Abstract
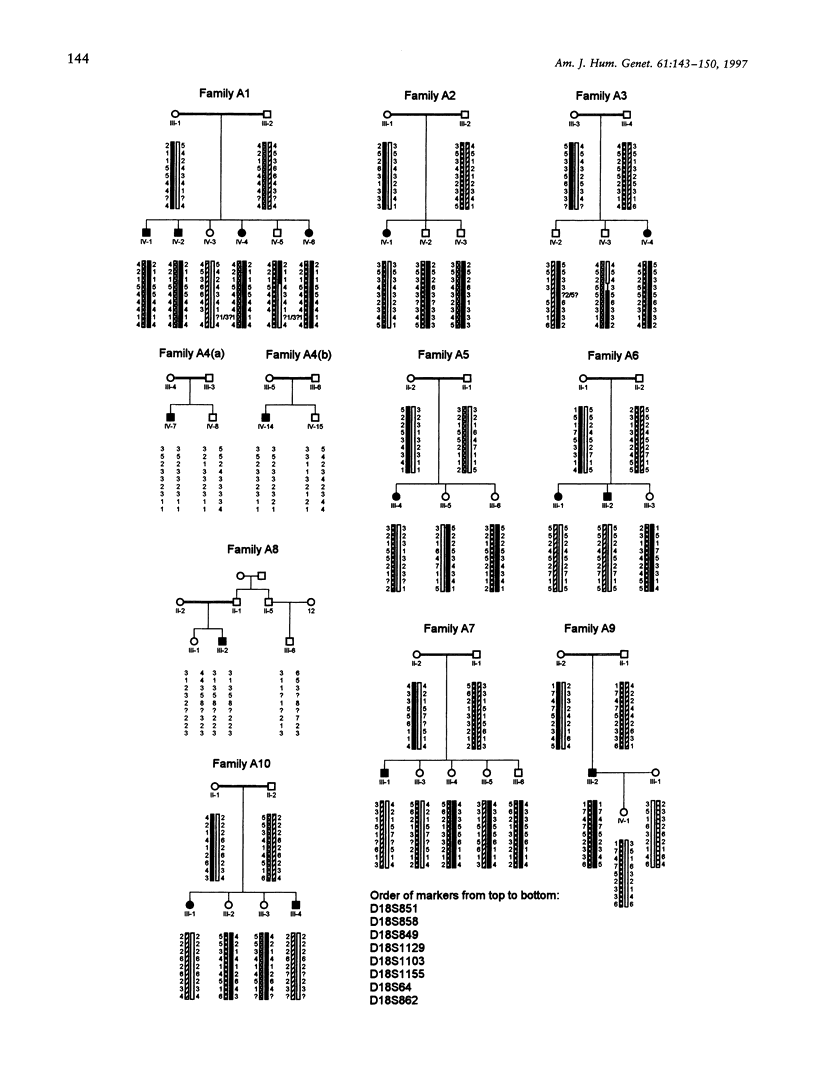
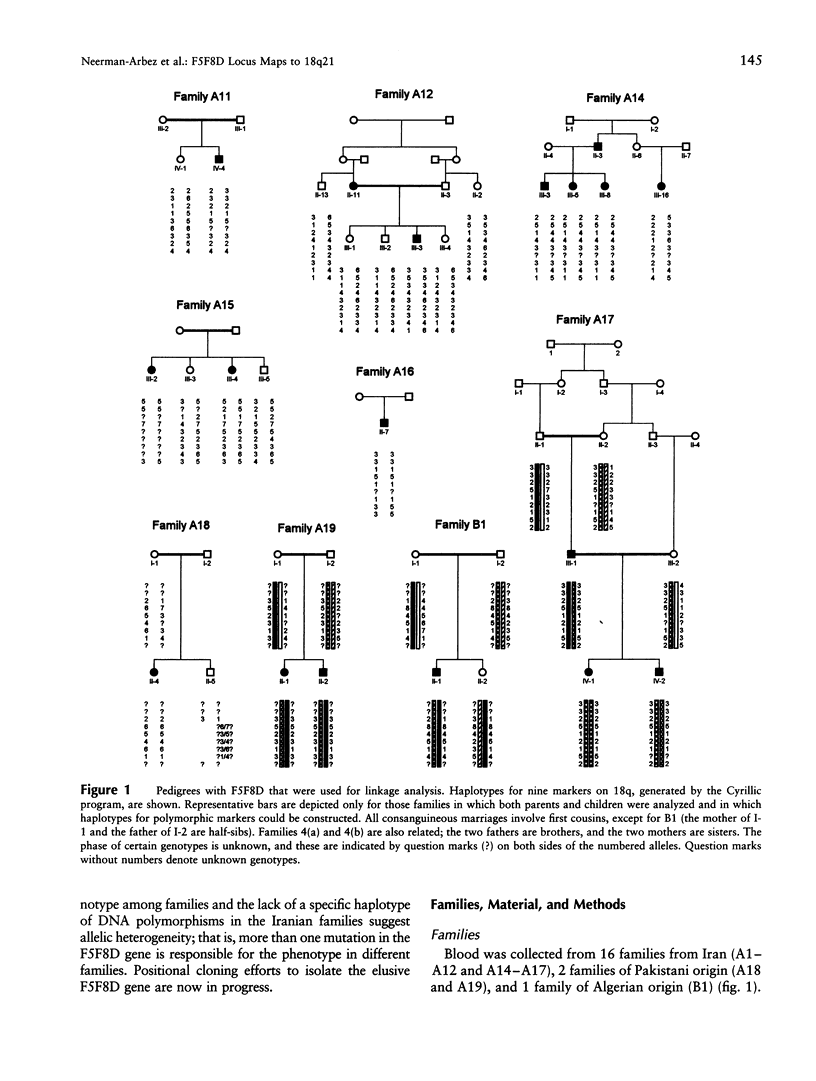
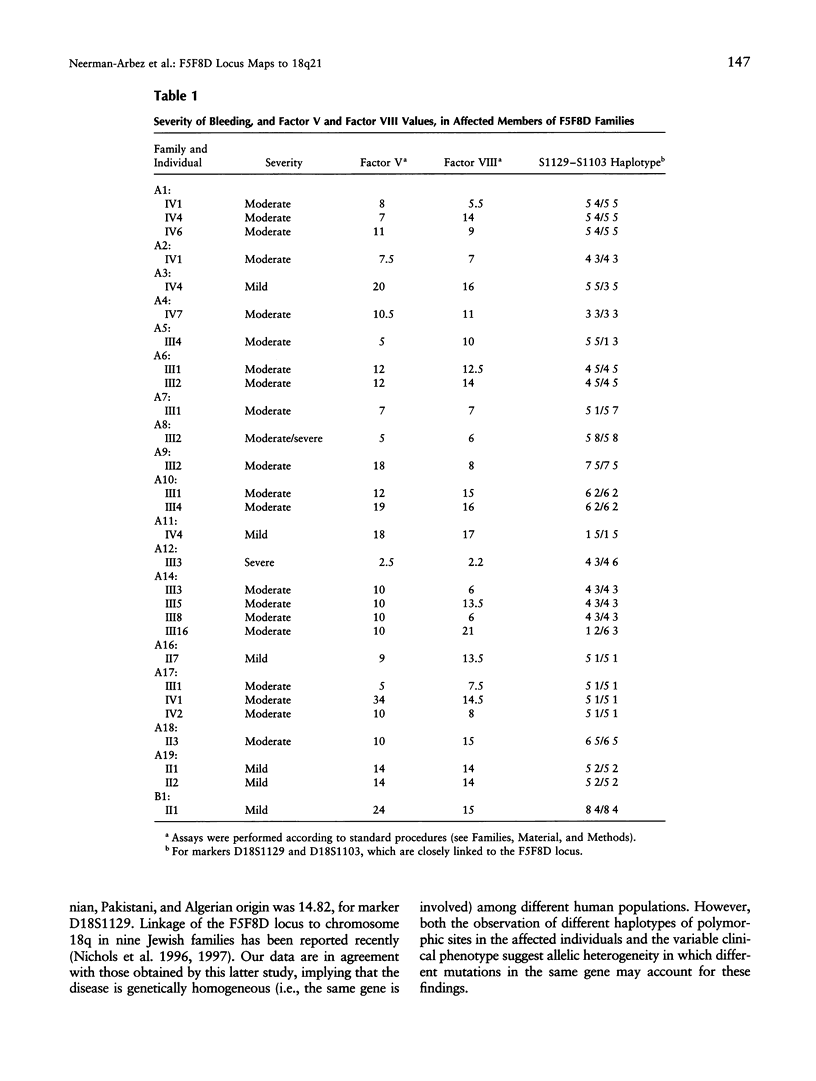
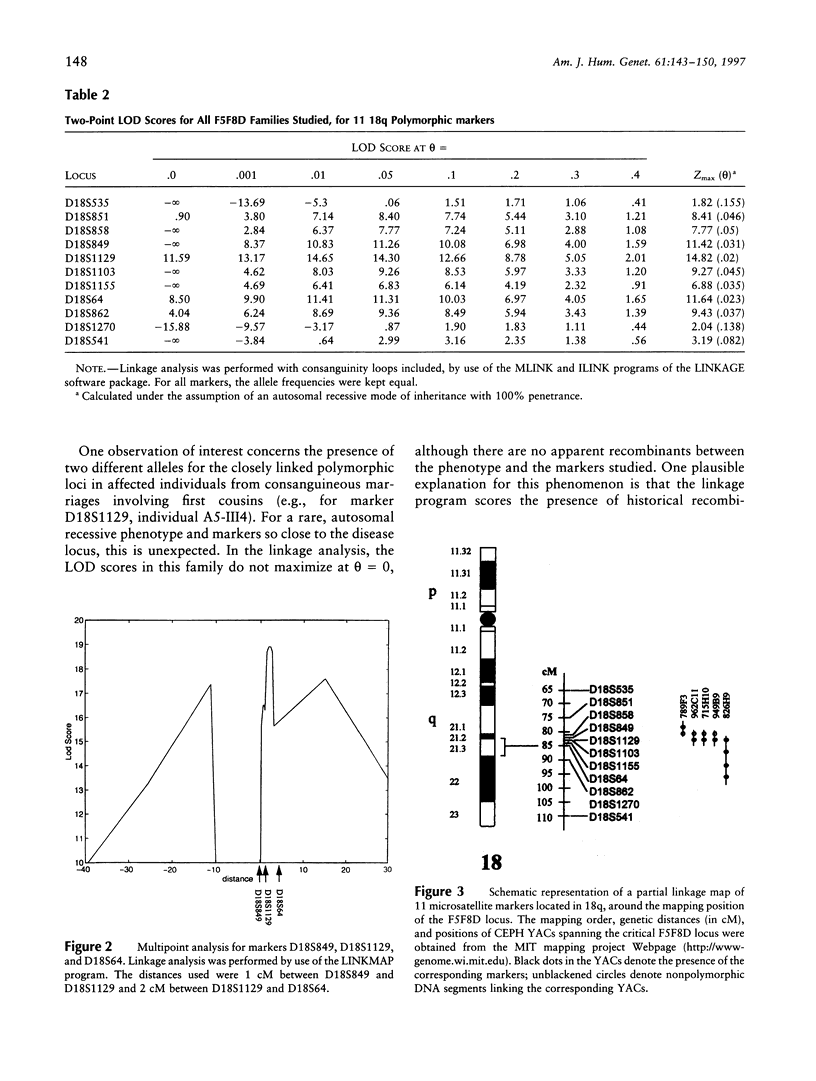
Combined factor V-factor VIII deficiency (F5F8D) is a rare, autosomal recessive coagulation disorder in which the levels of both coagulation factor V and coagulation factor VIII are diminished. In order to map and subsequently clone the gene responsible for this phenotype, DNAs from 19 families (16 from Iran, 2 from Pakistan, and 1 from Algeria) with a total of 32 affected individuals were collected for a genomewide linkage search using genotypes of highly informative DNA polymorphisms. All pedigrees except two contained at least one consanguineous marriage. A maximum LOD score (Zmax) of 14.82 for theta = .02 was generated with marker D18S1129 in 18q21; LOD scores > 9 were obtained for several other markers-D18S849, D18S1103, D18S64, and D18S862. Multipoint analysis resulted in Zmax = 18.91 for the interval between D18S1129 and D18S64. Informative recombinants placed the locus for F5F8D between D18S849 and D18S1103, in an interval of approximately 1 cM. These results are similar to the recently reported linkage of this disease to chromosome 18q in Jewish families (Nichols et al. 1997) and provide evidence that the same gene is responsible for all F5F8D among human populations. The difference in clinical severity of the phenotype in unrelated families, as well as the failure to detect a specific haplotype of DNA polymorphisms in the consanguineous Iranian families, suggests the existence of different molecular defects in the F5F8D gene. There exists an apparently gap-free contig with CEPH YACs linking the two markers on either side of the critical region. Positional cloning efforts are now in progress to clone the F5F8D gene.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Kazazian H. H., Tuddenham E. G. Molecular etiology of factor VIII deficiency in hemophilia A. Hum Mutat. 1995;5(1):1–22. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380050102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canfield W. M., Kisiel W. Evidence of normal functional levels of activated protein C inhibitor in combined Factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1260–1272. doi: 10.1172/JCI110725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D., Chumakov I., Weissenbach J. A first-generation physical map of the human genome. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):698–701. doi: 10.1038/366698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripe L. D., Moore K. D., Kane W. H. Structure of the gene for human coagulation factor V. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 21;31(15):3777–3785. doi: 10.1021/bi00130a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner J. E., Griffin J. H. Studies on human protein C inhibitor in normal and Factor V/VIII deficient plasmas. Thromb Res. 1984 Nov 1;36(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Goralka T. M., Wion K. L., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Vehar G. A., Capon D. J., Lawn R. M. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):326–330. doi: 10.1038/312326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson T. J., Stein L. D., Gerety S. S., Ma J., Castle A. B., Silva J., Slonim D. K., Baptista R., Kruglyak L., Xu S. H. An STS-based map of the human genome. Science. 1995 Dec 22;270(5244):1945–1954. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5244.1945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlar R. A., Griffin J. H. Deficiency of protein C inhibitor in combined factor V/VIII deficiency disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1186–1189. doi: 10.1172/JCI109952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzone D., Fichera A., Praticò G., Sciacca F. Combined congenital deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. Acta Haematol. 1982;68(4):337–338. doi: 10.1159/000207005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Buetow K. H., Weber J. L., Ludwigsen S., Scherpbier-Heddema T., Manion F., Quillen J., Sheffield V. C., Sunden S., Duyk G. M. A comprehensive human linkage map with centimorgan density. Cooperative Human Linkage Center (CHLC). Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2049–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8091227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. C., Seligsohn U., Zivelin A., Terry V. H., Arnold N. D., Siemieniak D. R., Kaufman R. J., Ginsburg D. Linkage of combined factors V and VIII deficiency to chromosome 18q by homozygosity mapping. J Clin Invest. 1997 Feb 15;99(4):596–601. doi: 10.1172/JCI119201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozsoylu S. Combined congenital deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. Acta Haematol. 1983;70(3):207–208. doi: 10.1159/000206726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahim Adam K. A., Al Rahman F., el Seed A., Karrar Z. A., Gader A. M. Combined factor V and factor VIII deficiency with normal protein C and protein C inhibitor. A family study. Scand J Haematol. 1985 May;34(5):401–405. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1985.tb00768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Ramot B. Combined factor-V and factor-VIII deficiency: report of four cases. Br J Haematol. 1969 May;16(5):475–486. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00426.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Zivelin A., Zwang E. Combined factor V and factor VIII deficiency among non-Ashkenazi Jews. N Engl J Med. 1982 Nov 4;307(19):1191–1195. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198211043071907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Weber J. L., Buetow K. H., Murray J. C., Even D. A., Wiles K., Gastier J. M., Pulido J. C., Yandava C., Sunden S. L. A collection of tri- and tetranucleotide repeat markers used to generate high quality, high resolution human genome-wide linkage maps. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Oct;4(10):1837–1844. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.10.1837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S., Kamiya T., Saito H. Normal titer of functional and immunoreactive protein-C inhibitor in plasma of patients with congenital combined deficiency of factor V and factor VIII. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1266–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


