Abstract
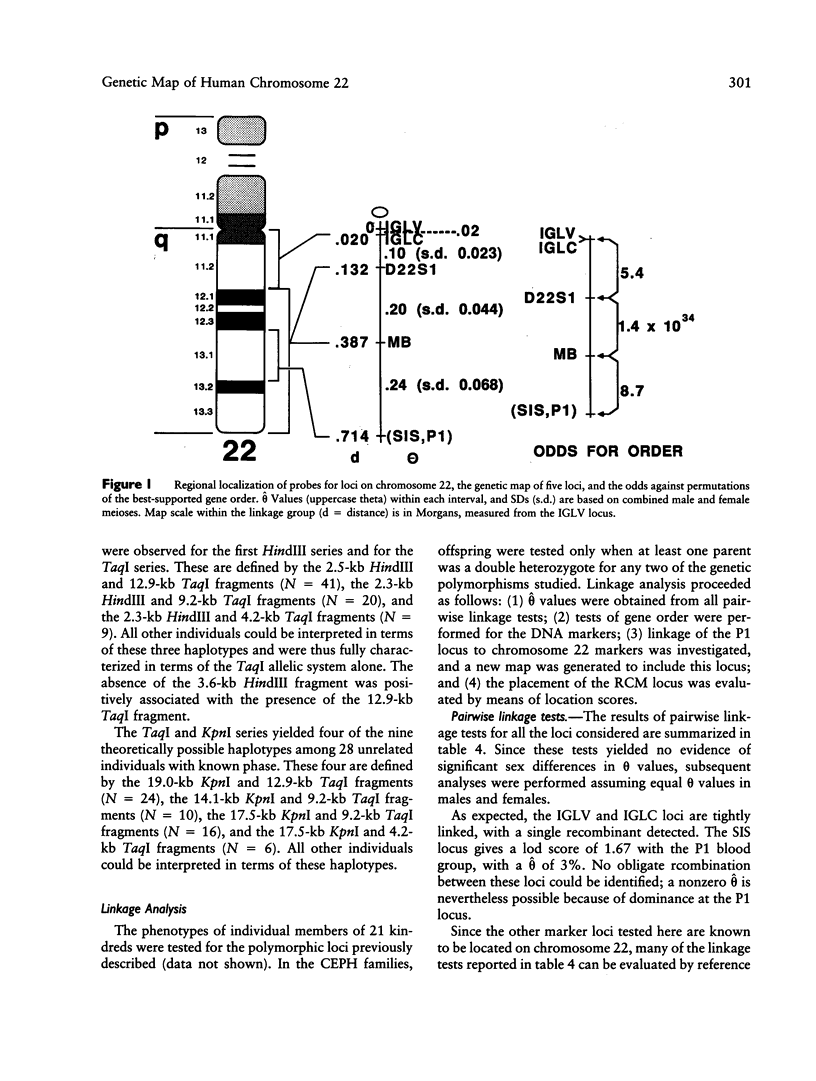
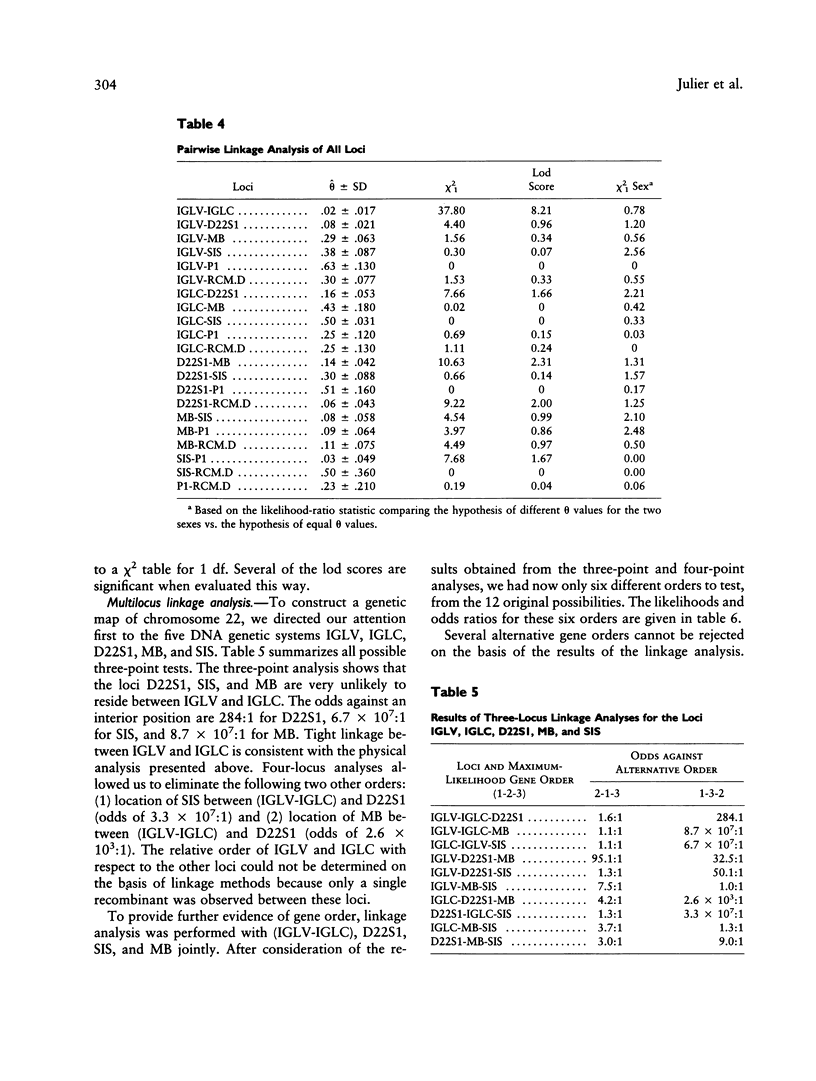
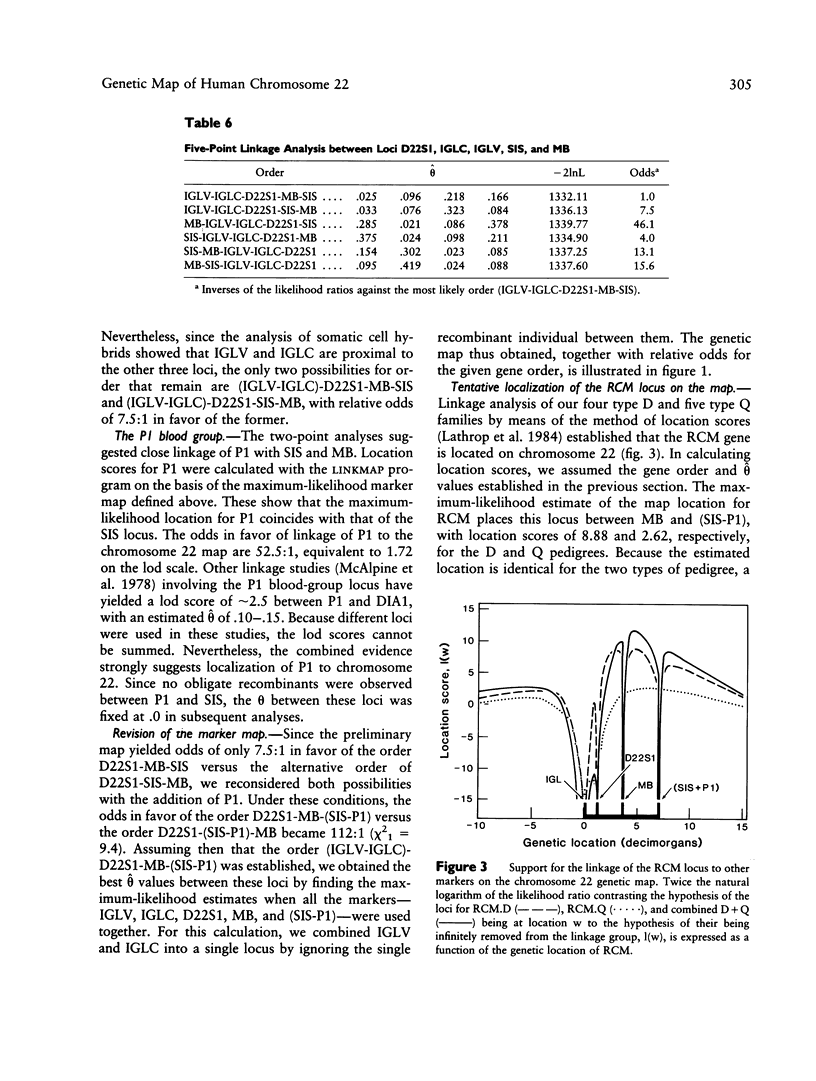
A genetic map of human chromosome 22 has been derived from physical assignments and multilocus linkage analysis. It consists of the loci for the immunoglobulin lambda light-chain variable (IGLV) and immunoglobulin lambda light-chain constant (IGLC) regions, myoglobin (MB), the sis proto-oncogene (SIS), and an arbitrary probe (D22S1). The first RFLPs at the loci for SIS, IGLV, and MB are described. The most likely gene order on the basis of multilocus analysis was cen-(IGLV-IGLC)-D22S1-MB-SIS. This map provides further evidence for localization of the P1 polymorphism of the P blood group to chromosome 22, close to the SIS locus. Analysis of families segregating recessive congenital methemoglobinemia (RCM), a disease in which the cytochrome b5 reductase is defective, as well as of families with cases of hereditary low levels of cytochrome b5 reductase activity, confirmed that the locus responsible for RCM is on chromosome 22. Biochemical studies had already suggested that mutation at the cytochrome b5 reductase locus (DIA1) is responsible for RCM. We found no evidence of genetic heterogeneity between the families segregating RCM and the families exhibiting cases of low cytochrome b5 reductase activity. Linkage analysis indicated that the most probable location of DIA1 lies between MB and SIS.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. L., Szajnert M. F., Kaplan J. C., McColl L., Young B. D. The isolation of a human Ig V lambda gene from a recombinant library of chromosome 22 and estimation of its copy number. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6647–6661. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu I. M., Reddy E. P., Givol D., Robbins K. C., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Nucleotide sequence analysis identifies the human c-sis proto-oncogene as a structural gene for platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90307-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Buckton K. E., Robinson J. A. Family studies with chromosomes 21 and 22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):518–520. doi: 10.1159/000131013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gallo R. C., Giallongo A., Croce C. M. Chromosomal localization of the human homolog (c-sis) of the simian sarcoma virus onc gene. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.6291150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiberg H., Møller N., Mohr J., Nielsen L. S. Linkage of transcobalamin II (TC2) to the P blood group system and assignment to chromosome 22. Clin Genet. 1986 May;29(5):354–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb00504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanuel B. S., Selden J. R., Wang E., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. In situ hybridization and translocation breakpoint mapping. I. Nonidentical 22q11 breakpoints for the t(9;22) of CML and the t(8;22) of Burkitt lymphoma. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(2):127–131. doi: 10.1159/000132044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellous M., Billardon C., Dausset J., Frézal J. Linkage probable entre les locus "HLA" et "P". C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Jun 28;272(26):3356–3359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. A., Povey S., Bobrow M., Solomon E., Boyd Y., Carritt B. Assignment of the DIA1 locus to chromosome 22. Ann Hum Genet. 1977 Oct;41(2):151–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1977.tb01909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Mandel J. L., Tolstoshev P., Jaye M., De la Salle H., Lecocq J. P. Carrier detection of Hemophilia B by using a restriction site polymorphism associated with the coagulation Factor IX gene. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1491–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollis G. F., Mitchell K. F., Battey J., Potter H., Taub R., Lenoir G. M., Leder P. A variant translocation places the lambda immunoglobulin genes 3' to the c-myc oncogene in Burkitt's lymphoma. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):752–755. doi: 10.1038/307752a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hors-Cayla M. C., Junien C., Heuertz S., Mattei J. F., Frézal J. Regional assignment of arylsulfatase A, mitochondrial aconitase and NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase by somatic cell hybridization. Hum Genet. 1981;58(2):140–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00278698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Blanchetot A., Weller P., Geurts van Kessel A., Spurr N., Solomon E., Goodfellow P. The human myoglobin gene: a third dispersed globin locus in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3235–3243. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Seeburg P. H., Gray A., Ullrich A., Scrace G. The c-sis gene encodes a precursor of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):921–928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephs S. F., Guo C., Ratner L., Wong-Staal F. Human-proto-oncogene nucleotide sequences corresponding to the transforming region of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1984 Feb 3;223(4635):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.6318322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junien C., Vibert M., Weil D., Van-Cong N., Kaplan J. C. Assignment of NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase (DIA1 locus) to human chromosome 22. Hum Genet. 1978 Jun 27;42(3):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00291301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. C., Aurias A., Julier C., Prieur M., Szajnert M. F. Human chromosome 22. J Med Genet. 1987 Feb;24(2):65–78. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.2.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. C., Leroux A., Beauvais P. Formes cliniques et biologiques du déficit en cytochrome b5 réductase. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1979;173(2):368–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Cavenee W., Callahan P., Holm T., O'Connell P., Thompson K., Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., White R. A primary genetic map of chromosome 13q. Am J Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;39(4):425–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux A., Junien C., Kaplan J., Bamberger J. Generalised deficiency of cytochrome b5 reductase in congenital methaemoglobinaemia with mental retardation. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):619–620. doi: 10.1038/258619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlpine P. J., Kaita H., Lewis M. Is the DIA1 locus linked to the P blood group locus? Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):629–632. doi: 10.1159/000131040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. L., Mayall B. H., Bogart E., Moore D. H., 2nd, Perry B. H. DNA content and DNA-based centromeric index of the 24 human chromosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1126–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naiki M., Marcus D. M. An immunochemical study of the human blood group P1, P, and PK glycosphingolipid antigens. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 4;14(22):4837–4841. doi: 10.1021/bi00693a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Barker D., White R., Shows T. B. DNA polymorphic loci mapped to human chromosomes 3, 5, 9, 11, 17, 18, and 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. A simple scheme for the analysis of HLA linkages in pedigrees. Ann Hum Genet. 1978 Oct;42(2):255–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1978.tb00657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reghis A., Benabadji M., Tchen P., Kaplan J. C. Quantitative variations of red-cell cytochrome b5 reductase (NADH-methemoglobin-reductase) in the Algerian population: evidence for defective alleles. Hum Genet. 1981;59(2):148–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00293065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reghis A., Troungos C., Lostanlen D., Krishnamoorthy R., Kaplan J. C. Characterization of weak alleles at the DIA1 locus (Mustapha 1, Mustapha 2, and Mustapha 3) in the Algerian population. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):173–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00327119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Aaronson S. A. Molecular cloning of integrated simian sarcoma virus: genome organization of infectious DNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2918–2922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. M., Wright R. C. The absence of close linkage of methemoglobinemia and other loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1969 Mar;21(2):194–195. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R. A., Hollis G. F., Hieter P. A., Korsmeyer S., Waldmann T. A., Leder P. Variable amplification of immunoglobulin lambda light-chain genes in human populations. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):172–174. doi: 10.1038/304172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tippett P., Kaplan J. C. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 20, 21, and 22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):268–295. doi: 10.1159/000132177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P., Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Blanchetot A. Organization of the human myoglobin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):439–446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Leppert M., Bishop D. T., Barker D., Berkowitz J., Brown C., Callahan P., Holm T., Jerominski L. Construction of linkage maps with DNA markers for human chromosomes. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):101–105. doi: 10.1038/313101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]