Abstract
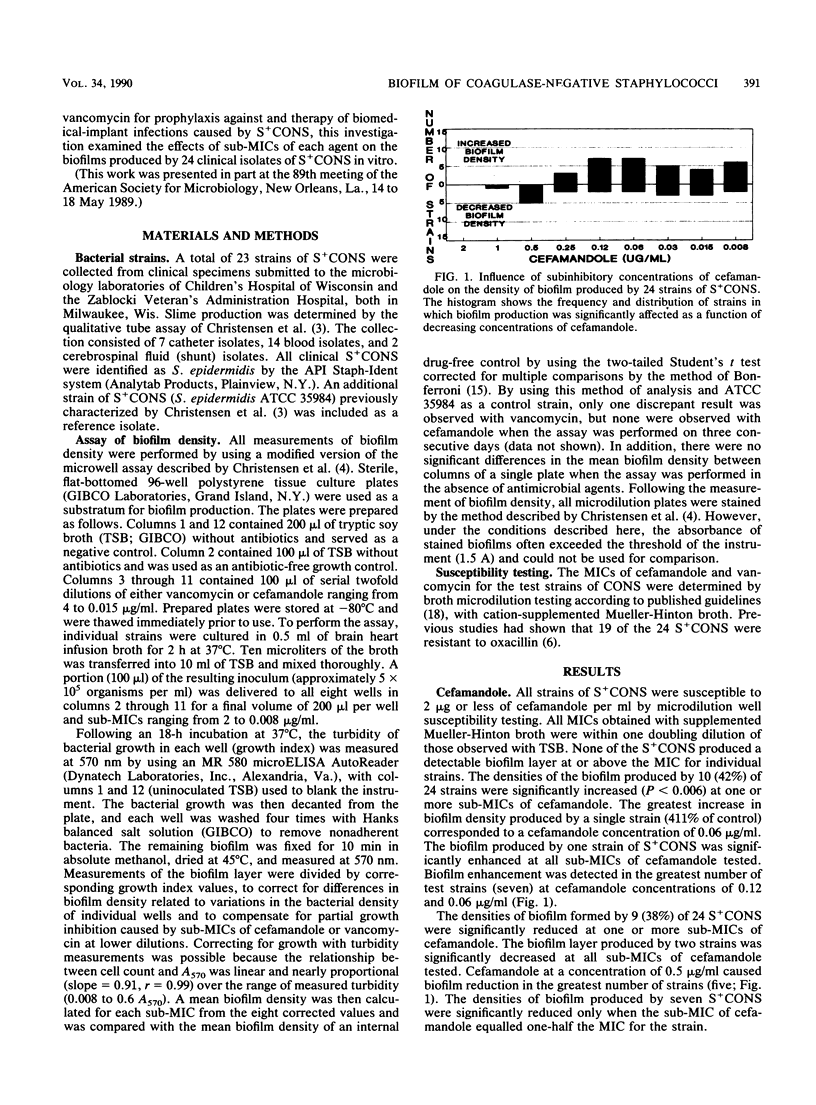
The density of the biofilm layer produced on a plastic surface by 23 clinical isolates and 1 reference strain of slime-positive, coagulase-negative staphylococci was measured following growth in subinhibitory concentrations (sub-MICs) of cefamandole or vancomycin ranging from 2 to 0.008 micrograms/ml. All strains were susceptible to less than or equal to 2 micrograms of each agent per ml. The mean biofilm density produced by each strain was calculated from a total of eight determinations at each sub-MIC and was compared with the mean biofilm density of a drug-free control after correcting for differences in growth. The results showed that the density of the biofilm layer produced by 10 (42%) of 24 strains and 13 (54%) of 24 strains was significantly increased (P less than 0.006) at one or more sub-MICs of cefamandole or vancomycin, respectively. In contrast, the density of the biofilm produced by 9 (38%) of 24 and 2 (8%) of 24 strains was significantly reduced at one or more sub-MICs of cefamandole and vancomycin, respectively, and the biofilm density of 7 of these strains was decreased only when the sub-MIC was one-half the MIC. The biofilm density of six strains (five versus cefamandole and one versus vancomycin) was both enhanced and reduced by different sub-MICs of the same agent. None of the strains produced a detectable biofilm at or above the MIC for the strain. These data indicate that antimicrobial agents such as cefamandole or vancomycin could potentially enhance the biofilm matrix produced by certain slime-positive, coagulase-negative staphylococci on the surface of a biomedical implant if concentrations of these agents fall below the MIC for the infecting strain.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen G. D., Parisi J. T., Bisno A. L., Simpson W. A., Beachey E. H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Aug;18(2):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.2.258-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Younger J. J., Baddour L. M., Barrett F. F., Melton D. M., Beachey E. H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):996–1006. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.996-1006.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport D. S., Massanari R. M., Pfaller M. A., Bale M. J., Streed S. A., Hierholzer W. J., Jr Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Infect Dis. 1986 Feb;153(2):332–339. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne W. M., Jr, Nelson D. B., Chusid M. J. Epidemiologic markers of pediatric infections caused by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Nov;6(11):1031–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etienne J., Brun Y., el Solh N., Delorme V., Mouren C., Bes M., Fleurette J. Characterization of clinically significant isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis from patients with endocarditis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):613–617. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.613-617.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franson T. R., Sheth N. K., Rose H. D., Sohnle P. G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):500–505. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.500-505.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frongillo R. F., Bianchi P., Moretti A., Pasticci M. B., Ripa S., Pauluzzi S. Cross-resistance between methicillin and cephalosporins for staphylococci: a general assumption not true for cefamandole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):666–668. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frongillo R. F., Donati L., Federico G., Martino P., Moroni M., Ortona L., Palumbo M., Pasticci B. M., Pizzigallo E., Privitera G. Clinical comparative study on the activity of cefamandole in the treatment of serious staphylococcal infections caused by methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 May;29(5):789–796. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.5.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak M. A., Gröschel D. H., Mandell G. L., Wenzel R. P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Dec;22(6):1025–1029. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.6.1025-1029.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. M., Lee D. A., Regelmann W. E., Gray E. D., Peters G., Quie P. G. Interference with granulocyte function by Staphylococcus epidermidis slime. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):13–20. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.13-20.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy F. D., Hammer S. M. Staphylococcus epidermidis infections. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Dec;99(6):834–839. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-6-834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schadow K. H., Simpson W. A., Christensen G. D. Characteristics of adherence to plastic tissue culture plates of coagulase-negative staphylococci exposed to subinhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial agents. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):71–77. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. E., Walshe J. J., Krol C. P., Amsterdam D. Staphylococcal peritonitis in patients on continuous peritoneal dialysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 May;23(5):809–812. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.5.809-812.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younger J. J., Christensen G. D., Bartley D. L., Simmons J. C., Barrett F. F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cerebrospinal fluid shunts: importance of slime production, species identification, and shunt removal to clinical outcome. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):548–554. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




