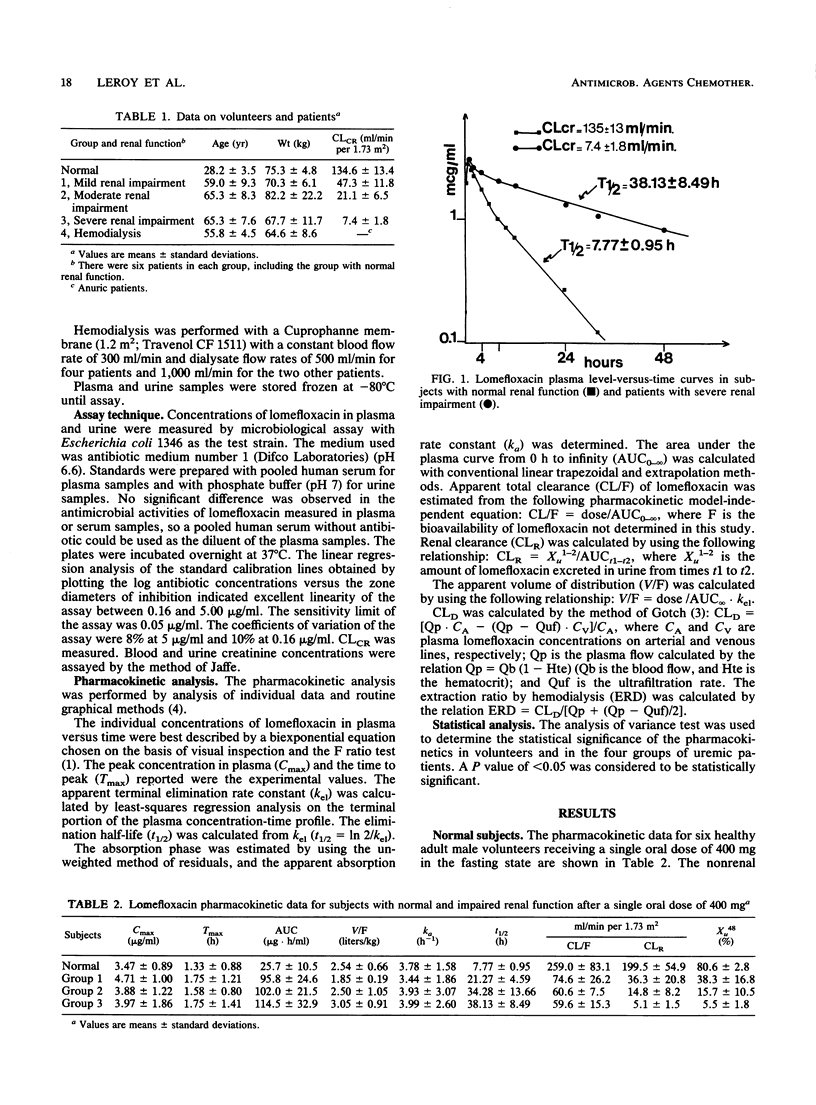
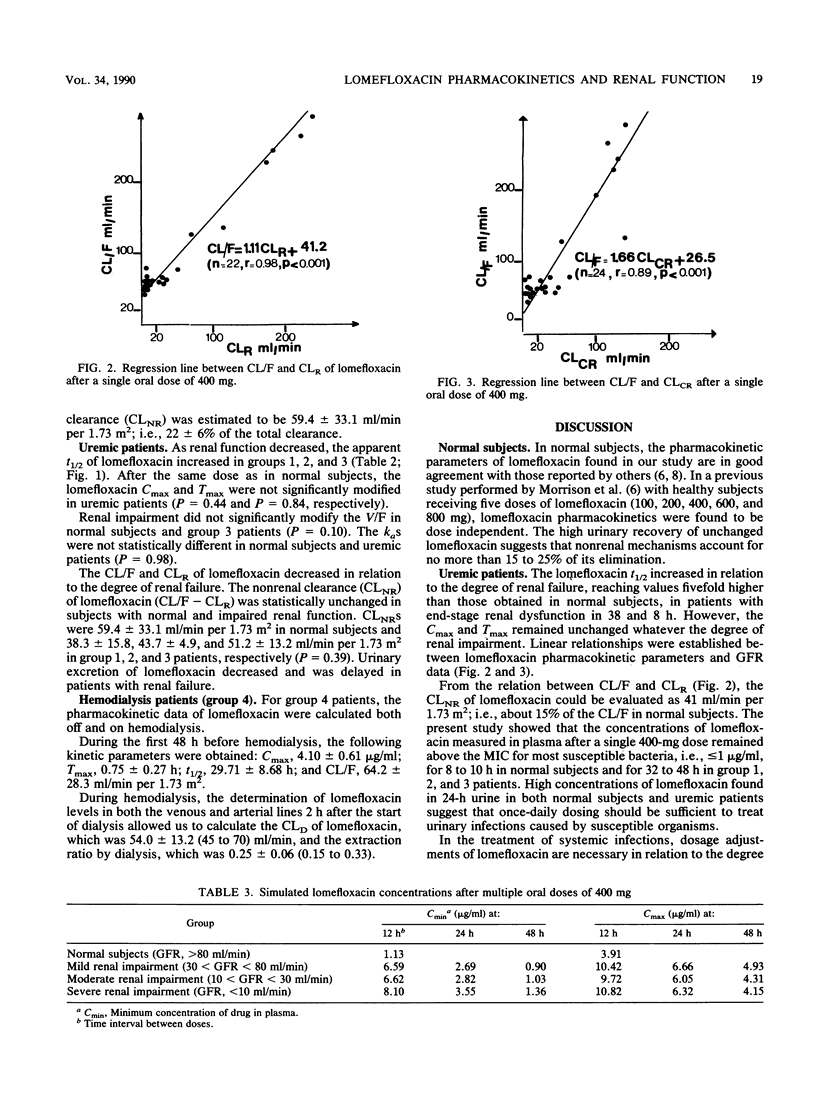
Lomefloxacin pharmacokinetics were investigated in 6 normal subjects and 24 uremic patients after a single oral dose of 400 mg. In subjects with normal renal function, the peak level in plasma averaged 3.5 +/- 0.9 micrograms/ml (mean +/- standard deviation) and was obtained at 1.3 +/- 0.9 h. The absorption rate constant was 3.8 +/- 1.6 h-1. The terminal half-life was 7.77 +/- 0.95 h. The apparent volume of distribution was 2.54 +/- 0.66 liters/kg. Total body and renal clearances were 259 +/- 83 and 200 +/- 55 ml/min per 1.73 m2, respectively. The percentage of the dose recovered unchanged in 48-h urine was 80.6 +/- 2.8. In uremic patients, the terminal half-life increased in relation to the degree of renal failure: from 8 h in normal subjects to 38 h in severely uremic patients (glomerular filtration rate, less than 10 ml/min). Renal insufficiency did not significantly modify the peak level in plasma, the time to peak, the apparent volume of distribution, or the nonrenal clearance of lomefloxacin. The dialysis clearance of lomefloxacin was 54 +/- 13 ml/min. Linear relationships were found between lomefloxacin pharmacokinetic parameters and glomerular filtration rate data. Dosage adjustments are necessary in uremic patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boxenbaum H. G., Riegelman S., Elashoff R. M. Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1974 Apr;2(2):123–148. doi: 10.1007/BF01061504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillastre J. P., Leroy A., Humbert G. Ofloxacin pharmacokinetics in renal failure. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):156–160. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt D. J., Kock-Weser J. Drug therapy. Clinical Pharmacokinetics (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 2;293(14):702–705. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510022931406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose T., Okezaki E., Kato H., Ito Y., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro and in vivo activity of NY-198, a new difluorinated quinolone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jun;31(6):854–859. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.6.854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison P. J., Mant T. G., Norman G. T., Robinson J., Kunka R. L. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of lomefloxacin after sequentially increasing oral doses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1503–1507. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the newer antibacterial 4-quinolones. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):96–121. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. W., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Griggs D., Wise R. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of orally administered lomefloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Oct;32(10):1508–1510. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.10.1508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Andrews J. M., Ashby J. P., Matthews R. S. In vitro activity of lomefloxacin, a new quinolone antimicrobial agent, in comparison with those of other agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 May;32(5):617–622. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.5.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


