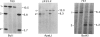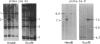Abstract
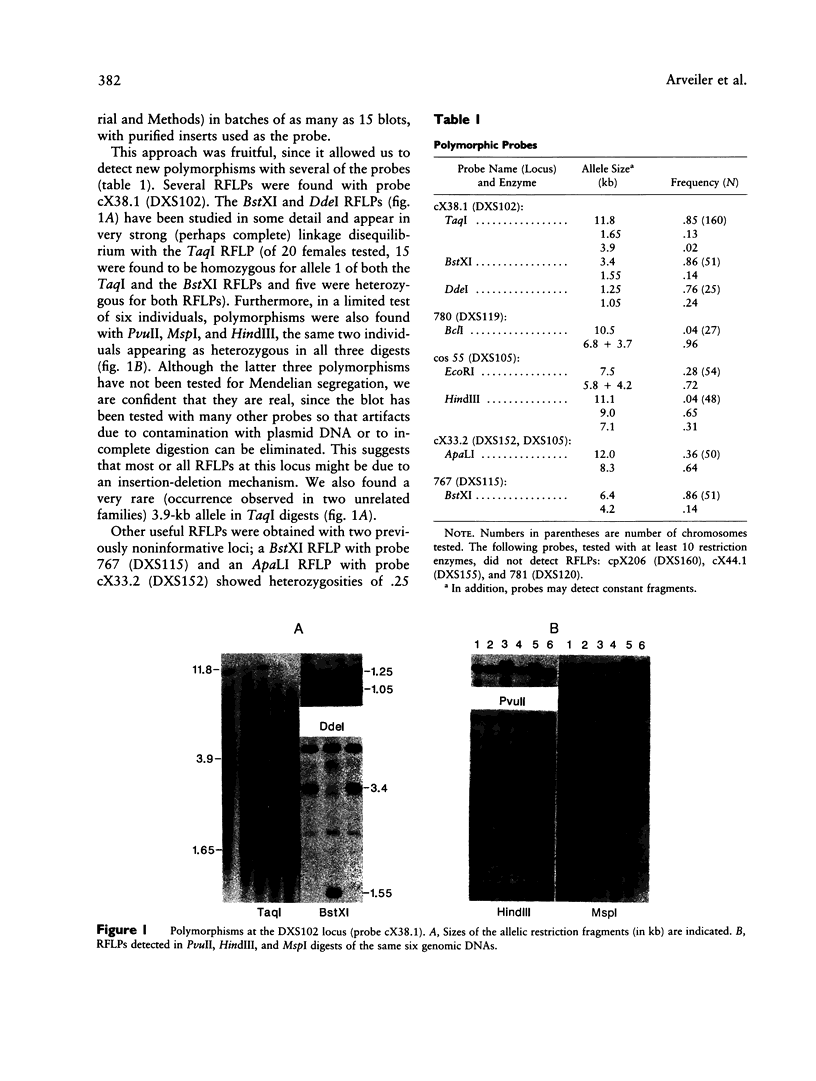
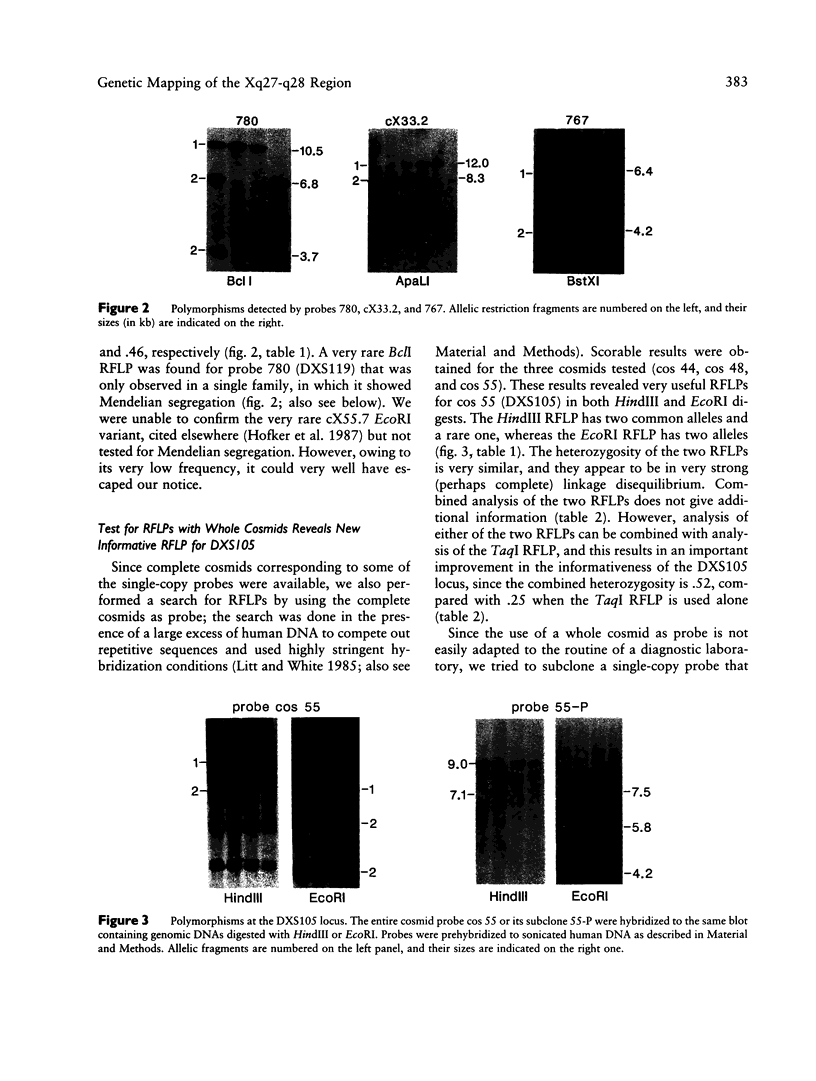
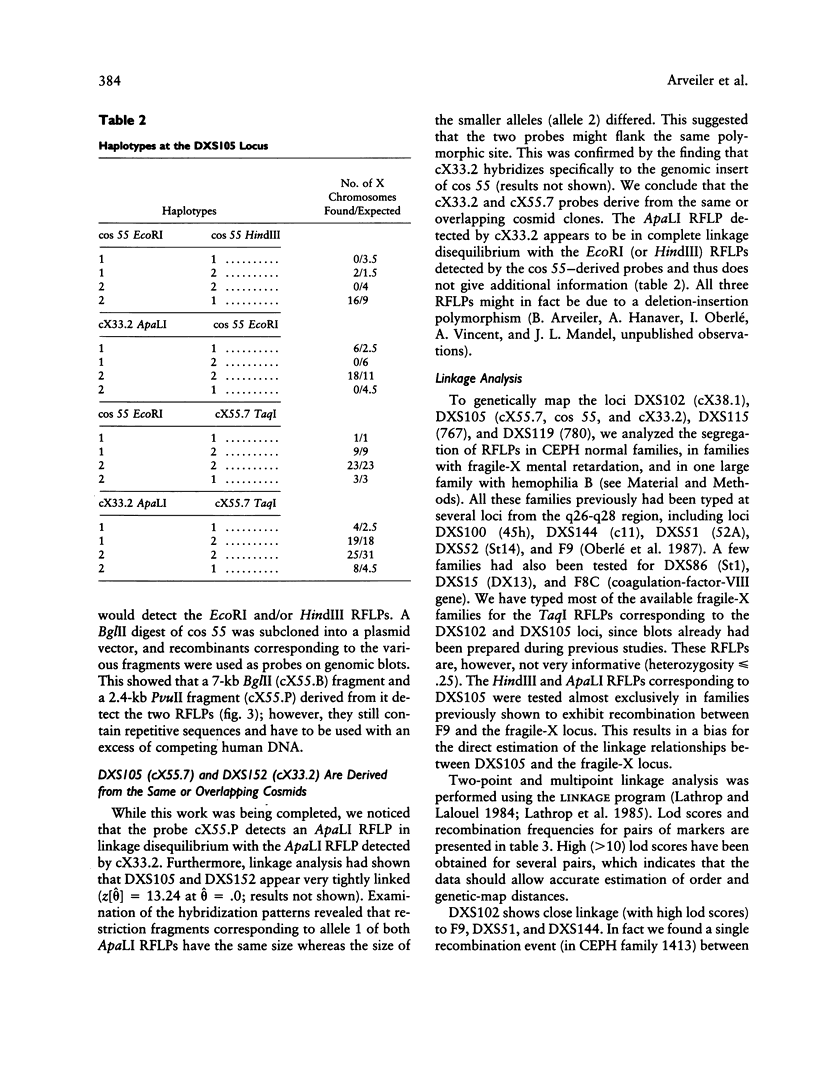
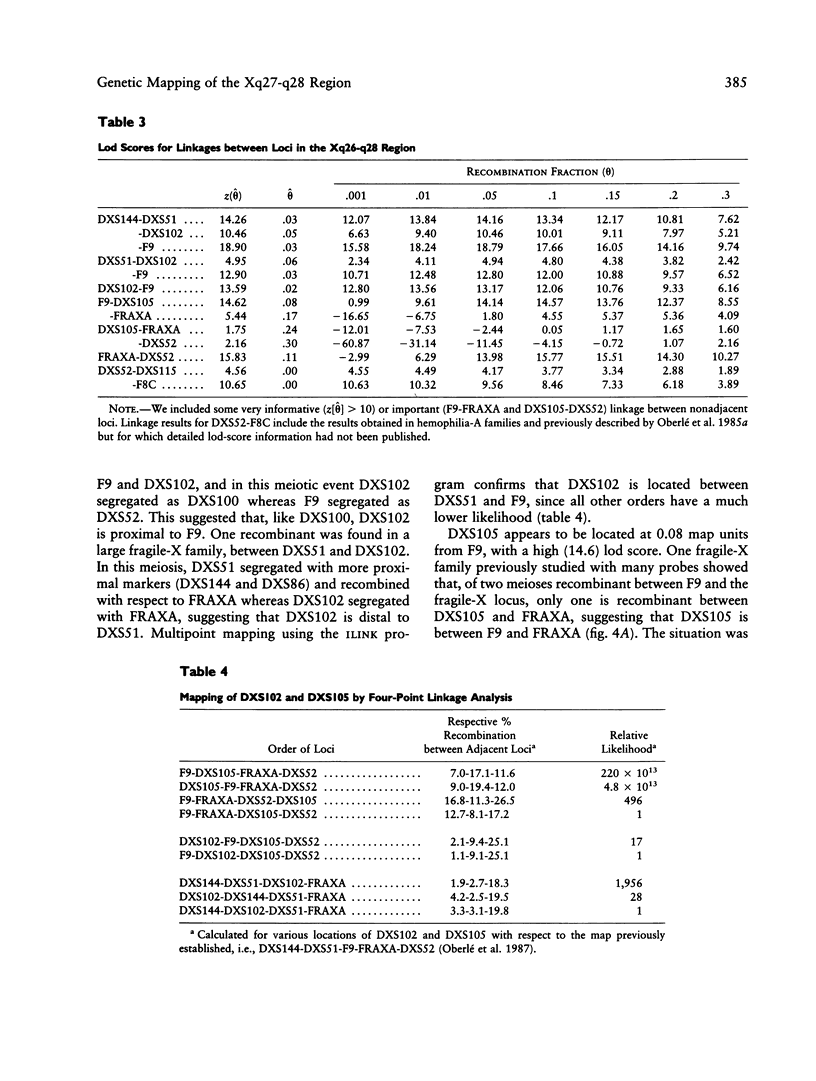
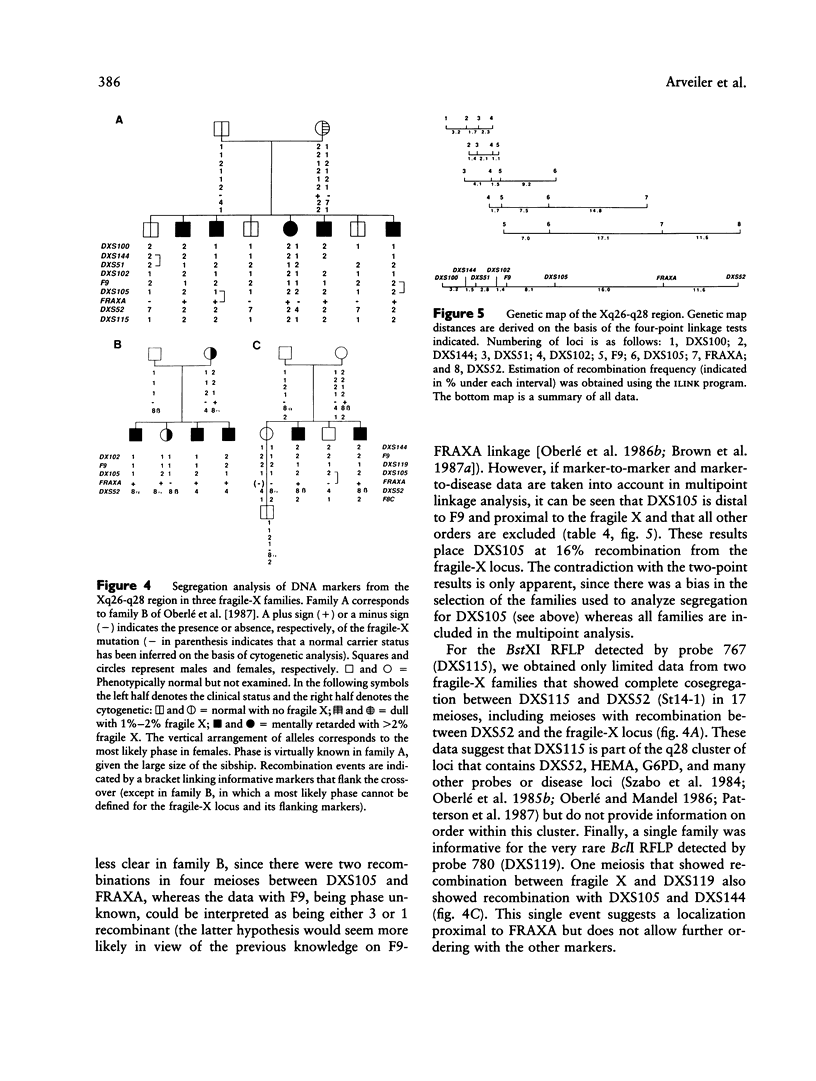
We have characterized and genetically mapped new polymorphic DNA markers in the q27-q28 region of the X chromosome. New informative RFLPs have been found for DXS105, DXS115, and DXS152. In particular, heterozygosity at the DXS105 locus has been increased from 25% to 52%. We have shown that DXS105 and DXS152 are contained within a 40-kb region. A multipoint linkage analysis was performed in fragile-X families and in large normal families from the Centre d'Etudes du Polymorphisme Humain (CEPH). This has allowed us to establish the order centromere-DXS144-DXS51-DXS102-F9-DXS105-FRAX A-(F8, DXS15, DXS52, DXS115). DXS102 is close to the hemophilia-B locus (z[theta] = 13.6 at theta = .02) and might thus be used as an alternative probe for diagnosis in Hemophila-B families not informative for intragenic RFLPs. DXS105 is 8% recombination closer to the fragile-X locus than F9 (z[theta] = 14.6 at theta = .08 for the F9-DXS105 linkage) and should thus be a better marker for analysis of fragile-X families. However, the DXS105 locus appears to be still loosely linked to the fragile-X locus in some families. The multipoint estimation for recombination between DXS105 and FRAXA is .16 in our set of data. Our data indicate that the region responsible for the heterogeneity in recombination between F9 and the fragile-X locus is within the DXS105-FRAXA interval.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown W. T., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Jenkins E. C. DNA linkage studies in the fragile X syndrome suggest genetic heterogeneity. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):643–664. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Jenkins E. C., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Krawczun M. S., Duncan C. J., Sklower S. L., Fisch G. S. Further evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):311–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00284100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Wu Y., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Dobkin C. S., Jenkins E. C. RFLP for linkage analysis of fragile X syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Jan 31;1(8527):280–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Jaye M., Mandel J. L. Close linkage of fragile X-mental retardation syndrome to haemophilia B and transmission through a normal male. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):701–704. doi: 10.1038/306701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. M., Pirrit L. A., Yates J. R., Crossley J. A., Imrie S. J., Colgan J. M. Linkage analysis using multiple Xq DNA polymorphisms in normal families, families with the fragile X syndrome, and other families with X linked conditions. J Med Genet. 1987 Jan;24(1):14–22. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Veenema H., McGlade S., Harper K., Tommerup N., Nielsen K. B., Mikkelsen M., Beighton P. Linkage studies of X-linked mental retardation: high frequency of recombination in the telomeric region of the human X chromosome (fragile site/linkage/recombination/X chromosome). Hum Genet. 1985;70(3):249–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00273451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., White R. The genetic linkage map of the human X chromosome. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):753–758. doi: 10.1126/science.4059909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Skraastad M. I., Carpenter N. J., Veenema H., Connor J. M., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Efficient isolation of X chromosome-specific single-copy probes from a cosmid library of a human X/hamster hybrid-cell line: mapping of new probes close to the locus for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Wapenaar M. C., Goor N., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome-specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet. 1985;70(2):148–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins E. C., Brown W. T., Wilson M. G., Lin M. S., Alfi O. S., Wassman E. R., Brooks J., Duncan C. J., Masia A., Krawczun M. S. The prenatal detection of the fragile X chromosome: review of recent experience. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):297–311. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320230123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., White R. L. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA revealed by cosmid-derived probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan L., Holden J. J., White B. N. A DNA marker closely linked to the factor IX (haemophilia B) gene. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):381–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00284113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberle I., Camerino G., Heilig R., Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Crapanzano C., Mannucci P. M., Mandel J. L. Genetic screening for hemophilia A (classic hemophilia) with a polymorphic DNA probe. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 14;312(11):682–686. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503143121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Moisan J. P., Grzeschik K. H., Hellkuhl B., Hors-Cayla M. C., Van Cong N., Weil D., Mandel J. L. Characterization of a set of X-linked sequences and of a panel of somatic cell hybrids useful for the regional mapping of the human X chromosome. Hum Genet. 1986 Jan;72(1):43–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00278816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Camerino G., Wrogemann K., Arveiler B., Hanauer A., Raimondi E., Mandel J. L. Multipoint genetic mapping of the Xq26-q28 region in families with fragile X mental retardation and in normal families reveals tight linkage of markers in q26-q27. Hum Genet. 1987 Sep;77(1):60–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00284716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Drayna D., Camerino G., White R., Mandel J. L. The telomeric region of the human X chromosome long arm: presence of a highly polymorphic DNA marker and analysis of recombination frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Heilig R., Moisan J. P., Kloepfer C., Mattéi G. M., Mattéi J. F., Boué J., Froster-Iskenius U., Jacobs P. A., Lathrop G. M. Genetic analysis of the fragile-X mental retardation syndrome with two flanking polymorphic DNA markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1016–1020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberlé I., Mandel J. L. From hemophilia B to hemophilia A via the fragile X locus: genes and recombination in the distal region of the human X chromosome long arm. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1986;8:51–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Kenwrick S., Thibodeau S., Faulk K., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Davies K. E. Mapping of DNA markers close to the fragile site on the human X chromosome at Xq27.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2639–2651. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. L., Jacobs P. A., Morton N. E., Froster-Iskenius U., Howard-Peebles P. N., Nielsen K. B., Partington M. W., Sutherland G. R., Turner G., Watson M. Further segregation analysis of the fragile X syndrome with special reference to transmitting males. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):289–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00291644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo P., Purrello M., Rocchi M., Archidiacono N., Alhadeff B., Filippi G., Toniolo D., Martini G., Luzzatto L., Siniscalco M. Cytological mapping of the human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase gene distal to the fragile-X site suggests a high rate of meiotic recombination across this site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7855–7859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G., Jacobs P. Marker (X)-linked mental retardation. Adv Hum Genet. 1983;13:83–112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8342-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenema H., Carpenter N. J., Bakker E., Hofker M. H., Ward A. M., Pearson P. L. The fragile X syndrome in a large family. III. Investigations on linkage of flanking DNA markers with the fragile site Xq27. J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;24(7):413–421. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winship P. R., Anson D. S., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Carrier detection in haemophilia B using two further intragenic restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8861–8872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]