Abstract
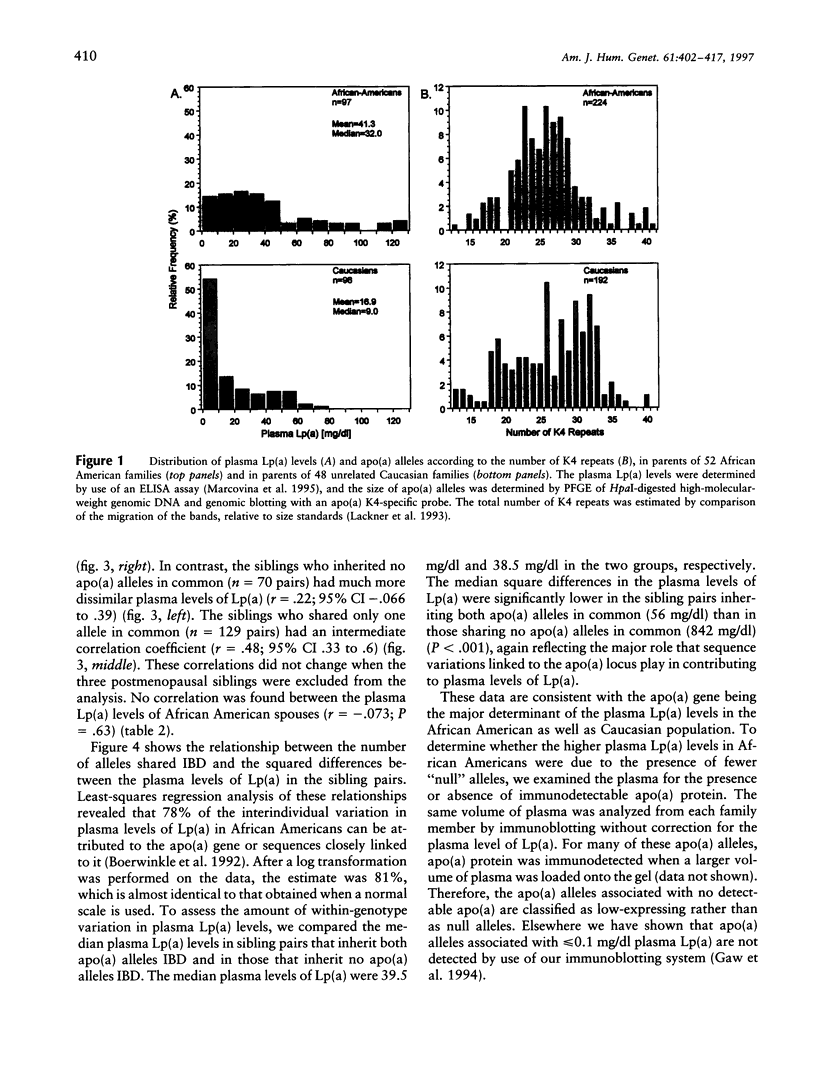
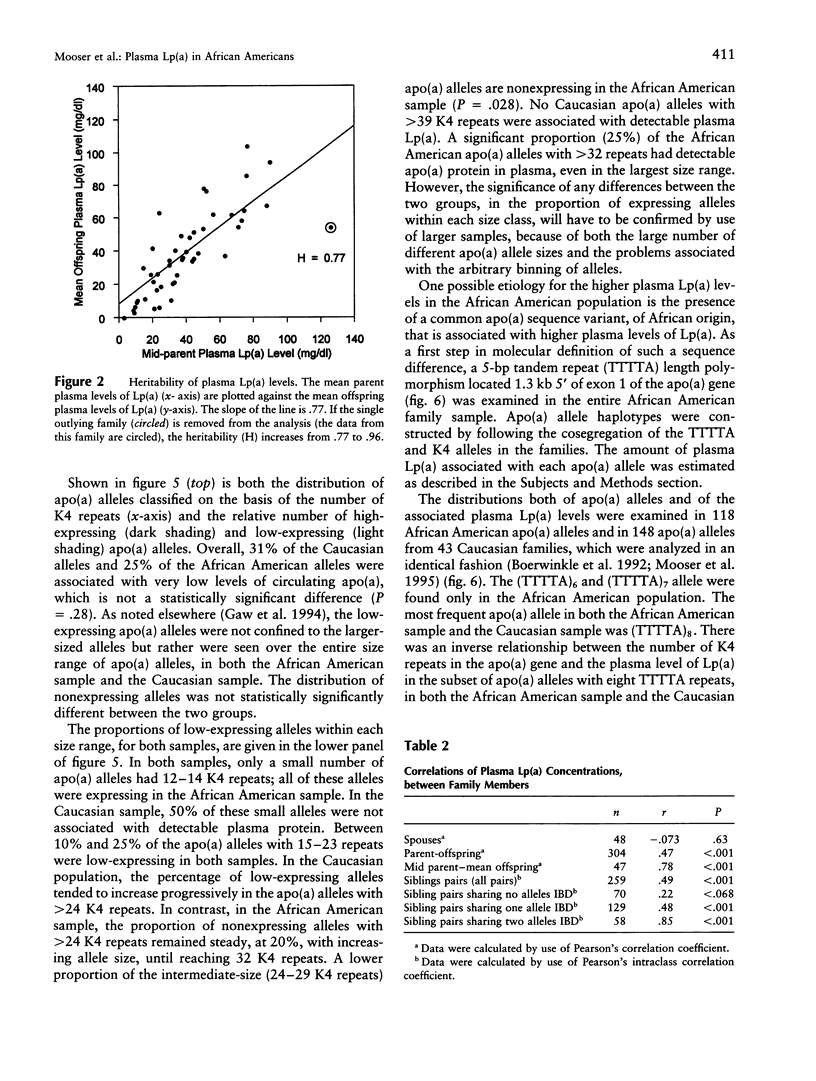
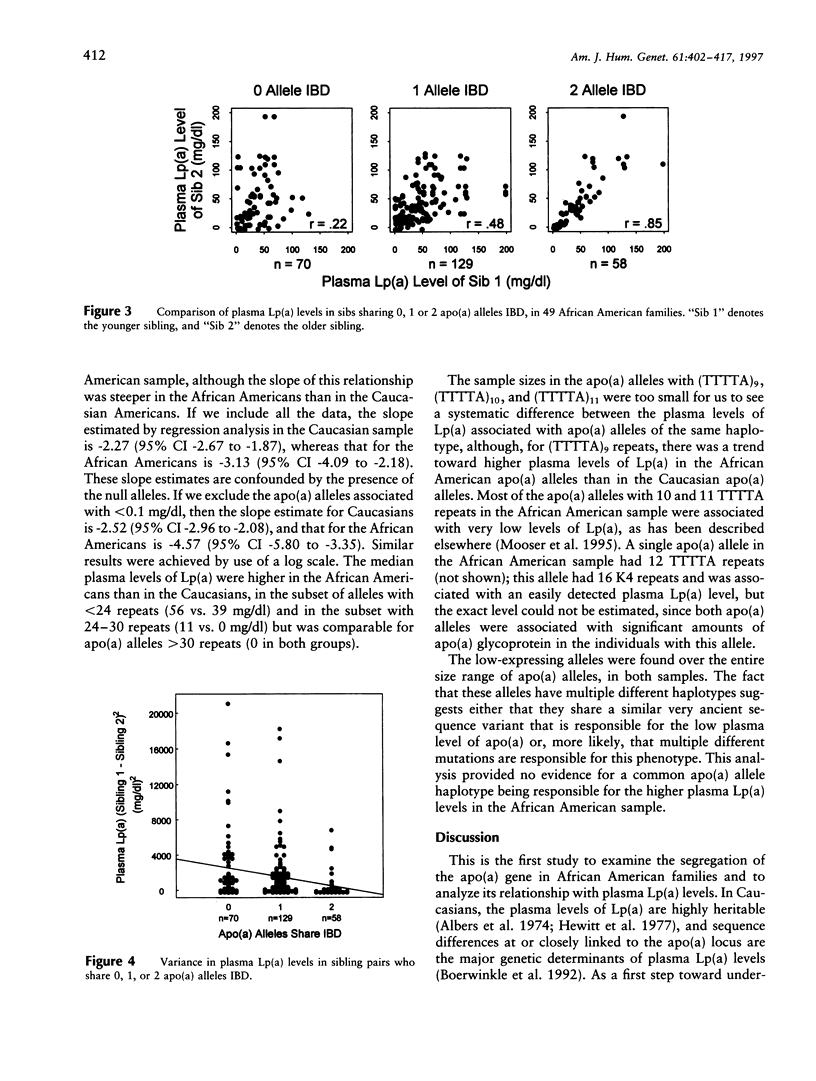
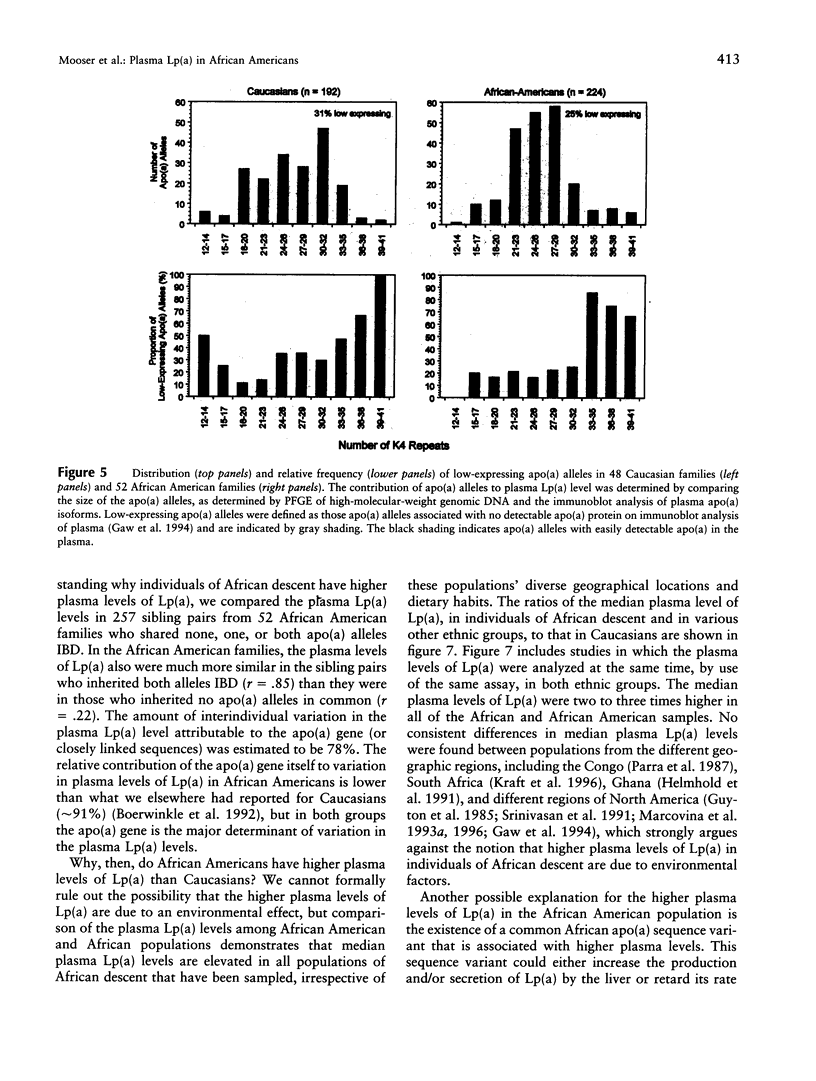
The distributions of plasma lipoprotein(a), or Lp(a), levels differ significantly among ethnic groups. Individuals of African descent have a two- to threefold higher mean plasma level of Lp(a) than either Caucasians or Orientals. In Caucasians, variation in the plasma Lp(a) levels has been shown to be largely determined by sequence differences at the apo(a) locus, but little is known about either the genetic architecture of plasma Lp(a) levels in Africans or why they have higher levels of plasma Lp(a). In this paper we analyze the plasma Lp(a) levels of 257 sibling pairs from 49 independent African American families. The plasma Lp(a) levels were much more similar in the sibling pairs who inherited both apo(a) alleles identical by descent (IBD) (r = .85) than in those that shared one (r = .48) or no (r = .22) parental apo(a) alleles in common. On the basis of these findings, it was estimated that 78% of the variation in plasma Lp(a) levels in African Americans is attributable to polymorphism at either the apo(a) locus or sequences closely linked to it. Thus, the apo(a) locus is the major determinant of variation in plasma Lp(a) levels in African Americans, as well as in Caucasians. No molecular evidence was found for a common "high-expressing" apo(a) allele in the African Americans. We propose that the higher plasma levels of Lp(a) in Africans are likely due to a yet-to-be-identified trans-acting factor(s) that causes an increase in the rate of secretion of apo(a) or a decrease in its catabolism.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. J., Marcovina S. M., Lodge M. S. The unique lipoprotein(a): properties and immunochemical measurement. Clin Chem. 1990 Dec;36(12):2019–2026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albers J. J., Wahl P., Hazzard W. R. Quantitative genetic studies of the human plasma Lp(a) lipoprotein. Biochem Genet. 1974 Jun;11(6):475–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00486079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos C. I., Elston R. C., Wilson A. F., Bailey-Wilson J. E. A more powerful robust sib-pair test of linkage for quantitative traits. Genet Epidemiol. 1989;6(3):435–449. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370060306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin M. A., Sandholzer C., Selby J. V., Newman B., Krauss R. M., Utermann G. Lipoprotein(a) in women twins: heritability and relationship to apolipoprotein(a) phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Oct;51(4):829–840. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Leffert C. C., Lin J., Lackner C., Chiesa G., Hobbs H. H. Apolipoprotein(a) gene accounts for greater than 90% of the variation in plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):52–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI115855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerwinkle E., Menzel H. J., Kraft H. G., Utermann G. Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. III. Contribution of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes to normal lipid variation. Hum Genet. 1989 Apr;82(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00288277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma D. I., Kaptein A., Kempen H. J., Gevers Leuven J. A., Princen H. M. Lipoprotein(a): relation to other risk factors and genetic heritability. Results from a Dutch parent-twin study. Atherosclerosis. 1993 Feb;99(1):23–33. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(93)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R., Kamboh M. I., Nwankwo M., Ferrell R. E. Caucasian genes in American blacks: new data. Am J Hum Genet. 1992 Jan;50(1):145–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbaert C., Kesteloot H. Serum lipoprotein(a) levels in racially different populations. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Aug 15;136(4):441–449. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. C., Chiesa G., Hobbs H. H. Sequence polymorphisms in the apolipoprotein (a) gene. Evidence for dissociation between apolipoprotein(a) size and plasma lipoprotein(a) levels. J Clin Invest. 1993 Apr;91(4):1630–1636. doi: 10.1172/JCI116370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCroo S., Kamboh M. I., Ferrell R. E. Population genetics of alpha-1-antitrypsin polymorphism in US whites, US blacks and African blacks. Hum Hered. 1991;41(4):215–221. doi: 10.1159/000154004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester C. A., Bu X., Gray R. J., Lusis A. J., Rotter J. I. Genetic variation in lipoprotein (a) levels in families enriched for coronary artery disease is determined almost entirely by the apolipoprotein (a) gene locus. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jan;56(1):287–293. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edén S., Wiklund O., Oscarsson J., Rosén T., Bengtsson B. A. Growth hormone treatment of growth hormone-deficient adults results in a marked increase in Lp(a) and HDL cholesterol concentrations. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Feb;13(2):296–301. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.2.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaw A., Boerwinkle E., Cohen J. C., Hobbs H. H. Comparative analysis of the apo(a) gene, apo(a) glycoprotein, and plasma concentrations of Lp(a) in three ethnic groups. Evidence for no common "null" allele at the apo(a) locus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jun;93(6):2526–2534. doi: 10.1172/JCI117263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyton J. R., Dahlen G. H., Patsch W., Kautz J. A., Gotto A. M., Jr Relationship of plasma lipoprotein Lp(a) levels to race and to apolipoprotein B. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 May-Jun;5(3):265–272. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffner S. M., Gruber K. K., Morales P. A., Hazuda H. P., Valdez R. A., Mitchell B. D., Stern M. P. Lipoprotein(a) concentrations in Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic whites: the San Antonio Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1992 Nov 1;136(9):1060–1068. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a116571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseman J. K., Elston R. C. The investigation of linkage between a quantitative trait and a marker locus. Behav Genet. 1972 Mar;2(1):3–19. doi: 10.1007/BF01066731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss G., Schonfeld G., Johnson J. L., Heyden S., Hames C. G., Tyroler H. A. Black-white differences in plasma levels of apolipoproteins: the Evans County Heart Study. Am Heart J. 1984 Sep;108(3 Pt 2):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90676-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmhold M., Bigge J., Muche R., Mainoo J., Thiery J., Seidel D., Armstrong V. W. Contribution of the apo[a] phenotype to plasma Lp[a] concentrations shows considerable ethnic variation. J Lipid Res. 1991 Dec;32(12):1919–1928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershkovitz E., Leiberman E., Limony Y., Shany S., Phillip M. Short-term growth hormone therapy increases serum lipoprotein (a) levels in normal short children without growth hormone deficiency. Horm Res. 1996 Jul;46(1):38–40. doi: 10.1159/000184975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewitt D., Milner J., Breckenridge C., Maguire G. Heritability of "sinking" pre-beta lipoprotein level: a twin study. Clin Genet. 1977 Mar;11(3):224–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungner I., Mendis S., Bjellerup P. Lipoprotein(a): levels in a Swedish population in relation to other lipid parameters and in comparison with a male Sri Lankan population. Clin Biochem. 1995 Aug;28(4):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(95)00009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil J. E., Sutherland S. E., Knapp R. G., Lackland D. T., Gazes P. C., Tyroler H. A. Mortality rates and risk factors for coronary disease in black as compared with white men and women. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 8;329(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307083290201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Köchl S., Menzel H. J., Sandholzer C., Utermann G. The apolipoprotein (a) gene: a transcribed hypervariable locus controlling plasma lipoprotein (a) concentration. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):220–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00220066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft H. G., Lingenhel A., Pang R. W., Delport R., Trommsdorff M., Vermaak H., Janus E. D., Utermann G. Frequency distributions of apolipoprotein(a) kringle IV repeat alleles and their effects on lipoprotein(a) levels in Caucasian, Asian, and African populations: the distribution of null alleles is non-random. Eur J Hum Genet. 1996;4(2):74–87. doi: 10.1159/000472175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krempler F., Kostner G. M., Bolzano K., Sandhofer F. Turnover of lipoprotein (a) in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1483–1490. doi: 10.1172/JCI109813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackner C., Cohen J. C., Hobbs H. H. Molecular definition of the extreme size polymorphism in apolipoprotein(a). Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):933–940. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini F. P., Mooser V., Guerra R., Hobbs H. H. Sequence microheterogeneity in apolipoprotein(a) gene repeats and the relationship to plasma Lp(a) levels. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Sep;4(9):1535–1542. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.9.1535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcovina S. M., Albers J. J., Gabel B., Koschinsky M. L., Gaur V. P. Effect of the number of apolipoprotein(a) kringle 4 domains on immunochemical measurements of lipoprotein(a). Clin Chem. 1995 Feb;41(2):246–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcovina S. M., Albers J. J., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Perkins L. L., Lewis C. E., Howard B. V., Savage P. Lipoprotein[a] concentrations and apolipoprotein[a] phenotypes in Caucasians and African Americans. The CARDIA study. Arterioscler Thromb. 1993 Jul;13(7):1037–1045. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.13.7.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcovina S. M., Albers J. J., Wijsman E., Zhang Z., Chapman N. H., Kennedy H. Differences in Lp[a] concentrations and apo[a] polymorphs between black and white Americans. J Lipid Res. 1996 Dec;37(12):2569–2585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcovina S. M., Zhang Z. H., Gaur V. P., Albers J. J. Identification of 34 apolipoprotein(a) isoforms: differential expression of apolipoprotein(a) alleles between American blacks and whites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):1192–1196. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moliterno D. J., Jokinen E. V., Miserez A. R., Lange R. A., Willard J. E., Boerwinkle E., Hillis L. D., Hobbs H. H. No association between plasma lipoprotein(a) concentrations and the presence or absence of coronary atherosclerosis in African-Americans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):850–855. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.7.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser V., Mancini F. P., Bopp S., Pethö-Schramm A., Guerra R., Boerwinkle E., Müller H. J., Hobbs H. H. Sequence polymorphisms in the apo(a) gene associated with specific levels of Lp(a) in plasma. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Feb;4(2):173–181. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano K., Swindle M. M., Spinale F., Ishihara K., Kanazawa S., Smith A., Biederman R. W., Clamp L., Hamada Y., Zile M. R. Depressed contractile function due to canine mitral regurgitation improves after correction of the volume overload. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jun;87(6):2077–2086. doi: 10.1172/JCI115238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parra H. J., Luyéyé I., Bouramoué C., Demarquilly C., Fruchart J. C. Black-white differences in serum Lp(a) lipoprotein levels. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Sep 15;168(1):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perombelon Y. F., Soutar A. K., Knight B. L. Variation in lipoprotein(a) concentration associated with different apolipoprotein(a) alleles. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1481–1492. doi: 10.1172/JCI117126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader D. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Lipoprotein(a). Clinical approach to a unique atherogenic lipoprotein. JAMA. 1992 Feb 26;267(8):1109–1112. doi: 10.1001/jama.267.8.1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rader D. J., Cain W., Zech L. A., Usher D., Brewer H. B., Jr Variation in lipoprotein(a) concentrations among individuals with the same apolipoprotein (a) isoform is determined by the rate of lipoprotein(a) production. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):443–447. doi: 10.1172/JCI116221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandholzer C., Hallman D. M., Saha N., Sigurdsson G., Lackner C., Császár A., Boerwinkle E., Utermann G. Effects of the apolipoprotein(a) size polymorphism on the lipoprotein(a) concentration in 7 ethnic groups. Hum Genet. 1991 Apr;86(6):607–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00201550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino M. J., Vielhauer C., Eisenbart J. D., Fless G. M., Scanu A. M., Feldman T. Plasma lipoprotein (a) protein concentration and coronary artery disease in black patients compared with white patients. Am J Med. 1992 Dec;93(6):658–662. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(92)90199-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan S. R., Dahlen G. H., Jarpa R. A., Webber L. S., Berenson G. S. Racial (black-white) differences in serum lipoprotein (a) distribution and its relation to parental myocardial infarction in children. Bogalusa Heart Study. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):160–167. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trommsdorff M., Köchl S., Lingenhel A., Kronenberg F., Delport R., Vermaak H., Lemming L., Klausen I. C., Faergeman O., Utermann G. A pentanucleotide repeat polymorphism in the 5' control region of the apolipoprotein(a) gene is associated with lipoprotein(a) plasma concentrations in Caucasians. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jul;96(1):150–157. doi: 10.1172/JCI118015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade D. P., Clarke J. G., Lindahl G. E., Liu A. C., Zysow B. R., Meer K., Schwartz K., Lawn R. M. 5' control regions of the apolipoprotein(a) gene and members of the related plasminogen gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1369–1373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y., Cohen J., Guerra R. A permutation test for the robust sib-pair linkage method. Ann Hum Genet. 1997 Jan;61(Pt 1):79–87. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-1809.1997.6110077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White A. L., Lanford R. E. Cell surface assembly of lipoprotein(a) in primary cultures of baboon hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28716–28723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright N. M., Renault J., Willi S., Veldhuis J. D., Pandey J. P., Gordon L., Key L. L., Bell N. H. Greater secretion of growth hormone in black than in white men: possible factor in greater bone mineral density--a clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Aug;80(8):2291–2297. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.8.7543111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Whitman I., Molmenti E., Moore K., Hippenmeyer P., Perlmutter D. H. A lag in intracellular degradation of mutant alpha 1-antitrypsin correlates with the liver disease phenotype in homozygous PiZZ alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9014–9018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Hoek Y. Y., Wittekoek M. E., Beisiegel U., Kastelein J. J., Koschinsky M. L. The apolipoprotein(a) kringle IV repeats which differ from the major repeat kringle are present in variably-sized isoforms. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Apr;2(4):361–366. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.4.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


