Abstract
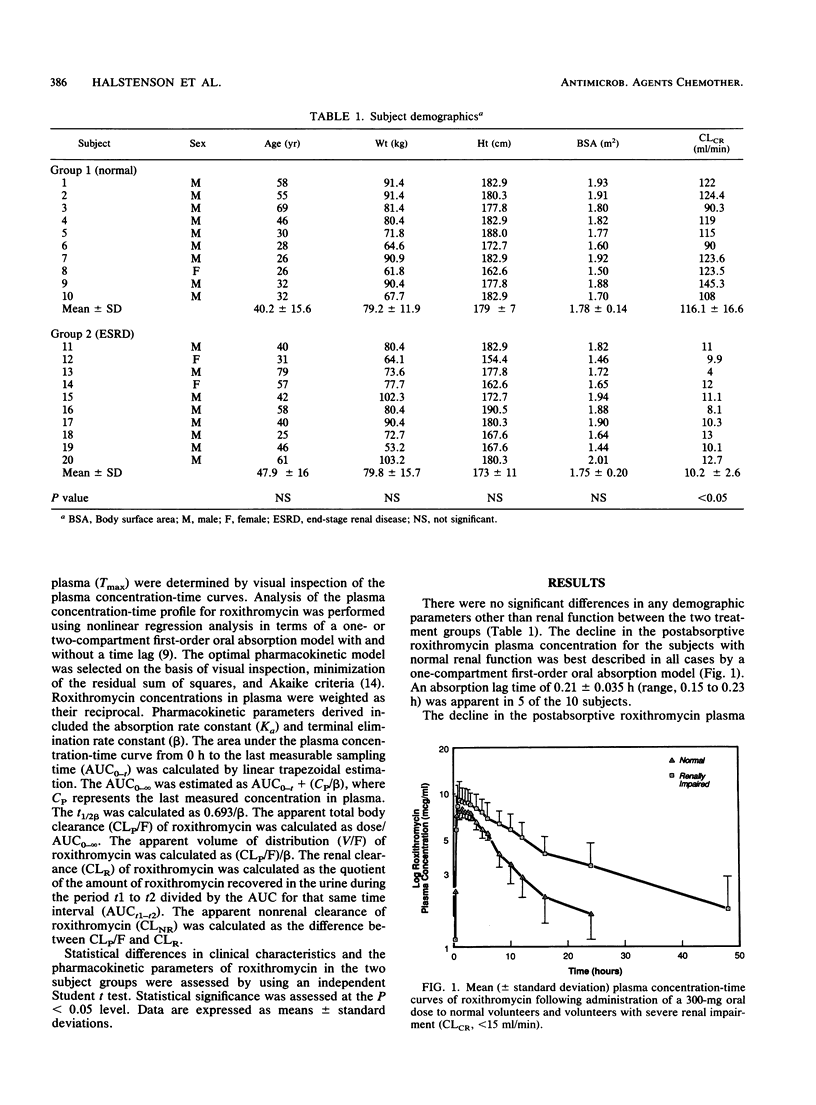
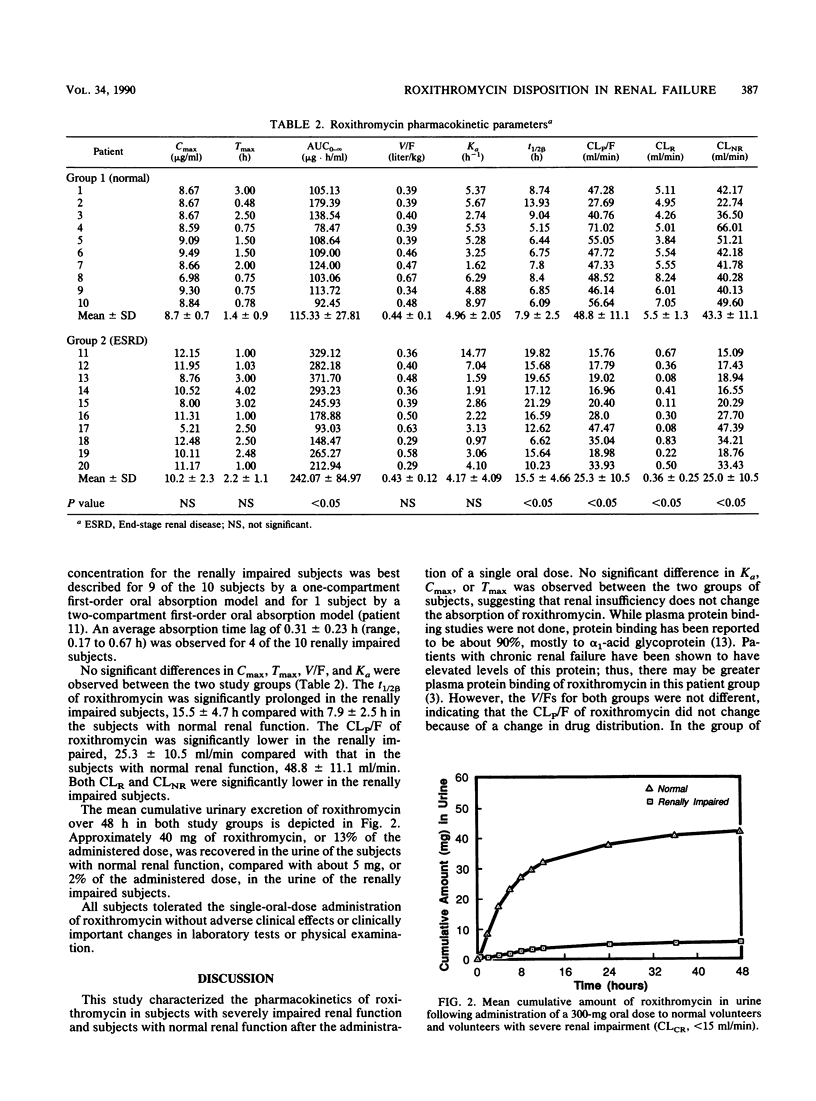
The disposition of roxithromycin, an investigational macrolide antibiotic, was evaluated in 20 subjects, 10 with normal renal function (creatinine clearance [CLCR] of 116 +/- 17 ml/min [mean +/- standard deviation]) and 10 with severely impaired renal function (CLCR of 10.2 +/- 2.6 ml/min) after a single 300-mg oral dose. Plasma concentration-time data were analyzed in terms of a one- or two-compartment oral absorption model utilizing nonlinear regression analysis. The terminal elimination half-life was significantly prolonged in the group with severely impaired renal function (15.5 +/- 4.7 h) compared with that of the group with normal renal function (7.9 +/- 2.5 h). Apparent total body clearance was significantly reduced in the renally impaired (25.3 +/- 10.5 ml/min) in relation to the group with normal renal function (48.8 +/- 11.1 ml/min). The first-order absorption rate constants and apparent volumes of distribution did not differ between the two groups. These data indicate that the disposition of roxithromycin is significantly delayed in subjects with CLCRs of less than 15 ml/min and suggest that the roxithromycin dosing interval be doubled for these patients.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlam T., Neu H. C. In vitro comparison of the activity of RU 28965, a new macrolide, with that of erythromycin against aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):529–531. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. P. Renal disease and drug metabolism: an overview. Am J Kidney Dis. 1986 Jul;8(1):7–17. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(86)80148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughey D. B., Kraft C. J., Matzke G. R., Keane W. F., Halstenson C. E. Protein binding of disopyramide and elevated alpha-1-acid glycoprotein concentrations in serum obtained from dialysis patients and renal transplant recipients. Am J Nephrol. 1985;5(1):35–39. doi: 10.1159/000166900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haydon R. C., Thelin J. W., Davis W. E. Erythromycin ototoxicity: analysis and conclusions based on 22 case reports. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1984 Dec;92(6):678–684. doi: 10.1177/019459988409200615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. N., Barry A. L., Thornsberry C. In vitro evaluation of three new macrolide antimicrobial agents, RU28965, RU29065, and RU29702, and comparisons with other orally administered drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Aug;24(2):209–215. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.2.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanfer A., Stamatakis G., Torlotin J. C., Fredj G., Kenouch S., Méry J. P. Changes in erythromycin pharmacokinetics induced by renal failure. Clin Nephrol. 1987 Mar;27(3):147–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroboth P. D., McNeil M. A., Kreeger A., Dominguez J., Rault R. Hearing loss and erythromycin pharmacokinetics in a patient receiving hemodialysis. Arch Intern Med. 1983 Jun;143(6):1263–1265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke G. R., Abraham P. A., Halstenson C. E., Keane W. F. Cefotaxime and desacetyl cefotaxime kinetics in renal impairment. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Jul;38(1):31–36. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri S. K., Lassman H. B. Roxithromycin: a pharmacokinetic review of a macrolide. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20 (Suppl B):89–100. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.suppl_b.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling P. G., Craig W. A. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous erythromycin. J Pharm Sci. 1978 Aug;67(8):1057–1059. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600670809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise R., Kirkpatrick B., Ashby J., Andrews J. M. Pharmacokinetics and tissue penetration of roxithromycin after multiple dosing. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Jul;31(7):1051–1053. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.7.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaoka K., Nakagawa T., Uno T. Application of Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in the evaluation of linear pharmacokinetic equations. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1978 Apr;6(2):165–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01117450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


