Abstract
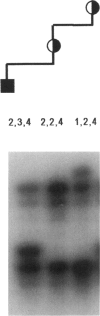
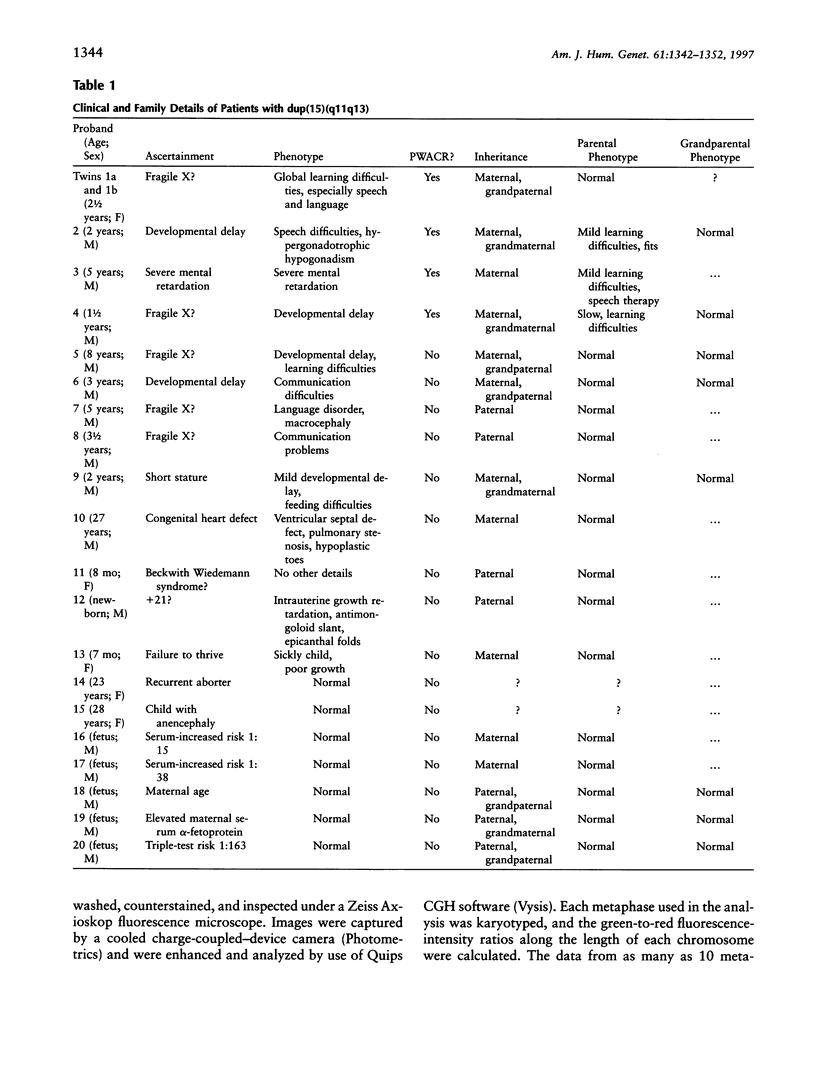
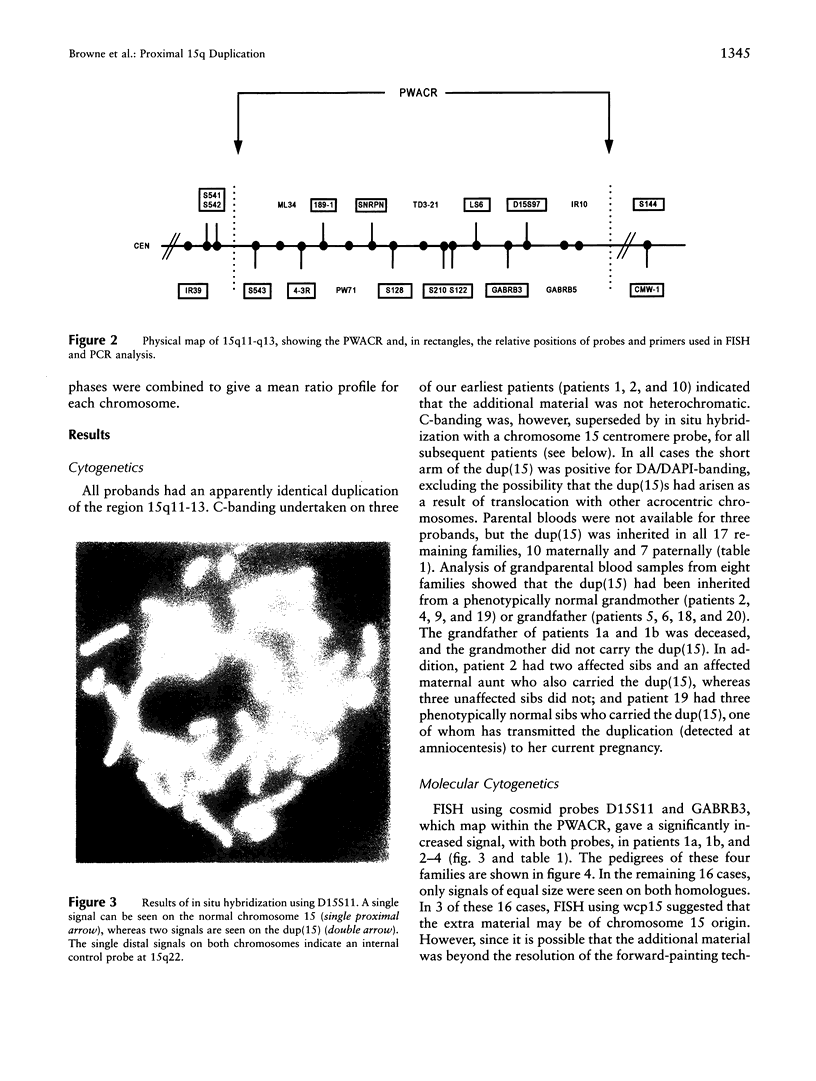
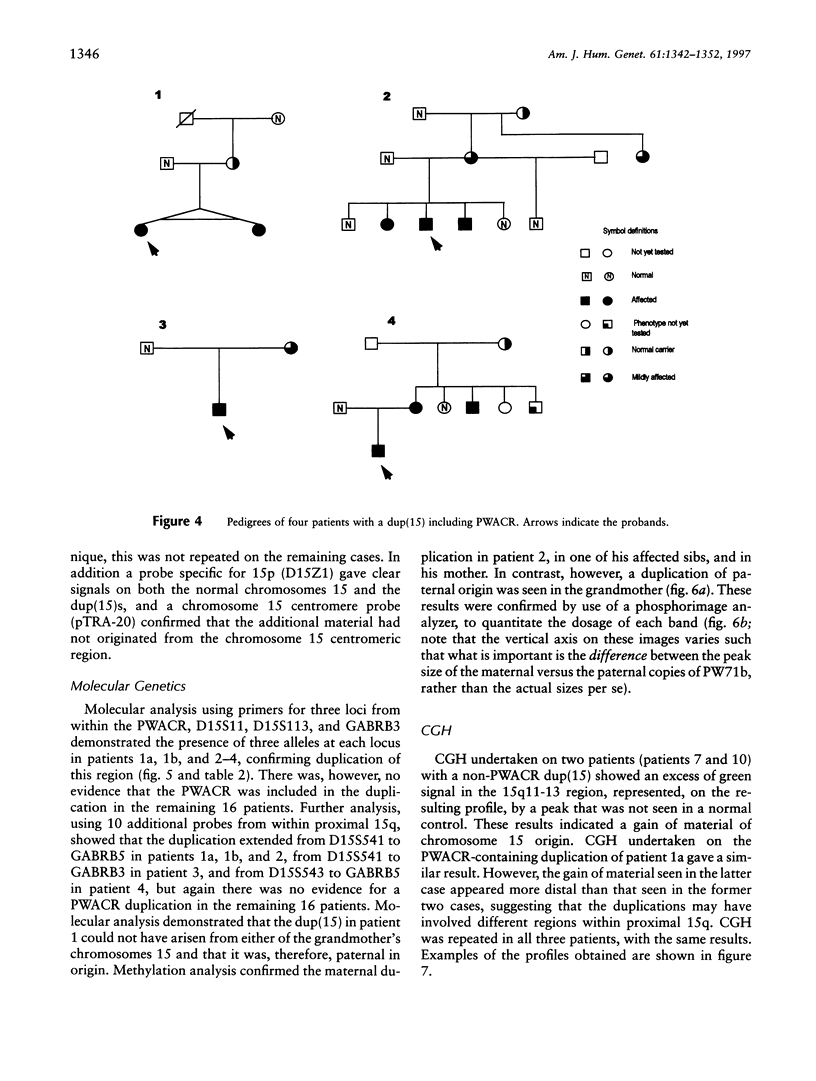
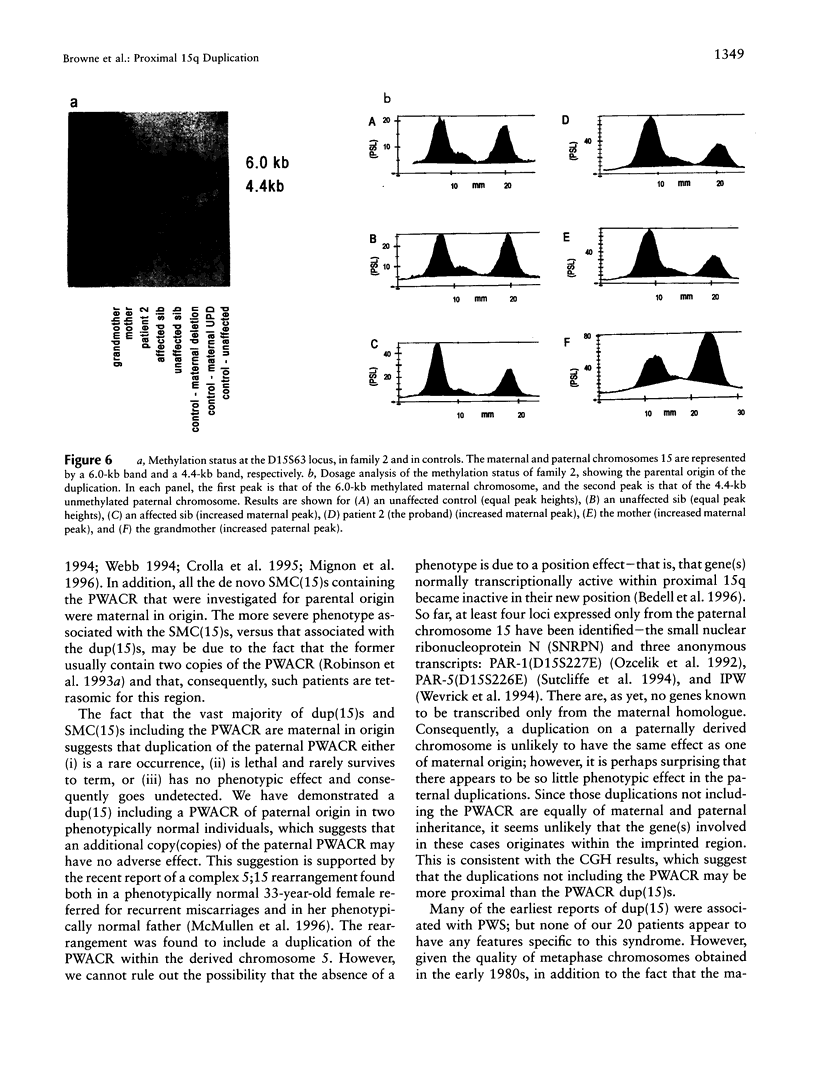
We present the cytogenetic, molecular cytogenetic, and molecular genetic results on 20 unrelated patients with an interstitial duplication of the proximal long arm of chromosome 15. Multiple probes showed that the Prader-Willi/Angelman critical region (PWACR) was included in the duplication in 4/20 patients, each ascertained with developmental delay. The duplication was also found in two affected but not in three unaffected sibs of one of these patients. All four probands had inherited their duplication from their mothers, three of whom were also affected. Two of the affected mothers also carried a maternally inherited duplication, whereas the duplication in the unaffected mother and in an unaffected grandmother was paternal in origin, raising the possibility of a parental-origin effect. The PWACR was not duplicated in the remaining 16 patients, of whom 4 were referred with developmental delay. In the 14 families for which parental samples were available, the duplication was inherited with equal frequency from a phenotypically normal parent, mother or father. Comparative genomic hybridization undertaken on two patients suggested that proximal 15q outside the PWACR was the origin of the duplicated material. The use of PWACR probes discriminates between a large group of duplications of no apparent clinical significance and a smaller group, in which a maternally derived PWACR duplication is consistently associated with developmental delay and speech difficulties but not with overt features of either Prader-Willi syndrome or Angelman syndrome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedell M. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Good genes in bad neighbourhoods. Nat Genet. 1996 Mar;12(3):229–232. doi: 10.1038/ng0396-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundey S., Hardy C., Vickers S., Kilpatrick M. W., Corbett J. A. Duplication of the 15q11-13 region in a patient with autism, epilepsy and ataxia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994 Aug;36(8):736–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1994.tb11916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. G. Prader-Willi syndrome: current understanding of cause and diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):319–332. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. D., Spinner N. B., Zackai E. H., Knoll J. H. Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of inverted duplicated chromosomes 15 from 11 patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 Oct;55(4):753–759. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Earle E., Vissel B., Filby R. G. Identification of two distinct subfamilies of alpha satellite DNA that are highly specific for human chromosome 15. Genomics. 1990 Jun;7(2):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton-Smith J., Webb T., Cheng X. J., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. Duplication of chromosome 15 in the region 15q11-13 in a patient with developmental delay and ataxia with similarities to Angelman syndrome. J Med Genet. 1993 Jun;30(6):529–531. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.6.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook E. H., Jr, Lindgren V., Leventhal B. L., Courchesne R., Lincoln A., Shulman C., Lord C., Courchesne E. Autism or atypical autism in maternally but not paternally derived proximal 15q duplication. Am J Hum Genet. 1997 Apr;60(4):928–934. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crolla J. A., Harvey J. F., Sitch F. L., Dennis N. R. Supernumerary marker 15 chromosomes: a clinical, molecular and FISH approach to diagnosis and prognosis. Hum Genet. 1995 Feb;95(2):161–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00209395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dittrich B., Robinson W. P., Knoblauch H., Buiting K., Schmidt K., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Horsthemke B. Molecular diagnosis of the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes by detection of parent-of-origin specific DNA methylation in 15q11-13. Hum Genet. 1992 Nov;90(3):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00220089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann-Rieger A., Köhler A., Fuhrmann W. Duplication or insertion in 15q11-13 associated with mental retardation-short stature and obesity-Prader-Willi or Cohen syndrome? Clin Genet. 1984 Apr;25(4):347–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb02002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. J., Wang H. S., Shtromas I., Haliotis T., Roder J. C., Holden J. J., White B. N. Organization of a repetitive human 1.8 kb KpnI sequence localized in the heterochromatin of chromosome 15. Chromosoma. 1985;93(1):77–86. doi: 10.1007/BF01259449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jalal S. M., Persons D. L., Dewald G. W., Lindor N. M. Form of 15q proximal duplication appears to be a normal euchromatic variant. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Oct 1;52(4):495–497. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Kallioniemi A., Piper J., Isola J., Waldman F. M., Gray J. W., Pinkel D. Optimizing comparative genomic hybridization for analysis of DNA sequence copy number changes in solid tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1994 Aug;10(4):231–243. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870100403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan L. C., Wharton R., Elias E., Mandell F., Donlon T., Latt S. A. Clinical heterogeneity associated with deletions in the long arm of chromosome 15: report of 3 new cases and their possible genetic significance. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Sep;28(1):45–53. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano A., Mutirangura A., Dittrich B., Buiting K., Horsthemke B., Saitoh S., Niikawa N., Ledbetter S. A., Greenberg F., Chinault A. C. Molecular dissection of the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region (15q11-13) by YAC cloning and FISH analysis. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Sep;1(6):417–425. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.6.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leana-Cox J., Jenkins L., Palmer C. G., Plattner R., Sheppard L., Flejter W. L., Zackowski J., Tsien F., Schwartz S. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of inv dup(15) chromosomes, using probes specific for the Prader-Willi/Angelman syndrome region: clinical implications. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):748–756. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter D. H., Mascarello J. T., Riccardi V. M., Harper V. D., Airhart S. D., Strobel R. J. Chromosome 15 abnormalities and the Prader-Willi syndrome: a follow-up report of 40 cases. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Mar;34(2):278–285. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludowese C. J., Thompson K. J., Sekhon G. S., Pauli R. M. Absence of predictable phenotypic expression in proximal 15q duplications. Clin Genet. 1991 Sep;40(3):194–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1991.tb03076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magenis R. E., Brown M. G., Lacy D. A., Budden S., LaFranchi S. Is Angelman syndrome an alternate result of del(15)(q11q13)? Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):829–838. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei J. F., Mattei M. G., Giraud F. Prader-Willi syndrome and chromosome 15. A clinical discussion of 20 cases. Hum Genet. 1983;64(4):356–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00292367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignon C., Malzac P., Moncla A., Depetris D., Roeckel N., Croquette M. F., Mattei M. G. Clinical heterogeneity in 16 patients with inv dup 15 chromosome: cytogenetic and molecular studies, search for an imprinting effect. Eur J Hum Genet. 1996;4(2):88–100. doi: 10.1159/000472176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Kuwano A., Ledbetter S. A., Chinault A. C., Ledbetter D. H. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the D15S11 locus in the Angelman/Prader-Willi region (AS/PWS) of chromosome 15. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 May;1(2):139–139. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.2.139-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutirangura A., Ledbetter S. A., Kuwano A., Chinault A. C., Ledbetter D. H. Dinucleotide repeat polymorphism at the GABAA receptor beta 3 (GABRB3) locus in the Angelman/Prader-Willi region (AS/PWS) of chromosome 15. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):67–67. doi: 10.1093/hmg/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozçelik T., Leff S., Robinson W., Donlon T., Lalande M., Sanjines E., Schinzel A., Francke U. Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide N (SNRPN), an expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome critical region. Nat Genet. 1992 Dec;2(4):265–269. doi: 10.1038/ng1292-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew A. L., Gollin S. M., Greenberg F., Riccardi V. M., Ledbetter D. H. Duplication of proximal 15q as a cause of Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Dec;28(4):791–802. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis A., Dittrich B., Greger V., Buiting K., Lalande M., Gillessen-Kaesbach G., Anvret M., Horsthemke B. Imprinting mutations suggested by abnormal DNA methylation patterns in familial Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes. Am J Hum Genet. 1994 May;54(5):741–747. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Binkert F., Giné R., Vazquez C., Müller W., Rosenkranz W., Schinzel A. Clinical and molecular analysis of five inv dup(15) patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1(1):37–50. doi: 10.1159/000472386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Bottani A., Xie Y. G., Balakrishman J., Binkert F., Mächler M., Prader A., Schinzel A. Molecular, cytogenetic, and clinical investigations of Prader-Willi syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;49(6):1219–1234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. P., Wagstaff J., Bernasconi F., Baccichetti C., Artifoni L., Franzoni E., Suslak L., Shih L. Y., Aviv H., Schinzel A. A. Uniparental disomy explains the occurrence of the Angelman or Prader-Willi syndrome in patients with an additional small inv dup(15) chromosome. J Med Genet. 1993 Sep;30(9):756–760. doi: 10.1136/jmg.30.9.756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schinzel A. A., Brecevic L., Bernasconi F., Binkert F., Berthet F., Wuilloud A., Robinson W. P. Intrachromosomal triplication of 15q11-q13. J Med Genet. 1994 Oct;31(10):798–803. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.10.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Webb T., Pembrey M. E., Nichols M., Malcolm S. Maternal origin of deletion 15q11-13 in 25/25 cases of Angelman syndrome. Hum Genet. 1992 Feb;88(4):376–378. doi: 10.1007/BF00215668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. S., Nakao M., Christian S., Orstavik K. H., Tommerup N., Ledbetter D. H., Beaudet A. L. Deletions of a differentially methylated CpG island at the SNRPN gene define a putative imprinting control region. Nat Genet. 1994 Sep;8(1):52–58. doi: 10.1038/ng0994-52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Tunnacliffe A., Carter N. P., Behmel A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Nordenskjöld M., Pfragner R., Ponder B. A. Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Apr;4(3):257–263. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T., Clayton-Smith J., Cheng X. J., Knoll J. H., Lalande M., Pembrey M. E., Malcolm S. Angelman syndrome with a chromosomal inversion 15 inv(p11q13) accompanied by a deletion in 15q11q13. J Med Genet. 1992 Dec;29(12):921–924. doi: 10.1136/jmg.29.12.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webb T. Inv dup(15) supernumerary marker chromosomes. J Med Genet. 1994 Aug;31(8):585–594. doi: 10.1136/jmg.31.8.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wevrick R., Kerns J. A., Francke U. Identification of a novel paternally expressed gene in the Prader-Willi syndrome region. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1877–1882. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. A., Zori R. T., Stone J. W., Gray B. A., Cantu E. S., Ostrer H. Maternal origin of 15q11-13 deletions in Angelman syndrome suggests a role for genomic imprinting. Am J Med Genet. 1990 Mar;35(3):350–353. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320350308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de France H. F., Beemer F. A., Ippel P. F. Duplication in chromosome 15q in a boy with the Prader-Willi syndrome; further cytogenetic confusion. Clin Genet. 1984 Oct;26(4):379–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1984.tb01075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]