Abstract
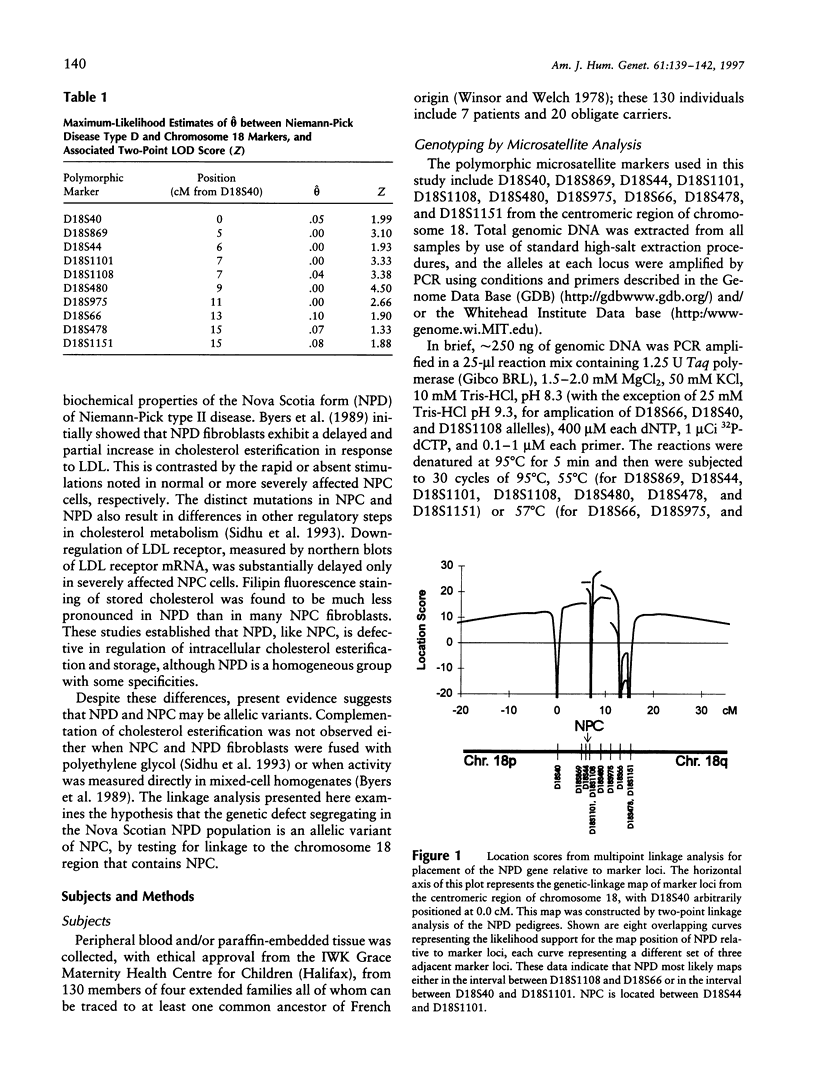
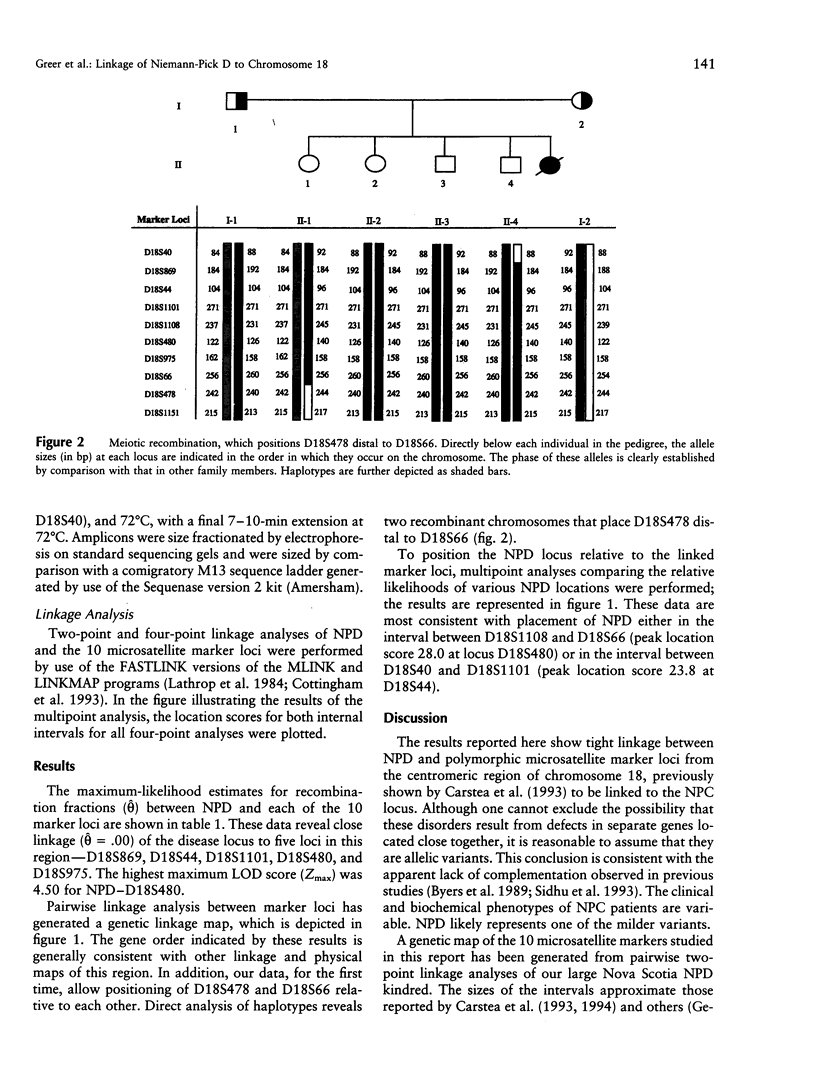
Niemann-Pick type II disease is a severe disorder characterized by accumulation of tissue cholesterol and sphingomyelin and by progressive degeneration of the nervous system. This disease has two clinically similar subtypes, type C (NPC) and type D (NPD). NPC is clinically variable and has been identified in many ethnic groups. NPD, on the other hand, has been reported only in descendants of an Acadian couple who lived in Nova Scotia in the early 18th century and has a more homogeneous expression resembling that of less severely affected NPC patients. Despite biochemical differences, it has not been established whether NPC and NPD are allelic variants of the same disease. We report here that NPD is tightly linked (recombination fraction .00; maximum LOD score 4.50) to a microsatellite marker, D18S480, from the centromeric region of chromosome 18q. Carstea et al. have reported that the NPC gene maps to this same site; therefore we suggest that NPC and NPD likely result from mutations in the same gene.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers D. M., Rastogi S. R., Cook H. W., Palmer F. B., Spence M. W. Defective activity of acyl-CoA:cholesterol O-acyltransferase in Niemann-Pick type C and type D fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 15;262(3):713–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2620713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROCKER A. C., FARBER S. Niemann-Pick disease: a review of eighteen patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1958 Feb;37(1):1–95. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195802000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROCKER A. C. The cerebral defect in Tay-Sachs disease and Niemann-Pick disease. J Neurochem. 1961 Apr;7:69–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13499.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstea E. D., Polymeropoulos M. H., Parker C. C., Detera-Wadleigh S. D., O'Neill R. R., Patterson M. C., Goldin E., Xiao H., Straub R. E., Vanier M. T. Linkage of Niemann-Pick disease type C to human chromosome 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2002–2004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottingham R. W., Jr, Idury R. M., Schäffer A. A. Faster sequential genetic linkage computations. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Jul;53(1):252–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins J. J., Patterson M. C., Dambrosia J. M., Pikus A. T., Pentchev P. G., Sato S., Brady R. O., Barton N. W. A clinical staging classification for type C Niemann-Pick disease. Neurology. 1992 Dec;42(12):2286–2290. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.12.2286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscum L., Faust J. R. Low density lipoprotein (LDL)-mediated suppression of cholesterol synthesis and LDL uptake is defective in Niemann-Pick type C fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17002–17008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Comly M. E., Kruth H. S., Vanier M. T., Wenger D. A., Patel S., Brady R. O. A defect in cholesterol esterification in Niemann-Pick disease (type C) patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8247–8251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentchev P. G., Kruth H. S., Comly M. E., Butler J. D., Vanier M. T., Wenger D. A., Patel S. Type C Niemann-Pick disease. A parallel loss of regulatory responses in both the uptake and esterification of low density lipoprotein-derived cholesterol in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16775–16780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu H. S., Rastogi S. A., Byers D. M., Guernsey D. L., Cook H. W., Palmer F. B., Spence M. W. Regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor and 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase activities are differentially affected in Niemann-Pick type C and type D fibroblasts. Biochem Cell Biol. 1993 Sep-Oct;71(9-10):467–474. doi: 10.1139/o93-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg S. J., Ward C. P., Fensom A. H. Complementation studies in Niemann-Pick disease type C indicate the existence of a second group. J Med Genet. 1994 Apr;31(4):317–320. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Duthel S., Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., Pentchev P., Carstea E. D. Genetic heterogeneity in Niemann-Pick C disease: a study using somatic cell hybridization and linkage analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1996 Jan;58(1):118–125. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanier M. T., Rodriguez-Lafrasse C., Rousson R., Gazzah N., Juge M. C., Pentchev P. G., Revol A., Louisot P. Type C Niemann-Pick disease: spectrum of phenotypic variation in disruption of intracellular LDL-derived cholesterol processing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 5;1096(4):328–337. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90069-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vethamany V. G., Welch J. P., Vethamany S. K. Type D Niemann-Pick disease (Nova Scotia variant). Ultrastructure of blood, skin fibroblasts, and bone marrow. Arch Pathol. 1972 Jun;93(6):537–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winsor E. J., Welch J. P. Genetic and demographic aspects of Nova Scotia Niemann-Pick disease (type D). Am J Hum Genet. 1978 Sep;30(5):530–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


