Abstract
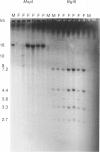
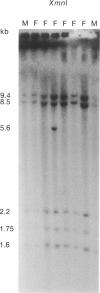
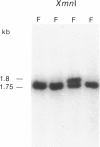
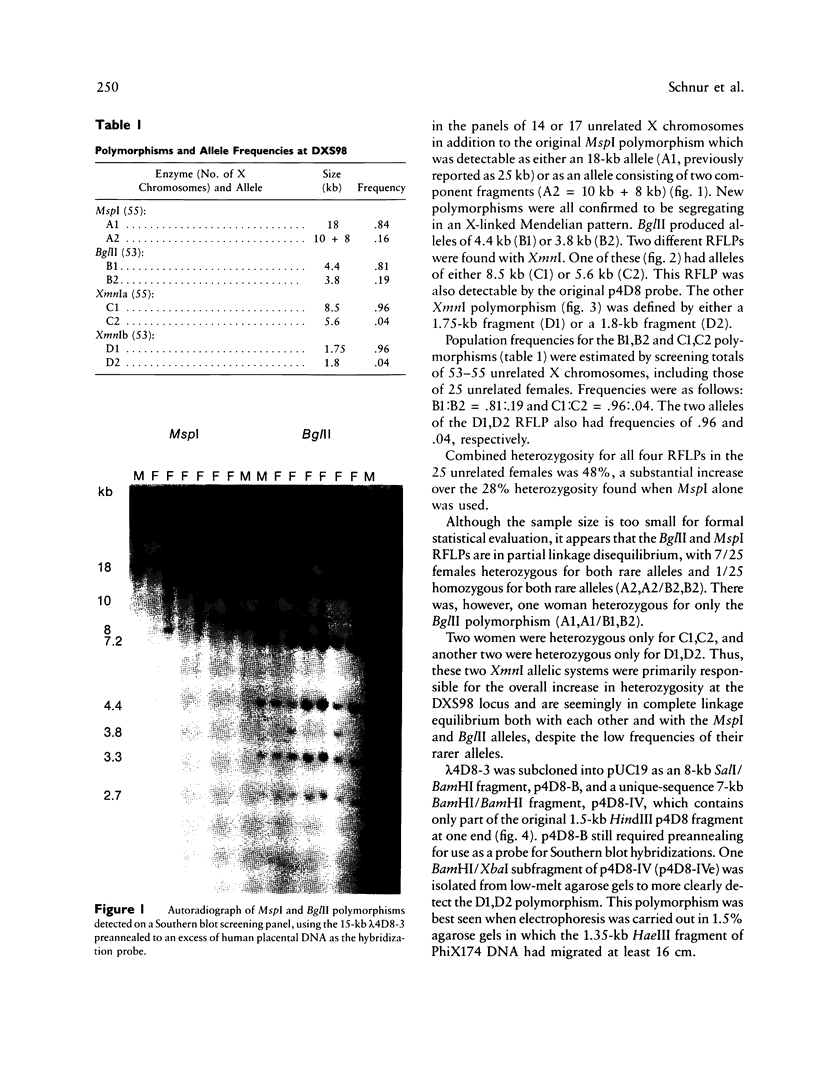
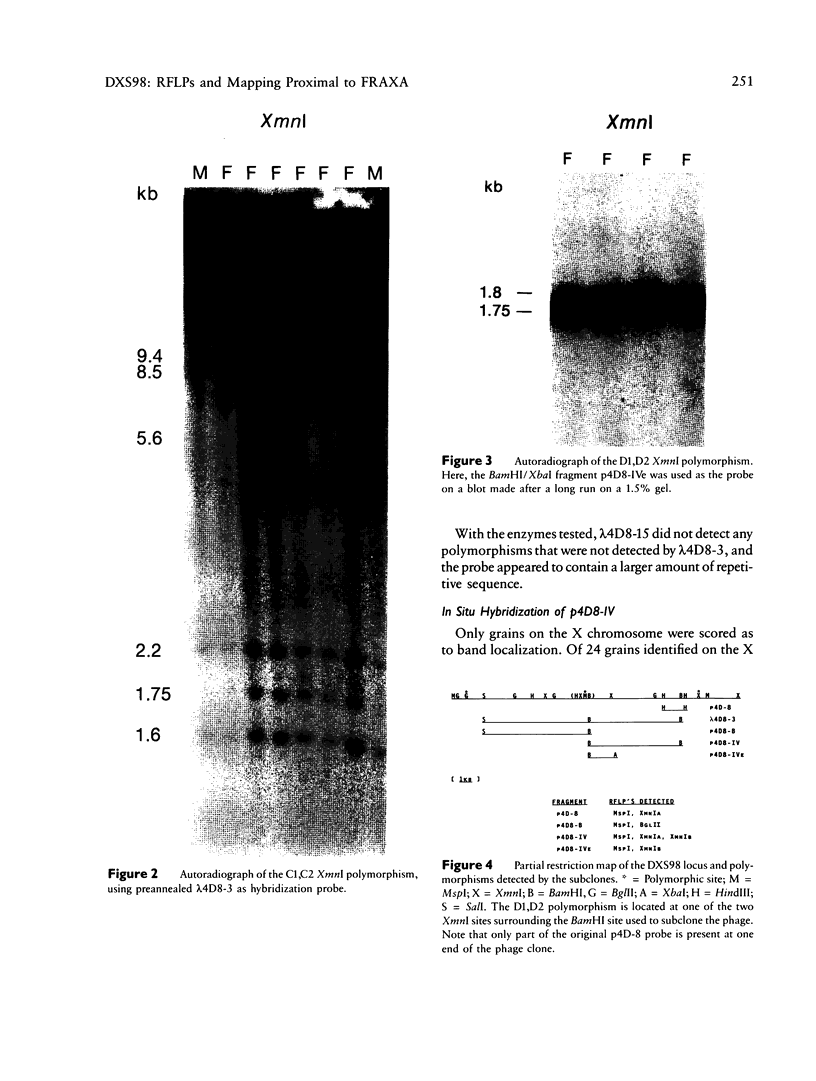
The locus DXS98, detected with the 1.5-kb anonymous probe p4D-8, was recently shown to be closely linked and proximal to the locus for the fragile X syndrome, with theta = .05 at lod = 3.406, by utilizing a limited number of meioses informative for a two-allele MspI RFLP. Because DXS98 may be the closest available marker to the fragile X locus (FRAXA), we sought to increase its utility for linkage studies by extending its PIC and confirming its localization to Xq27, proximal to FRAXA. We have isolated 15 kb of genomic DNA (lambda 4D8-3) from the DXS98 locus by using p4D-8 to screen a genomic phage library containing partial Sau3A-digested human DNA. Three additional RFLPs for the enzymes BglII and XmnI were found by using the entire lambda 4D8-3 as probe. Combined heterozygosity for the four RFLPs in 25 unrelated females was 48%, as compared with only 28% when the MspI RFLP alone was used. In situ hybridization of unique sequences from lambda 4D8-3 was performed on metaphase chromosomes of lymphocytes and lymphoblasts from patients with the fragile X syndrome. Grains on the X chromosome were significantly clustered at band Xq27. Following fragile site induction, all nine grains in the q27-28 region were proximal to the fragile site. Confirmation of the location of DXS98 proximal to FRAXA and the new RFLPs at this locus make DXS98 more useful for linkage analysis and physical mapping in the region of the fragile X mutation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Vincent A., Hofker M. H., Pearson P. L., Mandel J. L. Genetic mapping of the Xq27-q28 region: new RFLP markers useful for diagnostic applications in fragile-X and hemophilia-B families. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;42(2):380–389. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs B. A., Nussbaum R. L. Two anonymous X-specific human sequences detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms in region Xq26----qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):607–613. doi: 10.1007/BF01535226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Jenkins E. C. Genetic linkage heterogeneity in the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1985;71(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00295659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Jenkins E. C., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Krawczun M. S., Duncan C. J., Sklower S. L., Fisch G. S. Further evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the fragile X syndrome. Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;75(4):311–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00284100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Wu Y., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Dobkin C. S., Jenkins E. C. RFLP for linkage analysis of fragile X syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Jan 31;1(8527):280–280. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. T., Ye W., Gross A. C., Chan C. B., Dobkin C. S., Jenkins E. C. Multipoint linkage of 9 anonymous probes to HPRT, factor 9, and fragile X. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):551–566. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. An improved method for G-banding chromosomes after in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):308–309. doi: 10.1159/000132079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Weissenbach J., Fellous M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X and Y chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):277–315. doi: 10.1159/000132481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley D. A., Davies K. E., Drayna D., White R. L., Williamson R. A cytological map of the human X chromosome--evidence for non-random recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5277–5285. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., Bergen A. A., Skraastad M. I., Carpenter N. J., Veenema H., Connor J. M., Bakker E., van Ommen G. J., Pearson P. L. Efficient isolation of X chromosome-specific single-copy probes from a cosmid library of a human X/hamster hybrid-cell line: mapping of new probes close to the locus for X-linked mental retardation. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Apr;40(4):312–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Ledbetter S. A., Nussbaum R. L. Implications of fragile X expression in normal males for the nature of the mutation. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):161–163. doi: 10.1038/324161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litt M., White R. L. A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA revealed by cosmid-derived probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulley J., Turner G., Bain S., Sutherland G. R. Linkage between the fragile X and F9, DXS52 (St14), DXS98 (4D-8) and DXS105 (cX55.7). Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):567–580. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Airhart S. D., Ledbetter D. H. Expression of the fragile (X) chromosome in an interspecific somatic cell hybrid. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):148–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00327113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum R. L., Ledbetter D. H. Fragile X syndrome: a unique mutation in man. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:109–145. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Bell M., Kress W., Davies K. E., Froster-Iskenius U. Linkage studies in a large fragile X family. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):684–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Bell M., Schwartz C., Davies K. Pulsed-field gel mapping studies in the vicinity of the fragile site at Xq27.3. Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):581–591. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Schwartz C., Bell M., Sauer S., Hofker M., Trask B., van den Engh G., Davies K. E. Physical mapping studies on the human X chromosome in the region Xq27-Xqter. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veenema H., Carpenter N. J., Bakker E., Hofker M. H., Ward A. M., Pearson P. L. The fragile X syndrome in a large family. III. Investigations on linkage of flanking DNA markers with the fragile site Xq27. J Med Genet. 1987 Jul;24(7):413–421. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.7.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]