Abstract
The human chromosomal assignments of genes of the creatine kinase (CK) family--loci for brain (CKBB), muscle (CKMM), and mitochondrial (CKMT) forms--were studied by Southern filter hybridization analysis of DNAs isolated from a human x rodent somatic cell hybrid clone panel. Probes for the 3'-noncoding sequences of human CKBB and CKMM hybridized concordantly only to DNAs from somatic cell hybrids containing chromosomes 14 and 19, respectively. Thus the earlier assignment of the gene coding for the CKBB isozyme to chromosome 14 was confirmed by molecular means, as was the provisional assignment of CKMM to the long arm of chromosome 19. A probe containing canine sequences for CKMM cross-hybridized with human sequences on chromosomes 14 and 19, a result consistent with the assignments of CKBB and CKMM. A probe containing human sequences for CKMT enabled the provisional assignment of CKMT to human chromosome 15. Independent hybrids with portions of the long arm of chromosome 19 missing indicated the order of genes on the long arm of chromosome 19 as being cen-GPI-(TGFB, CYP1)-[CKMM, (APOC2-ERCC1)]-(CGB, FTL). The unexpectedly more distal location of APOC2 among the genes on the long arm--and APOC2's close association with CKMM--is discussed with respect to the close linkage relationship of APOC2 to myotonic muscular dystrophy.
Full text
PDF

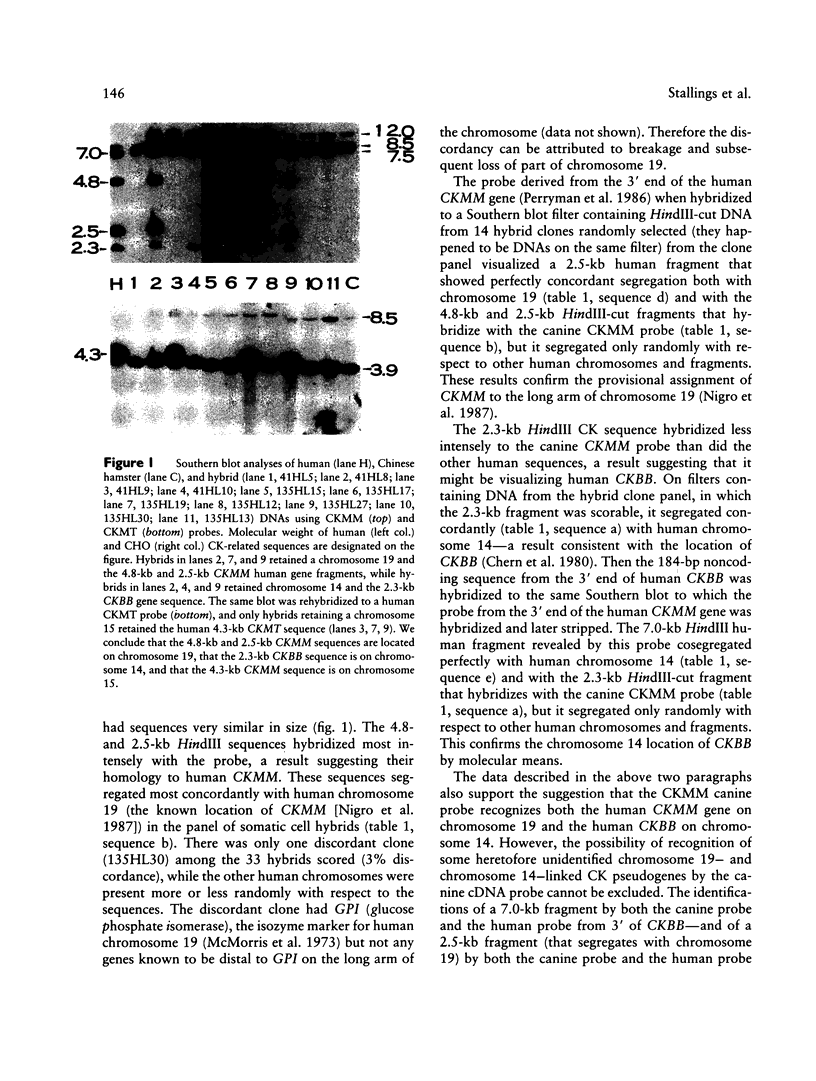





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartlett R. J., Pericak-Vance M. A., Yamaoka L., Gilbert J., Herbstreith M., Hung W. Y., Lee J. E., Mohandas T., Bruns G., Laberge C. A new probe for the diagnosis of myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1648–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.3029876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Vecoli C., Belcher D. M., Jain S. K., Drysdale J. W. Structural and functional relationships of human ferritin H and L chains deduced from cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11755–11761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook J. D., Shaw D. J., Thomas N. S., Meredith A. L., Cowell J., Harper P. S. Mapping genetic markers on human chromosome 19 using subchromosomal fragments in somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;41(1):30–37. doi: 10.1159/000132192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Hauschka S. D. The mouse muscle creatine kinase cDNA and deduced amino acid sequences: comparison to evolutionarily related enzymes. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(4):334–341. doi: 10.1007/BF02115689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chern C. J., Tan P., Park H. Chromosomal mapping of human creatine kinase (brain type) using human-rodent somatic cell hybrids. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(4):232–237. doi: 10.1159/000131491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald J. A., Wallis S. C., Kessling A., Tippett P., Robson E. B., Ball S., Davies K. E., Scambler P., Berg K., Heiberg A. Linkage relationships of the gene for apolipoprotein CII with loci on chromosome 19. Hum Genet. 1985;69(1):39–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00295527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. The cDNA for the beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin suggests evolution of a gene by readthrough into the 3'-untranslated region. Nature. 1980 Aug 14;286(5774):684–687. doi: 10.1038/286684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich U., Brunner H., Smeets D., Lambermon E., Ropers H. H. Three-point linkage analysis employing C3 and 19cen markers assigns the myotonic dystrophy gene to 19q. Hum Genet. 1987 Mar;75(3):291–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00281077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii D., Brissenden J. E., Derynck R., Francke U. Transforming growth factor beta gene maps to human chromosome 19 long arm and to mouse chromosome 7. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 May;12(3):281–288. doi: 10.1007/BF01570787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace A. M., Perryman M. B., Roberts R. Purification and characterization of human mitochondrial creatine kinase. A single enzyme form. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15346–15354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulsebos T., Wieringa B., Hochstenbach R., Smeets D., Schepens J., Oerlemans F., Zimmer J., Ropers H. H. Toward early diagnosis of myotonic dystrophy: construction and characterization of a somatic cell hybrid with a single human der(19) chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1986;43(1-2):47–56. doi: 10.1159/000132297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Bruns G. A., Breslow J. L. Isolation and sequence of a human apolipoprotein CII cDNA clone and its use to isolate and map to human chromosome 19 the gene for apolipoprotein CII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda Y., Hayes H., Uchida T., Yoshida M. C., Okada Y. Regional assignment of five genes on human chromosome 19. Chromosoma. 1987;95(1):8–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00293835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusis A. J., Heinzmann C., Sparkes R. S., Scott J., Knott T. J., Geller R., Sparkes M. C., Mohandas T. Regional mapping of human chromosome 19: organization of genes for plasma lipid transport (APOC1, -C2, and -E and LDLR) and the genes C3, PEPD, and GPI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3929–3933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorris F. A., Chen T. R., Ricciuti F., Tischfield J., Creagan R., Ruddle F. Chromosome assignments in man of the genes for two hexosephosphate isomerases. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1129–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Schweinfest C. W., Rajkovic A., Pavlovic J., Jamal S., Dottin R. P., Hart J. T., Kamarck M. E., Rae P. M., Carty M. D. cDNA cloning and mapping of the human creatine kinase M gene to 19q13. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Feb;40(2):115–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pericak-Vance M. A., Yamaoka L. H., Assinder R. I., Hung W. Y., Bartlett R. J., Stajich J. M., Gaskell P. C., Ross D. A., Sherman S., Fey G. H. Tight linkage of apolipoprotein C2 to myotonic dystrophy on chromosome 19. Neurology. 1986 Nov;36(11):1418–1423. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.11.1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman M. B., Kerner S. A., Bohlmeyer T. J., Roberts R. Isolation and sequence analysis of a full-length cDNA for human M creatine kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):981–989. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90732-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perryman M. B., Strauss A. W., Buettner T. L., Roberts R. Molecular heterogeneity of creatine kinase isoenzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 28;747(3):284–290. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90107-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. R., Shephard E. A., Ashworth A., Rabin B. R. Isolation and sequence of a human cytochrome P-450 cDNA clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick J. H., Bundey S. E., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Izatt M. M. Confirmation of linkage of the loci for myotonic dystrophy and ABH secretion. J Med Genet. 1971 Dec;8(4):407–416. doi: 10.1136/jmg.8.4.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman D., Billadello J., Gordon J., Grace A., Sobel B., Strauss A. Complete nucleotide sequence of dog heart creatine kinase mRNA: conservation of amino acid sequence within and among species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8394–8398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Brook J. D., Meredith A. L., Harley H. G., Sarfarazi M., Harper P. S. Gene mapping and chromosome 19. J Med Genet. 1986 Feb;23(1):2–10. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.1.2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siciliano M. J., Carrano A. V., Thompson L. H. Assignment of a human DNA-repair gene associated with sister-chromatid exchange to chromosome 19. Mutat Res. 1986 Aug;174(4):303–308. doi: 10.1016/0165-7992(86)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Carrano A. V., Sato K., Salazar E. P., White B. F., Stewart S. A., Minkler J. L., Siciliano M. J. Identification of nucleotide-excision-repair genes on human chromosomes 2 and 13 by functional complementation in hamster-human hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01534495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Burkhart-Schultz K., Carrano A. V., Siciliano M. J. Correction of a nucleotide-excision-repair mutation by human chromosome 19 in hamster-human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01534738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worwood M., Brook J. D., Cragg S. J., Hellkuhl B., Jones B. M., Perera P., Roberts S. H., Shaw D. J. Assignment of human ferritin genes to chromosomes 11 and 19q13.3----19qter. Hum Genet. 1985;69(4):371–374. doi: 10.1007/BF00291657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka L. H., Bartlett R. J., Ross D. A., Fey G. H., Ledbetter D. H., Bruns G., Pericak-Vance M. A., Herbstreith M. H., Roses A. D. Localization of cloned unique DNA to three different regions of chromosome 19: screen for linkage probes for myotonic dystrophy. J Neurogenet. 1985 Dec;2(6):403–412. doi: 10.3109/01677068509101426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



